KNEC KCSE Agriculture Paper 1 Question Paper / 2015 KCSE Gem Sub-County Joint Evaluation
AGRICULTURE PAPER 1 QUESTION PAPER
2015 KCSE Gem Sub-County Joint Evaluation
Agriculture Paper 1
SECTION A (30 Marks)
Answer all the questions in this section in the spaces provided
Give four reasons why colostrum should be fed to calf.
2 marks
State three disadvantages of natural methods of calf rearing.
1.5 marks
Name five milking materials and equipment required during milking of a cow.
2.5 marks
Sate the functions of a carburetor in fuel system.
1 marks
State the functions of the following parts of a disc plough.
2.5 marks
i) The beam
ii) Disc
iii) Scrapers
iv) Standards
v) Furrow wheel
2.5 marks
Give two notifiable diseases in cattle.
1 marks
State four factors that determine the quality of honey.
2 marks
Give four properties of a good vaccine.
2 marks
Define predisposing factors as used in livestock.
1 marks
State four predisposing factors that can lead to cow contracting mastitis.
2 marks
State four reasons for handling livestock in the farm.
2 marks
Differentiate between the following livestock breed terms:
i) Bull and bullock
ii) Ram and ewe
2 marks
Name two meat breeds of sheep reared in Kenya today.
1 marks
Identify the colour of the following breeds of poultry.
i) Light Sussex
ii) New Hampshire
1 marks
Name two dual purpose breeds of cattle.
1 marks
State three precautions observed when using workshop tool and equipment.
1.5 marks
State four signs of parturition shown by a sow.
2 marks
SECTION B (20 Marks)
Answer all the questions in this section in the space provided
a) Using Pearson square, calculate how much of wheat (35% DCP) would be mixed with sunflower seed cake (10% DCP) to come up with Duck mash (20% DCP) on a ration weighing 100kg. (2 marks)
b) Below is a diagram of a cow suffering from a nutritional deficiency diseases. Study it and answer the question below.
i) Identify the disease the animal is suffering from. (1/2 mark)
ii) List two symptoms shown by a cow suffering from the disease mentioned in b (i) above. (1 mark)
iii) Name the mineral deficient that cause the above disease. (1/2 mark)
iv) Sate the two control measures of the disease mentioned above. (1 mark)
5 marks
Study the tools below and answer the questions below.
a) Identify the tools X,Z and W (11/2 marks)
b) What are the functions of tools W and X (2 marks)
5 marks
The diagram below shows a practice carried out in poultry.
i) Name the practice above. (1/2 mark)
ii) Identify the diagram that shows the correct method of carrying out the practice mentioned in (i)
above. (1/2 mark)
iii) Name two tools used to carry out the practice above. (1 mark)
iv) Give two reasons for carrying out the practice shown above. (1 mark)
5 marks
The diagram below shows power transmission system of a tractor. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
a) Name parts labeled A , B, C and D (4 marks)
b) State three maintenance practice of sprayers. (11/2mks)
5.5 marks
The illustration below represents an equipment used in poultry production. Study it and answer the questions that follow
i) Identify the equipment (1 mark)
ii) Identify the parts labeled C , D (1 mark)
iii) Why is it important to turn the eggs 1800 every 6-8 hours within the equipment. (1 mark)
5.5 marks
SECTION C (40 Marks)
Answer any two questions in this section.
a) Highlight four advantages of deep litter system. (4 marks)
b) State four ways in which stress can be controlled in poultry management. (4 marks)
c) Outline five disadvantages of animal-drawn implements over tractor-drawn implements. (5 marks)
d) i) Sate three characteristics of a poor layer. (3 marks)
ii)Outline four advantages of artificial insemination in cattle management. (4 marks)
20 marks
a) i) Distinguish between close breeding and line breeding.
ii) Give three reasons for out breeding as used in livestock production. (3 marks)
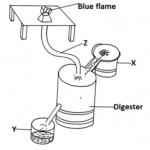
b) Describe the function of various parts of a plunge dip. (10 marks)
c) Sate five disadvantages of live fences. (5 marks)
20 marks
a) Describe coccidiosis under the following sub heading.
