KNEC KCSE Biology Paper 1 Question Paper / 2015 KCSE Kericho West Joint Examination
2015 KCSE Kericho West Joint Examination
Biology Paper 1
State the name given to the study of :
a) The cell (1 mark)
b) Micro-organism (1 mark)
2 marks
a) Write the dental formula of an adult human (1 mark)
b) Name two dental diseases. (2 marks)
3 marks
The diagram below represents a certain organism collected by a student at the sea shore.
a) Name the class to which the organism belongs. (1 mark)
b) Give three reasons for your answer in (a) above. (3 marks)
4 marks
Give three reasons for classifying organisms.
3 marks
In an investigation, a student extracted three pieces of pawpaw cylinders using a cork borer. The cylinders were cut back to 50mm length and placed in a beaker containing a solution. The results after 40 minutes were shown in the table below.
Feature Results
Average length of cylinders mm 56mm
Stiffness of cylinders Stiff
a) Account for the results in the table above. (3 marks)
b) What would be a suitable control set-up for the investigation. (1 mark)
4 marks
State three ways in which a respiratory surface is adapted to its function.
3 marks
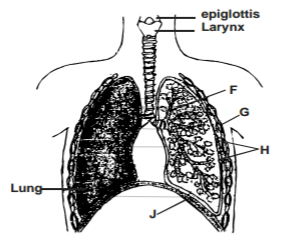
The diagram below represents part of the gaseous exchange system in human.
a) Name the parts labelled F and G. (2 marks)
b) State one function of each of the parts labelled H and J. (2 marks)
4 marks
What is meant by the following terms?
a) Ecology (1 mark)
b) Carrying capacity. (1 mark)
2 marks
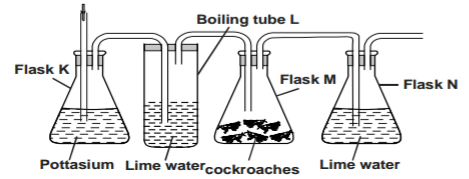
The diagram below represents a set-up that a students used in an investigation.
a) Name the physiological process that was being investigated. (1 mark)
b) State the role of potassium hydroxide in a flask K. (1 mark)
c) Account for the observation in boiling tube L and flask N (2 marks)
4 marks
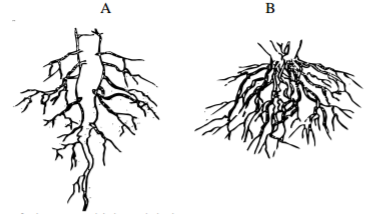
The diagrams below illustrate the organs of some flowering plants.
State the classes of plants to which each belong.
2 marks
State the functions of the following parts of a light microscope.
a) Fine adjustment knob. (1 mark)
b) Stage (1 mark)
2 marks
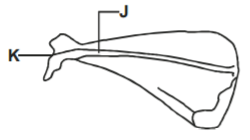
The diagram below represents a bone obtained from a mammal.
a) Name the bone (1 mark)
b) Name the
i) Bone which articulates with the bone named in (a) above at the cavity labelled K. (1 mark)
ii) Joint formed by the two bones. (1 mark)
c) State the function of the part labeled J. (1 mark)
4 marks
State the importance of divergent evolution to organisms.
2 marks
Explain why it is not advisable to be in a poorly ventilated room with a burning charcoal stove.
3 marks
The diagram below represents a certain plant.
a) What is the likely habitat for the plant? (1 mark)
b) Give two reasons for your answer in (a) above. (2 marks)
3 marks
Give reasons for carrying out the following procedures when preparing temporary wet mounts of plant tissues.
a) Making this plant sections. (1 mark)
b) Adding water on the plant section. (1 mark)
c) Placing cover slip over the plant section. (1 mark)
3 marks
Name three mechanisms that ensure cross pollination takes place in flowering plants.
3 marks
Name two substances that leave the foetal blood through the placenta.
2 marks
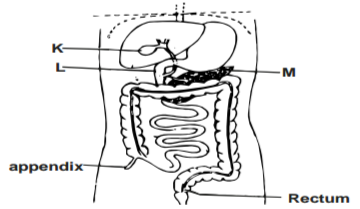
The diagram below represents a part of the human digestive system.
a) Name the organs labelled L and M (2 marks)
b) i) Name the substances produced by the organ labelled K. (1 mark)
ii) State the function of the substances named in b(i) above. (1 mark)
4 marks
Name the flower part that produces gametes.
