KNEC KCSE Geography Paper 1 Question Paper / 2015 KCSE Meru South Form 4 Joint Examination
GEOGRAPHY PAPER 1 QUESTION PAPER
2015 KCSE Meru South Form 4 Joint Examination
Geography Paper 1
SECTION A (25 Marks)
Answer all questions in section A.
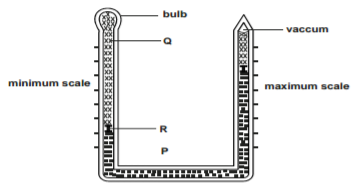
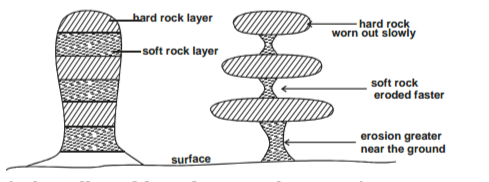
The diagram below shows a six’s thermometer.
a) Name the parts marked P, Q and R. (3 marks)
b) The table below represents the rainfall and temperatures data of station X (4 marks)
| Month | J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
| Temp °C | 28.9 | 29.7 | 30.3 | 29.9 | 29.7 | 29.2 | 28.4 | 28.7 | 29.6 | 30.1 | 29.2 | 28.7 |
| Rainfall mm | 9.0 | 8.0 | 21.0 | 49.0 | 25.0 | 9.0 | 20.0 | 10.0 | 4.0 | 10.0 | 17.0 | 11.0 |
i) What is the annual range of temperature? (1 mark)
ii) Calculate the total rainfall of the station. (1 mark)
9 marks
a) What is rock metamorphism? (2 marks)
b) Give the examples of chemically formed sedimentary rocks. (3 marks)
5 marks
a) Name the fold mountains found in the following countries
i) Morocco
ii) Peru
iii) Switzerland. (3 marks)
b) Apart from fold mountains, name two other features resulting from folding. (2 marks)
5 marks
a) State three causes of soil creep. (3 marks)
b) State two ways in which downwash occurs. (2 marks)
5 marks
a) State two causes of chemical soil degeneration. (2 marks)
b) State three factors influencing the formation of soil. (3 marks)
5 marks
SECTION B (75 Marks)
Answer question 6 and any other two questions in this section
Study the map of Migwani 1 : 50,000 (Sheet 151 / 1) provided and answer the following
a) i) Give the latitudinal extent of the area covered by the map. (2 marks)
ii) What is the bearing of the borehole at grid reference 073698 from the settlement at grid reference 095 731 ? (2 marks)
iii) Measure the distance of the dry weather Road marked D 502 from the drift at grid square 9879 to the Northern end. Give your answer in kilometers. (2 marks)
iv) Calculate the area to the West of the All weather Road loose surface C94. Give your answer in square kilometres. (2 marks)
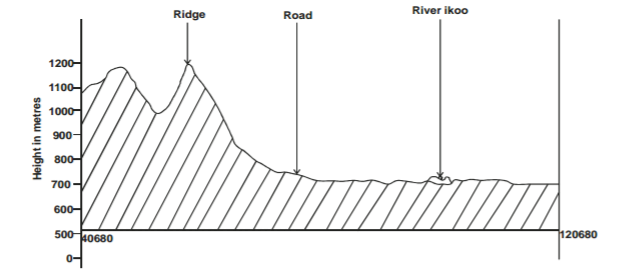
b) i) Using a vertical scale of 1cm to represent 100 metres, draw a cross-section from grid reference 040680 to grid reference 120 680 (4 marks)
ii) On it mark and label the following
– River Ikoo. (1 mark)
– Road (1 mark)
– Ridge (1 mark)
c) i) Identify two types o vegetation found in the area covered by the map. (2 marks)
ii) Citing evidence from the map, state two social functions of GWANI TOWN (2 marks)
d) Describe the drainage of the area covered by the map. (5 marks)
5 marks
a) i) State three types of faults. (3 marks)
ii) Explain two processes that may cause faulting. (4 marks)
b) i) Apart from the Rift valley, name two other features resulting from faulting. (2 marks)
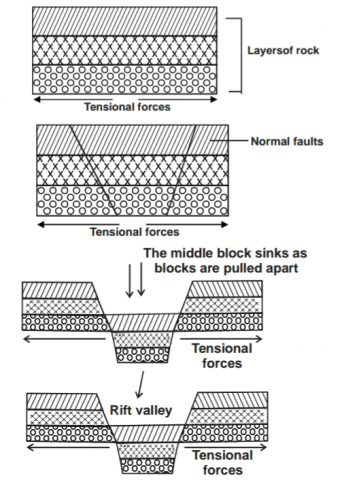
ii) With the aid of diagrams, explain how a Rift valley is formed by tensional forces. (8 marks)
c) Explain four positive effects of faulting. (8 marks)
25 marks
a) i) Give three physical factors which contribute to the development of deserts. (3 marks)
ii) Describe two processes of wind transportation. (4 marks)
b) State three factors that facilitate wind deposition. (3 marks)
c) By use of diagrams, explain how a rock pedestal is formed. (5 marks)
d) Explain three effects of desert features on human environment. (6 marks)
e) Some students carried out a field study in Chalbi desert.
