KNEC KCSE Agriculture Paper 2 Question Paper / 2015 KCSE Meru South Form 4 Joint Examination
2015 KCSE Meru South Form 4 Joint Examination
Agriculture Paper 2
SECTION A (30 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section.
Name a breed of goat kept hair production.
1 marks
State two ways in which barbed wire fences may be reinforced in the farm.
1 marks
Broadly, classify two causes of infertility in herd of cattle.
2 marks
Name the tool that is used together with the following as a pair.
i Hypodermic needle
ii Leading stick:
iiiElastrator:
ivCanula:
2 marks
State three signs of anthrax observed in the carcass of cattle.
1.5 marks
State four ways by which cannibalism in poultry could be avoided.
2 marks
Name the intermediate host of the following parasites.
a. Tapeworm
b.Liver fluke
2 marks
List down two groups of cattle that are susceptible to milk fever.
2 marks
Give two situations which may necessitate the preparation of artificial colostrum.
2 marks
Give two uses of gears in a tractor.
2 marks
List four tools used for laying concrete blocks when constructing a wall.
2 marks
State four characteristics of clean ,high quality milk.
2 marks
Give three maintenance practices that should be carried out on cross cut saw.
1.5 marks
What is the cause of grass staggers in animals?
1 marks
Give the meaning of the following terms used in livestock health.
i incubation period
ii Mortality rate
2 marks
Write down two common examples of chemical cause of diseases among livestock.
2 marks
Name two main part of a farm building.
2 marks
SECTION B (20 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section.
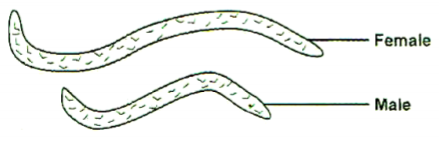
Study the diagram of an internal parasite of livestock in the farm and answer the questions that follow.
a) What disease condition would an animal infected with the above parasite develop? ( ½ mark)
b) A cow is suspected to have suffered the disease condition in (a) above before it was slaughtered for meat. State four
postmortem symptoms that would confirm occurrence of this disease. (2 mark)
c) Write down four ways of controlling the internal parasite in the diagram above. (2 marks)
5 marks
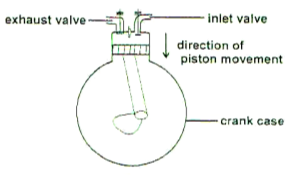
The diagram below illustrates a stroke in a four stroke cycle engine. Study it then answer the questions that follow. The arrow shows the direction of motion of the piston.
a) Identify the stroke illustrated by the diagram. (1 mark)
b) Identify the type of tractor engine illustrated in the diagram on the basis of type of fuel it uses. (1 mark)
c) Give a reason for your answer in (b) above. (1 mark)
d) Name in the correct order, the next two strokes which follow the one illustrated above. (1 mark)
e) What is a compression ignition engine? (1 mark)
5 marks
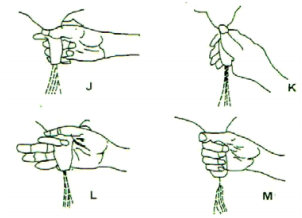
The diagrams labelled J, K,L and M below show possible ways of drawing milk from the teat of a cow during milking. Study the illustrations and then answer the following questions.
a) Which illustration shows the proper way of milking? ( ½ mark)
b) How long should it take to milk a cow from the start to the end of milking? ( ½ mark)
c) Outline the preparation you would carry out on the animal before it is ready for milking. (3 marks)
d) Mention two practices carried out on the milk after milking. (1 mark)
5 marks
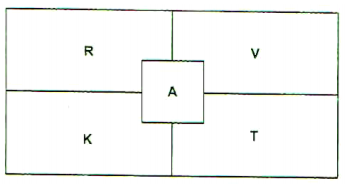
The diagram below illustrates a grazing system.
a) Name the type of grazing system indicated. ( ½ marks)
b) On the diagram, indicate the sequence of animal movement using arrows. (1 mark)
c) Name the part labelled A. (1 mark)
d) Give the main reason for locating the structure labelled A in the position as in the diagram. (1 mark)
e) Give three advantages of this system of grazing. (1 ½ marks)
5 marks
SECTION C (20 Marks)
Answer two questions in this section.
(a)Explain the measures that are taken to prevent occurrence of livestock diseases in the farm (10 marks)
(b)List five side effects of livestock. (5 marks)
(c)State five ways through which infectious disease can spread in livestock. (5 marks)
20 marks
(a)State the difference between exotic cattle (Bos taurus) and indigenous cattle (Bos indicus) (10 marks)
(b)Explain ten advantages of battery cage system in poultry rearing. (10 marks)
20 marks
(a)Outline factors that should be considered when sitting farm structures. (10 marks)
(b)Describe the factors that influence the selection of construction materials. (10 marks)
20 marks
AGRICULTURE PAPER 2 MARKING SCHEME
2015 KCSE Meru South Form 4 Joint Examination
Agriculture Paper 2
SECTION A (30 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section.
