KNEC KCSE Biology Paper 1 Question Paper / 2015 KCSE Tharaka South Joint Examination
2015 KCSE Tharaka South Joint Examination
Biology Paper 1
Give two characteristics that distinguish scientific names of organisms from the ordinary names.
2 marks
Identify the structure of the cell that perform the following functions: (1 mark)
a) Synthesize ribosomes (1 mark)
b) Regulate exchange of substance in and out of the nuclear. (1 mark)
c) Division of cells to form new ones. (1 mark)
3 marks
A student set up an experiment as shown in the diagram below.
a) (i)What was being investigated in the experiment? (1 mark)
ii.Draw a diagram to indicate the expected results of the experiment after three days. (1 mark)
iii.Why was it necessary to have wet cotton wool in the container. (1 mark)
b) What is the role of the following in a germinating seed. (1 mark)
i. Oxygen (1 mark)
ii. Cotyledons (1 mark)
3 marks
Name two enzymes and one ion metal that are needed in the blood clotting process.
3 marks
Name the polysaccharides found in the following structures. (1 mark)
a) Exoskeleton (1 mark)
b) Xylem vessels (1 mark)
3 marks
Outline three ways in which the gills of tilapia fish are modified to perform their functions.
3 marks
The graph below shows the effect of substrate concentration and the rate of enzyme reaction.
a) (i) Account for the shape of the graph between (2 marks)
i. A and B
ii. B and C
b) How can the rate of reaction be increased after point B? (1 mark)
3 marks
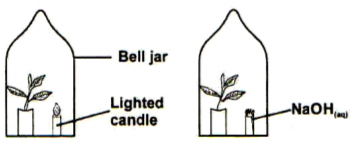
Two potted plants A and B were placed in the dark for two days. Each was then placed in an air tight bell jar as follows then transferred to light for four hours. Each plant was then tested for starch.
a) why were the plants put in the dark place for two days. (1 mark)
b) what was the result of the starch test in plant B.Expain your answer. (2 marks)
3 marks
identify two adaptations of vertebrae neurone that affects the speed of impulse transmission.
3 marks
(a)State the kingdom to which chladydomonas belong. (1 mark)
(b)An organism has the following characteristics:
_ Four pairs of wings
_ Cephalothorax and abdomen
_ Absence of antennae
_ Presence of a pair of chelicerae
Name the phylum and class that the organism belongs to? (2 marks)
Phylum
Class
3 marks
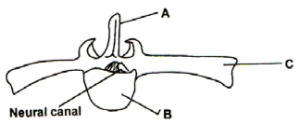
Study the diagram shown below of the anterior view of a lumbar vertebra of a mammal.
a) Name the parts labelled A and B (2 marks)
b) State the function of part C (1 mark)
3 marks
Name the type of response shown by:
a) Leaves of mimosa pudica when they fold after being touched. (1 mark)
b) Euglena when it swims towards the source of light. (1 mark)
c) Maggots moving from the lit side of a boiling tube to the side painted black. (1 mark)
3 marks
(a) Give two possible ways of establishing the genotype of an organism whose genotype is unknown. (2 marks)
(b) Euglena when it swims towards the source of light. (1 mark)
(c) Give the genotype of a male who could be born haemophiliac. (1 mark)
4 marks
The diagram below shows a structure for gaseous exchange in class Pisces.
a) Identify the structure. (1 mark)
b) State the function of the part labelled C.
c) How is the structure labelled B adapted for its function? (1 mark)
4 marks
a)State two advantages of internal fertilization. (2 marks)
b) Give reasons why a woman excretes less urea when she becomes pregnant. (2 marks)
4 marks
The diagram below represents part of phloem tissue.
a) Name the structures labelled R and S and the cell labelled T. (3 marks)
R
S
Cell labelled T
b) State the function of the structure labelled S (1 mark)
4 marks
Distinguish between natural and acquired immunity.
2 marks
a)What is the difference between Darwinian and Lamarkian theories of evolution? (2 marks)
b) What is meant by the term vestigial structures? Give one example. (2 marks)
4 marks
Name the hormone responsible for:
a) Conversion of glycogen to glucouse (1 mark)
b) Regulation of the amount of water in the blood (1 mark)
2 marks
Name the substances produced as a result of anaerobic respiration in:
i. Yeast (1 mark)
ii. Human muscles (1 mark)
2 marks
Account for the osmoregulatory changes that would take place in a marine amoeba if it was transferred to a fresh water environment.
3 marks
a) What is meant by resolving power of a microscope. (2 marks)
b) State the reason behind the addition of iodine solution, to an onion epidermis on a slide while being observed on alight microscope. (1 mark)
3 marks
Why is excretion of nitrogenous wastes more of a problem to animals than plants.
3 marks
Explain why sweat accumulates on a person’s skin in a hot humid environment.
2 marks
a)Name two kinds of nuclei found in a mature pollen grain. (2 marks)
b) State what is meant by double fertilization in flowering plants. (2 marks)
4 marks
a) State the role of active transport in animal nutrition. (1 mark)
b) Give two factors which affect active transport. (2 marks)
3 marks
BIOLOGY PAPER 1 MARKING SCHEME
2015 KCSE Tharaka South Joint Examination
Biology Paper 1
− Two names i.e ist genus and 2nd species
− Genus names start with capital letter while species start with small letter.