1 marks
Name support tissues in plants that is not thickened with lignin.
1 marks
Explain why plants do not require specialised excretory organs.
4 marks
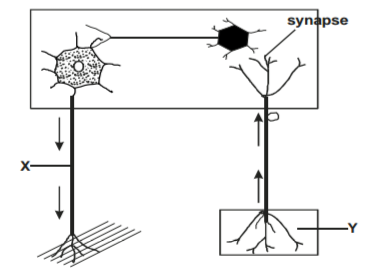
The diagram below represents a reflex arc in human.
Name the parts labelled X and Y.
2 marks
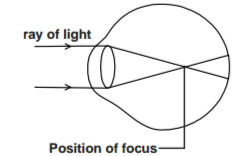
The diagram below illustrates a defect in the eye.
Explain how the defect illustrated above can be corrected.
2 marks
a) Differentiate between the following terms.
i) Dominant gene and recessive gene. (1 mark)
ii) Continuous variation and discontinuous variation. (1 mark)
b) What would be expected results from a a test cross? (2 marks)
4 marks
Explain what happens in human when the concentration of glucose in the blood decreases below the normal level.
4 marks
State two differences between open and closed circulatory systems.
2 marks
State four reasons why water is significant in seed germination.
4 marks
BIOLOGY PAPER 1 MARKING SCHEME
2015 KCSE Kericho West Joint Examination
Biology Paper 1
a) The cell
– cytology; (1mk)
b) Micro-organisms
– microbiology (1mk)
2 marks
a) Write the dental formula of an
(1mk)
b)
– Dental carries
– Periodontis/gingivitis/pyorhoea (2mks)
3 marks
a)
– Crustaceae; (1mk)
b)
− Head fused with thorax, has a cephalothorax.
− Has two pairs of antennae;
− Has compound eyes/A pair of compound eyes;
− Has five pairs of limbs;
− Has external Gills; (3mks)
4 marks
− Identifying similarities and differences between organism.;
− Organize scientific knowledge in an orderly system.;
− Monitor emergence presence and disappearance of organisms;
− Grouping organisms for easy study.;
3 marks
a) Account for the results in the table above .
– The solution was hypotonic/less concentrated compared to the cell sap of pawpaw cylinders cell;
– The tissue cells gain water by osmosis becoming turgid/stiff. (3mks)
b) What would be a suitable control set-up for the investigation?
– Boiled pawpaw cylinders of the same size/lengths placed in a similar solution; /
– Isotonic solution. (1mk)
4 marks
− Thin walls/epithelium for faster diffusion of gases reducing distance for diffusing molecules;
− Moist for gases to dissolve and diffuse in solution form;
− Large surface area for maximum diffusion.;
− Highly vascularised to maintain a steep concentration gradient;
− Permeable to respiratory gases;
3 marks
F- Bronchiole; rej Bronchioles,
G -Intercostal muscles; (2mks)
b) State one function of each of the parts labelled H and J.
H – (Pleural Membrane) – Secretes pleural fluid to lubricate lungs/protect lungs)
J – (Diaphragm) – Separates chest cavity from abdominal cavity; works to effect volume/pressure changes in chest cavity.
4 marks
a) Ecology
– Study of inter relationships between organisms and their environment.; (1mk
b) Carrying capacity
– The maximum number of a species that a particular habitat can support.; (1mk)
2 marks
a) Name the physiological process that was being investigated.
– Respiration; (1mk)
b) State the role of potassium hydroxide in a flask K.
– In flask K potassium hydroxide removes/absorbs carbon (iv) oxide from the atmospheric air. (1mk)
c) Account for the observation in boiling tube L and flask N.
L – lime water remains clear because carbon (IV) oxide has been removed;
N -flask N lime water forms a white precipitate because the respiring cockroach produce carbon (IV) oxide.; (2mks)
4 marks
A – Dicotyledonae;
B – Monocotyledonae; (2 mks)
2 marks
a) Fine adjustment knob
– Moves the body tube through smaller distances to bring the image into sharper focus; (1mk)
b) Stage
– Plat form where specimen in placed; (1mk)
2 marks
a) Name the bone.