i) State two objectives of their study. (2 marks)
ii) State two problems they encountered during their study. (2 marks)
25 marks
a) Define the following terms
i) Water table. (1 mark)
ii) Acquifer (1 mark)
b) Explain how the following factors influence the occurrence of underground water.
i) Nature of the rock. (2 marks)
ii) Slope gradient. (2 marks)
c) State three conditions necessary for the formation of an artesian well. (3 marks)
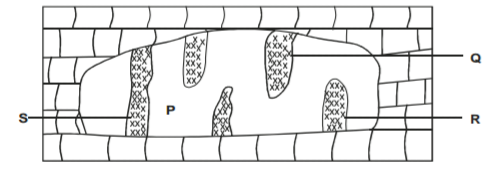
d) The diagram below shows the features found in a karst region.
i) Name the features marked P, Q, R and S (4 marks)
ii) Describe how feature S is formed (4 marks)
iii) Give three reasons why there are few settlements in the Karst region. (3 marks)
e) Students carried out a field study in a karst landscape
i) State two methods they used to record data. (2 marks)
ii) State three importance of studying a karst landscape through field work. (3 marks)
25 marks
a) State three factors that determine the size of a lake. (3 marks)
b) i) Explain three reasons why some Rift valley lakes have fresh water. (6 marks)
ii) Name two corrie lakes in Kenya. (2 marks)
c) Explain how the following lakes were formed.
i) Lake Tanganyika. (4 marks)
ii) Lake Paradise. (4 marks)
d) Explain three negative effects of lakes. (6 marks)
25 marks
GEOGRAPHY PAPER 1 MARKING SCHEME
2015 KCSE Meru South Form 4 Joint Examination
Geography Paper 1
SECTION A (25 Marks)
Answer all questions in section A.
a) Name the parts marked
P – Mercury
Q – Alcohol
R – Metal index 3 marks
b) i) Annual range of temperature
1.9°C 1 mark
ii) Total annual rainfall of the station
193mm 1 mark
9 marks
a) What is rock metamorphism
– It is the change that occur when pre-existing rocks (sedimentary, igneous) are subjected to heat, pressure or both heat and
pressure. 2 marks
b) Three examples of chemically formed sedimentary rocks
− Travertine / Tufa
− Dolomite / dolostone
− Trona
− Gypsum
− Rock salt
− Limonite
− Haematite
− Flint /chert 3 marks
5 marks
a) Fold mountains found in
i) Morocco – Atlas
ii) Peru – Andes
iii) Switzerland – Alps 3 marks
b) Two other features resulting from folding.