− Both names are written in intalics when printed / underlined when typed or handwritten. Mark any 2 x 1 = 2 marks
2 marks
a). Nucleus 1 mk
b). Nuclear membrane / pore 1mk
c). Centriole 1mk
3 marks
a). i). Region of elongation / rapid growth in root / radical 1mk
ii).
iii). To provide water / moisture for germination 1ml
b). i). oxygen – for oxidation of food to provide energy for germination 1mk
ii). Cotyledons – store food necessary for germination / protect plumule 1ml
3 marks
− enzymes – thrombin 1mk
− thromboplastin (thrombokinase) 1mk
− metal ion – calcium ions 1mk
3 marks
a). Chitin 1mk
b). Lignin 1mk
3 marks
− Gill filament are thin / cell thick to facilitate faster / rapid diffusion of respiratory gases 1mk
− The surface of the gill filaments are moist to facilitate dissolution of the repiratory gases 1mk
− The gill have numerous rakers that filter food / soild particles that may damage the gill filaments
− The gill is highly vascurised to ensure efficient transport of respiratory gases Mark any 3 – @1mk = 3 mks
3 marks
a).
i). More active sites of enzymes available for a large number of molecules of substrate hence increase in the rate of reaction
(rapid or fast increase in the rate of reaction)
ii). B and C
enzymes / substrate are in equilibrium / all active sites are occupied hence rate of reaction is constant
b). Raising concentration of enzymes
3 marks
a). So that they could be destarched / use up all the stored starch
b). No starch in the plant
the NaOH solution absorbed carbon (IV) oxides from the air hence no photosynthesis occurred to form starch
3 marks
− myelin sheath
− Nodes of ranvier
3 marks
a). Protoctista 1mk
b). Phylum – arthropoda; rej Arthropods
class – arachnida rej Arachnids
3 marks
a). A – Neural Spine
B- centrum
b). For attachment of abdominal muscles
3 marks
a). Nastic /Haptonasty Phototaxis
b). Positive Phototaxis
c). Negative phototaxis
3 marks
a). – selfig / self fertilization as in plants
– test cross / back cross
b). Haemophilia is a sex – link characteristic which is only carried by the X chromosome and a father can only donate x-
chromosome to his daughter but not son
c). Xh
Y
4 marks
a). Gill
b). Creates a large surface area for maximum gaseous exchange
c). Large and curved to provide large surface for attachement of numrtous gill filaments bony / rigid to offer support
4 marks
a). high chance of survival since zygote is highly protected in the body.
High chances of fertilization
b). Most of the excess amino acids are used in the development and growth of the foetus thus less amino acid are delaminated
4 marks
a). R – sieve pore
S – cytoplasmic strand cytoplasm filaments rej. proto plasmic strad)
Cell labeled T – companion cell
b). Translocation (L is tied with structures)
4 marks
Natural immunity is inherited / transmitted from parent to offspring
Acquired immunity is developed after suffering from a disease / through vaccination
Accept inmate / inborn for natural immunity rej. Born with it
2 marks
a). Lamarckia
Inheritance of acquired characterists / environment induces production of inheritable character which is then inherited
Darwinian
Inheritance of genetically acquired characteristics / character happends to appear spontaneously which then gives
advantage of organisms therefore better – adaptable characters are then inherited by natural selection
b). Are structured greatly reduced in size and therefore not used to function acc. Third digit og wing or bird
– Halteres in flies
– presence of hind limb / (buds) in python
– Human ear muscles
Example
Human appendix / kiwi (flightless bird) with reduced wings / vestiugial wings in flies human hair / presence of hind limbs in
python, reduced pelvic girdle of whale
4 marks
a). Glucagon
b). Antidiuretic hormone /ADH/vasopresin any first one
2 marks
i). Alcohol
ii). Lactic acid 2 mks
2 marks
More water will enter the amoeba by osmosis rate of water enter the amoeba by osmosis rate of water discharged by contractile vacuole will increase more contractile vacuoles formed
3 marks
a). The ability of microscope to separate images of objects that lie close to one another
b). Stains / colour parts of the cell making it more visible / clear
3 marks
− Plants are able to store the wastes in their bodies in non-toxic forms
− Plants are stationary and therefore less active hence realse less toxic wasted compared to plants which produce a lot
− Plants utilize simple inorganic substance to make their foods in amount required by the body hence less wastes while animals consume complex compounds whose breakdown releases more toxic wastes
3 marks
Sweat produced does not evaporate due to high humidity and the body does not cool hence more sweat produced leading to accumulation 2mks
2 marks
a). – generative nucleus 1mk
Pollen tube / tube nucleus 1mk
b). A kind of fertilization in which the male nucleus decides into two male nuclei. One of which fertilizes the functional egg
forming a zygote while the other fuses with the polar nuclei to form a primary endosperm nucleus
4 marks
a). Helps in absorption of some products of digestion from alimentary canal into blood stream
b). Oxygen concentration / amount t of oxygen
− Change of temperature
− substrate / glucose concentration
− Enzyme inhibitors / metabolic poisons Any first correct two
3 marks