– Scapula; Rej Scapular (1mk)
b) Name the:
i) Bone which articulates with the bone named in (a) above at the cavity labeled K.
– Humerus ; (1mk)
ii) Joint formed by the two bones
– Ball and socket joint; (1mk)
c) State the function of the part labelled J.
– Attachment of muscles; (1mk)
4 marks
– Homologous structures are modified to suit different functions; hence organisms are able to exploit their environment better.;
2 marks
– Charcoal in limited supply of air produces carbon (ii) oxide; which combines with haemoglobin forming carboxyhaemoglobin which is stable/does not dissociate reducing capacity of haemoglobin to carry oxygen leading to suffocation hence death.
3 marks
a) What is the likely habitat for the plant?
– Dry/arid/semi-arid/desert; (1mk)
b) Give two reasons for your answer in (a) above.
– Succulent/fleshy stem / reduced leaves/leaves reduced into thorns/spines; (2mks)
3 marks
a) Making this plant sections
– To reduce a layer of cells to allow light to pass through; (1mk)
b) Adding water on the plant section
– To make cells turgid/prevents drying up; (1mk)
c) Placing cover slip over the plant section.
– To protect the lens on the objectives;
– To exclude air/solid; (1mk)
3 marks
– Protogyny and protandry;
– Self sterility / incompatibility;
– Dioecious plants; (3mks)
3 marks
– Carbon (IV) Oxide;
– Nitrogen waste/urea;
2 marks
a) Name the organs labelled L and M.
L – Duodenum;
M- Pancrease; Rej Pancreases (2mks)
b) i) Name the substances produced by the organ labelled K.
– Bile; (1mk)
ii) State the function of the substances name in b(i) above.
– Emulsification/Emulsifies fats;
– Neutralises; chyme; (1mk)
4 marks
Name the flower part that produces gametes.
– Anther/ovary;
1 marks
– Parenchyma / collenchyma; (1mk)
1 marks
Explain why plants do not require specialized excretory organs.
− Some wastes i.e gases easily diffuse out of plant tissue;
− Some waste products are mainly made from carbohydrates and hence are not as harmful as portentous materials;
− Some wastes are formed slowly thus little accumulation of wastes;
− Plants are less active;
− Some products such as oxygen are reused/recycled;
− Some wastes products are stored in non-toxic forms in leaves, flowers, fruits and old bark then drop off; (4mks)
4 marks
Name the parts labelled X and Y.
X – Motor neurone; Rej; axon alone
Y – Receptor/sense organ; Acc; axon of motor neurone Rej; cells. (2mks)
2 marks
Explain how the defect illustrated above can be corrected.
– Short-sightedness is corrected by wearing concave/diverging lenses; it diverges light rays before reaching the lens which then
focuses light into the retina;
2 marks
a) Differentiate between the following terms
i) Dominant gene and recessive gene.
– Dominant gene expresses itself on both homozygous state and heterozygous state while recessive gene can only expresses
itself in the homozygous state; (1mk)
ii) Continuous variation and discontinuous variation
– Continuous variation – Characteristics for which there is a continuous range with many intermediaries;. Discontinuous
variation are discrete/distinct/separate/definite categories or units or clear out differences; (1mk)
b) What would be expected results from a test cross?
– Either all offspring’s show dominant characteristic or half offspring’s show the recessive while other half show dominant
characteristics. (2mks)
4 marks
Explain what happens in human when the concentration of glucose in the blood decreases below the normal level.
– Pancrease releases glycogen hence glycogen is converted to glucose;
– Fat is converted to glucose; reduced rate of respiration;
4 marks
State two differences between open and closed circulatory systems.
Blood flow in haemocoel; – Blood confined in vessels;
– Blood flow in low pressure; Blood flow in high pressure;
2 marks
State four reasons why water is significant in seed germination.
– Activate enzymes – Provide a medium for enzymatic activities to break down stored food to soluble forum;
– Hydrolyse; dissolves food materials.
– Medium of transportation;
– Soften seed coats to facilitate emergence of radicle.
4 marks