− Synclinal valleys
− Rolling plains
− Ridges
− Intermontane plateaus
− Intermontane basins. 2 marks
5 marks
a) Three causes of soil creep
o Temperature change causes soil particles to expand and contract making them to shift their position downslope.
o Moisture/rainwater causes soil to become wet and compact on drying the particles loosen and may shift their position
downslope.
o Human activities and action of burrowing animals may cause the removal of soil on the lower part of the slope. This trigger
soil from upper part of the slope which may be shift downslope
o Freezing of soil water expand the spaces between soil particles. The water thaws and particles fall by gravity and may shift
position downslope.
o Moisture act as a lubricant to soil particles causing their movement downslope.
o External forces such as moving vehicles / earth tremors have a trigger effect which causes downward movement of soil
particles. 1 × 3 = 3 marks
b) Two ways in which downwash occur
-Sheet wash
-Gullying 2 marks
5 marks
a) Two causes of chemical soil degeneration
− Poor land use practices like monoculture / overcropping.
− Wrong application of fertilizer degrade soils causing acidity.
− Leaching caused by heavy rainfall
− Excessive drought cause accumulation of salt on the top soil any 2 × 1 = 2 marks
b) Three factors influencing soil formation
− Climate / rainfall / temperature / wind.
− Parent rock
− Topography
− Living organisms
− Time any 3 × 1 = 3 marks
5 marks
SECTION B (75 Marks)
Answer question 6 and any other two questions in this section
Migwani map 1 : 50,000 sheet 151/1
a) i) Latitudinal extent of the area covered by the map
1°03′
S to 1°15′
S 2 marks
ii) Bearing of the borehole at Grid reference 073698 from the settlement at grid reference 095731
213°±1° (212°-214°) 2 marks
iii) The distance of dry weather road number D502 from the Drift at grid square 9879 to its northern end
5.3km ± 0.1 (5.2km – 5.4km)
iv) The area to the west of all weather road loose surface number C94
10.5km² ± 0.5 (10km² -11km²) 2 marks
b) i) A cross section from grid reference 040680 to grid reference 120680 (4 mks)
c) i) Two types of vegetation found in the area covered by the map.
− Scrub vegetation
− Scattered trees 2 marks
ii) Two social functions of Gwani town
Function Evidence
− Education centre School
− Administration centre Chiefs office/court house
− Health services Health centre
− Residential centre Rest house NB – No evidence no mark any 2 × 1 = 2 marks
d) Describe the drainage of the area covered by the map
− There are rivers
− The rivers are many
− The rivers are permanent
− There are disappearing rivers around Mtito
− The main river is R. Ikoo
− Some rivers are Originating from the hills
− Many rivers form dendritic drainage pattern
− Some rivers form parallel drainage pattern
− There are reservoirs
− R. Ikoo is flowing from North West to South Eastwards. any 6 × 1 = 6 marks
5 marks
a) i) Three types of faults
− Normal fault
− Reverse fault
− Shear/tear/transform fault
− Thrust fault
− Anticlinal fault any 3 × 1 = 3 marks
ii) Explain two processes that may cause faulting
− Faulting may be caused by forces acting horizontally away from each other which causes tension on crustal rocks.
− Due to tension rocks stretch and fracture causing faults.
− Faulting may be caused by forces acting horizontally towards each other which causes compression in crustal rocks.
− Due to compressional force the rocks shorten and fracture causing faults.
− Faulting may occur where horizontal forces act parallel to each other in the opposite or same direction resulting to shearing.
− Faulting may occur due to vertical movements which may exert a strain in the rocks making them to fracture / regional
upwarping. any 2 × 2 = 4 marks
b) i) Two other features resulting from faulting
− Fault scarp / escarpment / fault step.
− Tilt blocks
− Harst / block mountains any 2 × 1 = 2 marks
ii) Explain how the Rift valley is formed by tensional forces
− Layers of rocks are subjected to tensional forces
− Lines of weakness occur leading to development of normal faults.
− The central block sinks or subsides as side blocks are pulled apart
− The sunken part forms a depression or graben called Rift valley
c) Explain four positive effects of faulting
− Faulting leads to formation of features that provide beautiful scenery which attract tourists.
− Faulting lead to formation of lakes that are important fishing grounds / mining sites / provide water for irrigation / domestic /
industrial use.
− Faulting causes displacement of rocks which exposes minerals that are mined.
− Faulting causes formation of mountains /horst which attract rainfall that give rise to rivers which provide water for industrial /
domestic/agricultural / production of HEP.
− Block mountains formed through faulting on the windward side which favours agriculture settlement / forest.