i) Causal organism (1 mark)
ii) Signs of infection (5 mark)
iii) Control measures (4 mark)
b) Describe lifecycle of three host tick. (7 marks)
Describe how a calf is trained to drink milk from the bucket. ( 3 marks)
20 marks
AGRICULTURE PAPER 1 MARKING SCHEME
2015 KCSE Gem Sub-County Joint Evaluation
Agriculture Paper 1
SECTION A (30 Marks)
Answer all the questions in this section in the spaces provided
4 reasons why colostrum should be fed to a calf.
Highly digestible;
Highly nutritious and contains vitamins for growth and disease resistance;
Has antibodies that enable the calf resist early disease infection;
Cleans the bowels of the calf (has laxative effect);
Highly palatable; 4 × ½ mark = 2 marks
Mark the 1st four only
2 marks
3 disadvantages of natural method of calf rearing
Calf is underfed as the farmer removes all the milk from the udder (or calf is overfed as it suckles too much milk resulting in scours);
Cows may not let down milk in absence of the calf;
It is difficult to keep accurate records of milk yield; 3 × ½ mark = 1½ marks
Mark the 1st three only
1.5 marks
5 milking materials and equipment
Udder clothes / towels;
Filtering pads;
Milking jelly;
Warm water;
Milking pails / buckets;
Strip cup;
Milk cans / churns; 5 × ½ =2½ marks
mark the 1st five only
2.5 marks
Functions of a carburettor in fuel system
– Turns liquid petrol into vapour and mixes it with define amount of air; 1 × 1 = 1 mark
1 marks
Function of the following parts of a disc
i) Beam;
– Provides attachment for all other parts of the plough;
ii) Disc;
– Cut, turn and invert furrow slices;
iii) Scrappers;
– Remove wet soil from the disc/ AIDs in turning and inverting the furrow slice;
v) Furrow wheel;
– Rides over dead furrows counteracting thrust hence balancing the whole implement /
Adjust the depth of ploughing. 5 × ½ mark = 2½ marks
2.5 marks
2 Notificable diseases in cattle
Anthrax
Contagious abortion / accept Brucellosis / Bang’s disease;
Pneumonia
Rinderpest 2 × ½ = 1 mark
Mark 1st two only
2.5 marks
Factors that determine the quality of honey
Type of plant from which the nectar was obtained;
Maturity stage of honey at the time of harvesting
Method of harvesting;
Method of processing honey 4 × ½ mark = 2 marks
Mark 1st four only
1 marks
4 practices carried out on fish before preservation
Cleaning the fish to remove mud and any worms;
Removing scales and slims
Opening the fish on the side to remove gut and intestines / gutting
Cleaning the abdominal cavity thoroughly..
Keeping fish in open containers. 4 × ½ = 2 marks
2 marks
4 properties of a good vaccine
Immunity it produces should be as good as natural immunity
Should have long keeping life / long shelf life.
Should be easy to administer to the animal
Should have no side effects when innoculated.
Should be compatible with other vaccines given to the animal;
A singer dose should produce life long immunity. 4 × ½ = 2 marks
mark 1st four only
2 marks
Predisposing factor
– Are those conditions inside or outside the body of an animal which lead to the animal contracting a disease or injury. 1 × 1 mark = 1 mark
1 marks
Four predisposing factors that can lead to cow contracting mastitis.
Age
Stage of lactation
Udder attachment
Incomplete milking
Mechanical injuries
Poor sanitation
Poor milking technique 4 × ½ = 2 marks
2 marks
Four reasons for handling livestock in the farm
When inspecting the animal to a certain abnormality or signs of disease;
When administering any form of treatment to the animal;
When spraying or hand dressing the animal with chemicals to control external parasites
When milking the animal
When performing some management practices like dehorning, disbudding, castration, hoof trimming.