Breed of goat kept for hair production
− Angora goat / mohair 1 × 1 = 1 mark
1 marks
Reinforcing barbed wire fence
– Use of droppers.
– Use of concrete to fix posts;
– Use of wire and wooden strainers.
– Use of struts and braces. 2 × ½ = 1 mark
1 marks
Causes of infertility
– faulty / failure of the reproductive mechanism;
– poor feeding;
– breeding diseases; 2 × 1 = 2 marks
2 marks
Pairs tools:
i) Hypodermic needle hypodermic syringe.
ii) Leading stick – bull ring;
iii) Elastractor – rubber ring;
iv) Canula – Trocar; 4 × ½ = 2 marks
2 marks
Signs of anthrax
– Lack of rigor mortis.
– Dark red blood oozing out through the natural openings;
– Non clotting blood;
– Bloated / swollen stomach. 3 × ½ =1½ marks
1.5 marks
Control of cannibalism
– Debeaking perpetual cannibals;
– Use of battery, cage system;
– Laying boxes being as dark as possible;
– Dim light in poultry houses; 4 × ½ = 2 marks
2 marks
Intermediate hosts
a) Tapeworm – pig; cattle.
b) Liver fluke – mud snail / water snails. 2 × 1 = 2 marks
2 marks
Cattle susceptible to milk fever
– Heavy milking cows / high yielding cows.
– Animals fed on feeds lacking calcium.
– Cows at 3rd – 4th lactation.
– Cows which had past cases of milk fever. 2 × 1 = 2 marks
2 marks
When to prepare artificial colostrums
– Death of mother cow after birth.
– Absence of a foster mother.
– Mother cow having been milked upto four days prior to parturition 2 × 1 = 2 marks
2 marks
Uses of gears
– Provide different forward speeds.
– Enable reversing.
– Allows tractor stopping without switching off the engine. 2 × 1 = 2 marks
2 marks
Tools to lay concrete blocks
– Spirit level.
– Plumb bob / plumb line.
– Mason’s square / tape measure.
– String / line / masons hammer.
– Masons chisel / bolsters; 4 × ½ = 2 marks
2 marks
State four characteristics of clean milk
– Free from pathogens.
– Of standard chemical composition;
– No physical dirt (like hairs, dust, dung)
– Good milk flavour.
– High keeping quality. 4 × ½ = 2 marks
2 marks
Maintenance of cross cut saw
– Proper storage after use.
– Oil the blade to avoid rusting.
– Sharpen the teeth;
Set the teeth properly.
– Tighten the handle screws if loose / replace broken handles; 3 × ½ = 1½ marks
1.5 marks
Causes of grass staggers
– Magnesium deficiency 1 × 1 = 1 mark
1 marks
i) Incubation period – Time from entry of disease germ (pathogen) to the time symptoms show up
ii) Mortality rate – likelihood of death to occur in the herd in case of disease infection. 2 × 1 = 2 marks
2 marks
Chemical causes of diseases
– If an animal eats, swallow or inhales chemicals like acids, alkalis, insecticides and herbicides it can be poisoned.
– Stings from certain insects insensitive parts of the body can cause;
– Some weeds in pasture are poisonous if eaten by animal, for example
Thorn apply (Datura stramonia); 2 × 1 = 2 marks
2 marks
Give three parts of a building
– Foundation
– Walls
– The roof
2 marks
SECTION B (20 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section.
a) Ascariasis; 1 × ½ = ½ mark
b) Reasons
– Presence of adult worms
– Presence of eggs of the worms
– Haemorrhage on the intestines.
– Presence of cysts. 4 × ½ = 2 marks
c) Worms control methods
– Routine drenching.
– Maintain proper hygiene
– Practise rotational grazing.
– Burning of grazing pastures. 4 × ½ = 2 marks
5 marks
a) Induction stoke 1 × 1 = 1 mark
b) Petrol engine 1 × 1 = 1 mark
c) Presence of spark plug 1 × 1 = 1 mark
d) Compression stroke, followed by power stroke. 2 × ½ = 1 mark
e) Diesel engine 1 × 1 = 1 mark
5 marks
a) m; 1 × ½ = ½ mark
b) 8 – 10 minutes 1 × ½ = ½ mark
c) Preparation before milking
− Bringing the animal to the milking stall.
− Provide feed in the feed trough.
− Secure the animal’s hind legs properly.
− Wash the animal’s udder.