− When faulting occur across a ridge it may provide a dip which could form a mountain pass where transport and
communication lines can be constructed.
− Springs that occur at the foot of fault scarps attract settlement.
− Faulting create deep faults that can be utilized for Geothermal power.
− Rivers flowing over fault scarps may farm waterfalls which may be harnessed for HEP generation. any 4 × 2 = 8 marks
25 marks
a) i) Three physical factors which contribute to the development of deserts.
− Insufficient rainfall which doesn’t support luxuriant growth of vegetation.
− High temperature / very low temperature lead to aridity due to little precipitation / drought.
Layersof rock
− Relief barrier / rain shadow effect.
− Influence of wind system
− Cold ocean currents
− Continentality any 3 × 1 = 3 marks
ii) Describe two processes of wind transportation
− Saltation
This is where coarse grained sand particles are transported through a series of bouncing / jumping along the surface.
− Suspension
It is where very fine materials is picked by wind raised high and blown over long distances.
− Surface creep / rolling.
It is where large / heavy materials are rolled / pushed forward by wind along the surface. any 2 × 2 = 4 marks
b) i) Three factors that facilitate wind deposition
− Desert surface with water surfaces or moist grounds forces the wind to deposit its load.
− Obstacles – presence of obstacles like rocks, bushes on the path of wind forces the wind to drop some of its load.
− Strength of the wind – when the wind slakens it begin to drop some of its load / collision of wind blowing from different
directions cause wind to drop some load.
− When sudden showers start falling in the desert some of the suspended materials in the air are washed down.
− If the wind is carrying too many particles they constantly collide causing some of them to be dropped. any 3 × 1 = 3 marks
c) Describe how a rock pedestal is formed
− Wind abrassion attack a rock outcrop with alternating layers of hard and soft rocks (heterogeneous)
− The softer rocks are eroded faster than hard rocks.
− Wind abrassion is more effective nearer the ground surface where abrassive materials are heavier.
− This leads to the formation of rock outcrop of different shape called rock pedestal.
d) Explain three effects of desert features on human environment.
− Desert features form good sites for tourist attraction, thereby earning foreign exchange.
− Wind deflation hollows/ oasis are sources of water for domestic/agricultural use.
− Wind deposited sand / loess form fertile plains for farming.
− Salty flats are economically used for salt production
− Desert sceneries are ideal for film making
− Vast sand seas are ideal for military training / nuclear testing.
− Loes are curved into caves in China as dwellings.
− Shifting sand dunes hinder transport activities. any 3 × 2 = 6 marks
e) State two objectives of their study
− To find out the main desert landforms.
− To find out the human activities carried out in the area.
− To investigate the problems faced in the desert.
− -To find out the main agents of erosion and deposition in the desert. any 2 × 1 = 2 marks
ii) Two problems they encountered during the study
− Adverse weather condition like vey high temperatures during the day.
− Inadequate water.
− Poor transport network
− Attack by wild animals like snakes /scorpions
− Dust storms leading to poor visibility.
− Difficulty in identifying some features.
− Insecurity /attack by badits.
− Tiredness
− Inadequate time
− Getting lost in the desert. any 2 × 1 = 2 marks
25 marks
a) Define the following terms
i) Water table
− It is the upper part of the zone of saturation of water in permeable rock which keep on fluctuating. 1 mark
ii) Aquifer
− It is a permanently saturated permeable rock which can hold water in its mass that is found between layers of impermeable
rocks. 1 mark
b) How the following factors influence occurrence of underground water.
i) Nature of rock
− Rocks with pores, cracks allow more infiltration to occur / impermeable rocks don’t allow water to pass through them. 2marks
ii) The gradient of the slope.
− Flat areas like plains give water time to infiltrate as water remain there a long time.
− Steep gradient will allow a lot of surface run off hence less infiltration. 2 marks
c) i) Three conditions necessary for the formation of an artesian well
− An aquifer must be sandwiched between two layers of impermeable rocks so as to retain water.
− One or both ends of the aquifer must be exposed in a region which has high rainfall to prevent it from drying.
− The aquifer must be syncline to ensure that the water has sufficient pressure to flow out naturally.
− The aquifer must be of same permeable material.