4 × ½ = 2 marks Mark 1st four only
2 marks
i) Bull and bullock
A bull is a mature male cattle while a bullock is a mature castrated mate cattle;
ii) Ram and Ewe
A ram is a mature male sheep while an ewe is a mature female sheep;
2 marks
2 meat breeds of sheep
– Dorper
– Blackhead Persian
– Red Maasai sheep 2 × ½ = 1 mark
Mark the 1st two only
1 marks
Breed Colour
i) Light sussex White 1 × ½ = ½mk
ii) New hampshire Light red 1 × ½ = ½ mk
1 marks
2 Dual purpose breeds of cattle
– Sahiwal
– Red poll
– Simmental 2 × ½ = 1 mark
Mark the 1st two only
1 marks
3 precautions observed when using workshop tools and equipment
– Tools should be left in a safe place after use.
– Use the correct tool for the correct job
– Tools should be maintained and serviced
– tools should be handled correctly when in use.
– Use of safety devices e.g. fire extinguishers, goggles etc. 3 × ½ mark = 1½ mark
Mark 1st three only
1.5 marks
4 signs of parturition shown by a sow
– Restlessness
– Vulva turns red and swells.
– Udder becomes fully with a milky fluid.
– Sow starts to build a nest by collecting some bedding at one corner of the pen. 4 × ½ marks = 2 marks
Mark 1st four only
2 marks
SECTION B (20 Marks)
Answer all the questions in this section in the space provided
a)
b) i) Milk fever / parturient paresis / Hypocalcaemia ½ mark
ii)
Muscular twitching causing the animal to tremble.
Staggering as the animal is moving.
Inability to stand thus animal lies down on the side most of the time.
Dull eyes and dilated pupils
Animal falls down and becomes unconscious.
Body functions such as urination, defecation and milk secretion stops.
Sudden death if the animal is not treated immediately.
Stomach contents are drawn into the mouth which later cause lung fever when breathing in.
Complete loss of appetite 2 × ½ mark = 1 mark
Mark 1st two only
iii) – Calcium 1 × ½ = ½ mark
iv)
Give the animal intravenous injection of soluble calcium salt in form of calcium borogluconate.
Partial milking of the cow with past history of the disease.
Feed the animal on diet rich in calcium during pregnancy and lactation.
Susceptible / affected animals should be culled and kept in comfortable condition. 2 × ½ = 1 mark
Mark 1st two only
5 marks
a) X – spirit level
Z – try-square / mason’s square
W – cold chisel. 3 × ½ mark = 1½ marks
b) Functions of :
W – cutting thick sweets of metal.
X – checking whether a surface is vertical or horizontal. 2 × 1 = 2 marks
5 marks
i) – Debeaking (½ mark)
ii) C ½ mark
iii) – Debeaker
– knife
– Scissors
– Hot iron 2 × ½ mark = 1 mark
Mark the 1st two only
iv) – To control egg-eating
– To control cannibalism 2 × ½ mark = 1 mark
5 marks
a) A – Differential
B – Gear box
C – Fly wheel
D – Propeller shaft 4 × 1 mark = 4 marks
b) Maintenance practices on sprayers
– Tank should be drained before and after use.
– All nozzles should be removed and cleaned when blocked.
– Tank and other parts should be washed thoroughly with clean water and dried.
– Parts prone to rusting of should be cleaned and painted. 3 × ½ = 1½ marks
Mark 1st three only
5.5 marks
i) Artificial incubator 1 × 1 = 1 mark
Rej. Incubator alone
ii) C – thermometer
D – water bath / warm water. 2 × ½ mark = 1 mark
iii) To ensure even distribution of warmth hence facilitate even chick development 1 × 1 mark = 1 mark
5.5 marks
SECTION C (40 Marks)
Answer any two questions in this section.
a)
– Incidence of cannibalism, egg eating, teacher plucking are common.
– There is a likelihood of pests of disease accumulation in bitter.
– An individual record of e.g. production per bird is not possible hence not easy to know layers.
– Litter may be difficult to find in some areas.