− Wipe the udder with a clean cloth.
− For mastitis using a strip cup
− Milk the animal; 6 × ½ = 3 marks
d) Post milking practices
– Weighing and recording milk
– Sieving the milk.
– Cooling the milk 2 × ½ = 1 mark
5 marks
a) Rotational grazing. 1×½=½ mark
b) Sequence of rotation.
NB: Arrows must be continuous in one direction: 1 × 1 = 1 mark
c) A is water trough 1 × 1 = 1 mark
d) A is at the centre to make water available to livestock grazing in all paddocks. 1 × 1 = 1 mark
e) Advantages of rotational grazing
– Livestock make maximum use of pastures.
– Reduces the build-up of pest and diseases.
– Animals waste is distributed evenly in all fields or paddocks.
– Pastures area is given time to re grow before it is grazed on again.
– Excess pasture can be harvested for conservation.
– It is possible to apply fertilizers in parts of the pasture which are not in use.
– Reseeding and weeding can be done when livestock leaves a paddock for another.
5 marks
SECTION C (20 Marks)
Answer two questions in this section.
a) Explain the measures taken to prevent occurrence of livestock diseases.
– Deworming to control internal parasites:
– Rearing disease resistant breed of livestock; e.g. Zebu are resistant to ECF
– Proper nutrition by providing a balanced diet to avoid deficiency diseases.
Use of healthy breeding stock of AI;
– Control of disease vectors e.g. tsetse fly
– Vaccinating health animals before infection to create immunity against specific diseases; e.g. foot and mouth, black quarter;
– Mass slaughter / culling of animals suffering from zoonotic diseases like anthrax; rinderpests.
– Quarantine to prevent animal movement into or out of disease outbreak areas:
– Isolation of sick animals to prevent spread of contagious diseases.
– Use of antiseptics and disinfectants on equipments to kill pathogens.
– Administering prophylactic drugs to prevent infection.
– Feeding livestock on dry roughage before provide succulent roughage to prevent bloat,
– Hoof trimming to minimise occurrence of foot rot disease.
– Proper housing to prevent pneumonia. 10 × 1 = 10 marks
b) Side effects of livestock diseases:
– Reduce market value of livestock.
– Spread diseases to man e.g. anthrax and brucellosis.
– Reduce the quality of products e.g. mastitis reduce quality of milk.
– Shorten productive life of an animal.
– High mortality rate.
– Lowered production.
– Some like vaginitis cause infertility. 5 × 1 = 5 marks
c) Ways of diseases spread.
– Contaminated feeds and water.
– Insect vectors and contaminated equipments.
– Contact with affected animals.
– Open wounds.
– Inhalation of pathogens.
– Mating.
– Suckling of young ones by dams.
– During parturition / kidding / lambing / delivery. 5 × 1 = 5 marks
20 marks
a) Differences between Bostaurus and Bos indicus. 10 × 1 = 10 marks
b) Advantages of battery cage system in poultry rearing. (10 marks)
– Eggs produced remain clean
– Broodiness is discouraged.
– High stocking rate /many birds in a unit area.
– Feed and water are not contaminated.
– vices like cannibalism and egg eating are reduced.
– Individual records of egg laying can be kept
– More eggs are produced per bird.
– The system requires low labour.
– Is easy to clean and disinfect.
– Sick birds are easily identified and treated.
– Feeding and watering can be mechanised
– Different classes / ages of birds can be kept
– Less spread of diseases and parasites from a bird to others.
– It is easy to handle birds during routine management practices.
– Culls / culled birds have tender meat. 10 × 1 = 10 marks
20 marks
a) Siting factors for farm structures
– The location of the homestead; homestead should be sited at a point that give it panoramic view;
– Accessibility – to most part of the farm.
– Security – housing structure should be sited at safe place to avoid theft of livestock.
– Drainage, the area should have good drainage to avoid flooding.
– Direction of the prevailing wind – structures like latrines should be sited on the leeward side of homestead to avoid foul smell
in the houses.
– Relationship between structures – related structures like milking parlour and calf pen should be near one another to save time.
– Famer’s taste and preference influence site of a structure like homestead away from the roads.
– Proximity of structure to existing amenities like water supply and electricity;
– Topography of the area – a slopy ground make construction of a building very expensive due to levelling
– Future expansion – should have free space for extension 10 × 1 = 10 marks
b) Factors that influence selection of construction materials.
– Availability of materials – select construction materials that are locally /readily available.
– Cost of the materials – select material that are cheapest as long as they meet other qualifications.
– Suitability of the materials to drainage of floor – keep off rain – light the room and temperature regulation
– Suitability of materials to the prevailing weather conditions.
– Durability of materials to reduce cost of repairs and maintenance
20 marks