− There must be a partial or total blockage of exit for the water to be replaced under pressure. 3 marks
d) i) Name the features marked
P – cave
Q – stalactite
R – stalagmite
S – limestone pillar 4 marks
ii) How feature S was formed
− Rain water absorb carbondioxide forming carbonic acid.
− Rain water absorb calcium carbonate as it percolate in limestone joints.
− A solution of calcium carbonate trickles down slowly through the roof of caves / cavern
− Solution droplets hang on the roof of a cause.
− Water evaporate and calcium carbonate is precipitated.
− The precipitate calcium carbonate gradually builds downwards over a period of time as the solution continue to drip from the roof to form a stalactite.
− The solution splashes on the floor of the cave.
− Water evaporate and calcium carbonate precipitate
− The precipitate of calcium carbonate builds upwards to form stalagmite.
− Over time the stalactite and stalagmite join to form a limestone pillar / column. 4 marks
iii) Three reasons why there are a few settlements in the karst region.
− Limestone region are covered with thin soils which limit crop growing other than sheep grazing.
− The rugged terrain make development of transport network difficult and expensive
− The absence of surface streams lead to scarcity of water supply which discourage settlement.
− The area is rocky which discourage agriculture. 3 mark
e) i) Two methods they used to record data
− Photographing / filming / video taking.
− Writing notes.
− Drawing sketches / diagrams 2 marks
ii) Three importance of studying a karst landscape through fieldwork
− It gives first hand information
− It makes learning real
− It help students to develop manipulative skills of observation and recording data.
− It make learning interesting.
− It enhance visual memory hence not forgotten easily
− It help students to apply knowledge learnt in the classroom. 3 marks
25 marks
a) Three factors that determine the size of a lake.
− The depth and width of a depression or hollow.
− The amount of incoming water from river, rainfall, melt water or underground water.
− The amount of water lost through evaporation, seepage, through permeable rocks and outflow.3 marks
b) i) Three reasons why some rift valley lakes have fresh water.
− Some lakes in the Rift valley have outlets through which excess salts are carried away leaving the water fresh.
− Some lakes have underground outlets which drain the salts accumulated in their beds.
− Some lakes are situated in areas that receive high amount of rainfall which dilutes any salt in this lake keeping the water fresh.
− Some lakes have regular inflow of fresh water from rivers which dilute salts keeping the water fresh.
− Some of the lakes in the rift valley such as L. Baringo are situated in areas of low temperatures which result in low evaporation thus keeping the water fresh 3 × 2 = 6 marks
ii) Name two corrie lakes in Kenya
− Teleki Lake /Tyndall tarn
− Hut Tarn
− L. Hohnel
− Nanyuki tarm
− L. Hidden
− L. Thompson 2 × 1 = 2 marks
c) Explain how the following lakes were formed
i) Lake Tanganyika.
− Faulting lead to fracturing of rocks along lines of weakness to form faults.
− Some parts of the earth sink and others are tilted along faults.
− This lead to the formation of deep, narrow, steep, long sided depression on the earth surface
− When water from stream and rivers fill the depressions lake are formed.
− Faulting may also result in depressions in the floor of the rift valley
− The depression are filled with rain water, river water and underground water forming lakes e.g. L. Tanganyika.
ii) Lake Paradise
− Vent eruption emit acidic lava onto the earth surface to form volcanic cones.
− Magma in the vent also cools and solidify thus contracting.
− This lead to withdrawal of magma in the vent creating a depression on top of the cone called a crater.
− The depression may be filled with rain water or melt water to form a crater lake . e.g. L. Paradise. 4 marks
d) Explain three negative effects of lakes.
− High amount of convectional rainfall received around some lakes result in floods which may cause death of people, animals and destruction of property.
− Some lakes may form breeding sites for mosquitoes, snails which cause Malaria and Bilharzia to people who may die or spend much money being treated.
− Some lakes have dangerous animals such as crocodiles and hippopotamuses, which may attack and kill animals and fishermen discouraging activities in lakes.
− Some lakes create barriers to transport and communication network making roads to wind around them making construction expensive and difficult. 3 × 2 = 6 marks
25 marks