– Eggs may become dirty especially when laid on the ground.
– Feeders and waterers may be contaminated 1 × 4
b)- Keep the poultry house quiet by buildings if away from he road, where people and vehicles pass.
– Insolute the poultry house to maintain uniform temperature;
– Control diseases and parasites.
– Change of routine programmed must be grown.
– Provide enough feds and water. 1 × 4
c)- They are more tedious than tractor-drawn implements has to keep on guiding the animal and the implement.
– More than one person is required to guide the plough and the animal.
– Animal drawn implements are slower turn tractor drawn implement.
– Axinums get tired at times, hence work is slow.
– There are diseases in some areas which makes it difficult to use animals.
– A farmers needs to set aside a piece of land where he either grow toddler crop.
d) i)
– Combs and wattles are such, dry and cold.
– Vent is small, round and pigmented;
– The space between pelvic bones is narrow.
– Plumage is usually shiny, wear presented or sometimes moulting.
– Yellowish pigmentation is common in the vent, beak shark. 1 × 4
ii)
– Semens of superior bull can be used to serve may cows.
– Controls transmission of breeding diseases and parasites.
– Gives that are heavy can produce semen to serve cows.
– Prevents large bulls from injuring small cows.
– Reduce expenses of keeping balls on pastures. 1 × 4 = 4 marks
20 marks
a) i) Close breeding – It breeding of very close related animals.
– Line breeding – This the mating of distantly related animals that share a common ancestor – such as cousins with cousins. 1 × 2
ii)
– To introduce new genes in an existing breeding herd.
– To exploit hererosis that is hybrid vigour.
– To establish a new breed. 1 × 3
b)- Animal holding – used to hold animals before dipping.
– Foot path – To wash the feet of the animal before they get into dip wash.
– The jump – allows the animals to jump singly into dip tank
– Dip tank – contains acaricide solution for controlling ticks.
– Drowning race – The dip was from the animal’s body drip off and drains backs to the dip tank.
– Drying yard. – where the animals are held to dry before being released to pasture. (this prevents pastures contamination)
– Silt trap outlet.- prevents siltation.
– Dip tank south – prevent evaporation of the dip wash
– Also avoid dilution of the dip wash by the rain water.
– also serves as a roof catchment for collecting rain water to the tank.
– Water tank./ Reservoir tank – used for storing water either from the roof or any other area.
– Waste pit – used as a dumping site for sediments from the dip tank. Mentioning – ½ mark
Explanation – ½ mark
1 × 10
d)- They take may years to grow and make effective fence
– They cannot be used for paddocking.
– Hedges can be hiding out for rodents.
– Thorny species can cause injury to humus.
– Require regular trimming.
– Their growth may be irregular thus gases for thieves.
20 marks
a)
i) Coccidia / Eimenia spp. 1 × 1
ii) – Diameter
– Dysentery / blood in dung
– Emaciation
– Ruffled features
– Dullness with dropping wings.
– Sudden death. 1 × 5
iii)
– Use coccidiostats. (drug)
– Isolution / use of potable calf pen.
– Avoid, wet, filthy and unhygienic animals surroundings.
– Cattle from different firms should not drink in a common watching points.
– Avoid overcrowding. 1 × 4
b) Eggs hatch on the ground and larvae emerge; emerging larvae attach themselves to the first host ; feed on blood ; become engorged; drop off to the ground ; and moult into nymphs ;
These nymphs seek out a second host; feed on blood ; become engorged ; and drop off to the ground and moult into adults ; The adults climb onto the third host ; the feed ; become engorged ; and mate; before the females drop off to the ground to lay eggs. ;
c)- pot clean milk in clean bucket.
– Clean your hands.
– Place the index finger into the calf mouth, the calf start sucking.
– Lower the finger slaving until it is sub arranged in milk as the calf sucks, this allows the calf to chick milk.
– Slowly withdrawn the finger while the calf is sucking.
– Repent the whole procedure diary and continuously. ½ × 6 = 3 marks
20 marks