KNEC KCSE Biology Paper 2 Question Paper / 2015 KCSE Tharaka South Joint Examination
2015 KCSE Tharaka South Joint Examination
Biology Paper 2
SECTION A : (40 Marks)
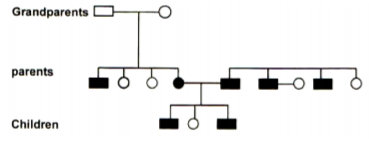
The diagram below shows a family tree. Squares represent males and circles representfemales. Normal individuals are indicated by unshaded squares and circles. Individuals who show genetically controlled defects are indicated by shaded squares and circles.
a) What is the name given to this type of a family tree? (1 mark)
b) In which of the grandparents is the genetically controlled defects likely to have developed and by what process. (2 marks)
c) Assume the genetically controlled defect was haemophilia,show the genotype of the following:
i. Grandparents (2 marks)
ii. The two couples
iii. The children of the couple that shoed the defect. (1 mark)
iv. What are the symptoms of the defect. (1 mark)
v. What is the remedy? (1 mark)
8 marks
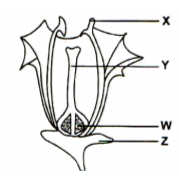
The diagram below represents a flower.
a) Name the parts labelled X and Y (2 marks)
X
Y
b) Describe the ovary position. (1 mark)
c) i) Suggest an agent of pollination of the flower above. (1 mark)
ii. Give a reason for your answer above. (1 mark)
d) On the diagram above, which part do you expect to find haploid nucleus after meiosis? (1 mark)
e) In the flower above its sepals cell was found to have 20 chromosomes. What would be the number of chromosomes found in the endosperm cell of the flower embryo sac after fertilization? (1 mark)
f) State one way in which flowers prevent self-pollination. (1 mark)
8 marks
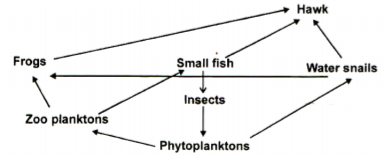
The flow chart below represents a feeding relationship in an ecosystem.
a) Name two organisms which are both secondary and tertiary consumers. (2 marks)
b) State two short term effects of immigration of insects in the ecosystem. (2 marks)
c) Name the organism which has the least Biomass in the food web. Explain. (2 marks)
d) State the role of the following in an ecosystem:
i. Saprophytes (1 mark)
ii. Leguminous plants. (1 mark)
e) Name one method that would be used to estimate the fish population in the ecosystem. (1 mark)
8 marks
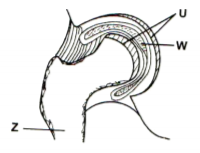
The diagram below represents one of the joints in the mammalian skeleton.
a) Name the type of joint shown in the diagram. (1 mark)
b) Name the parts labelled Z and U (2 marks)
c) Name two parts of the body where this type of joint is found. (2 marks)
d) State the functions of the fluid found in W. (2 marks)
e) Name the type of muscles found in the gut. (1 mark)
8 marks
Shown below is a section through the mammalian nephron.
a) Name the structures labelled: (2 marks)
A
N
b) Name all structures in a nephron which are normally present in the cortex region of kidney. (1 mark)
c) Which region in the nephron deals with conservation of body water. (1 mark)
d) Name one hormone that has an effect on part labelled X. (1 mark)
e) How is part labelled N adapted to its function. (2 marks)
8 marks
SECTION B : (40 Marks)
Answer question6 (compulsory) in the spaces provided and either question 7 or 8 in the spaces provided after question 8
Carbohydrates used during respiration and those formed during photosynthesis by a certain plant was measured over a period of 24 hours at an interval of 3 hours.
| Time of day | 12a.m | 3a.m | 6a.m | 9a.m | 12p.m | 3p.m | 6p.m | 9p.m | 11p.m |
| Carbohydrates formed during photosynthesis(mg) | 0 | 0 | 5 | 30 | 60 | 30 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
| Carbohydrates used during respiration(mg) | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
Using the same axes,
a) Plot a graph of carbohydrate formed during photosynthesis and carbohydrate used during respiration against time.
(8 marks)
b) Calculate the net carbohydrate formed by the plant. (2 marks)
c) At what time of the day do the light compensation points occur? (2 marks)
d) Account for the shape of graph on carbohydrates. (2 marks)
i. Between 12.00a.m and 3a.m (2 marks)
ii. Between 3.00a,m to 12.00 noon (2 marks)
e) How could foggy weather influence the net amount of carbohydrates formed over the 24 hour period? (1 mark)
f) Give other external factors apart from temperature and light intensity that influence the rate of photosynthesis. (2 marks)
g) In which form are carbohydrates stored in ( ½ mark)
i. Plant bodies
ii. Fungi ( ½ mark)
20 marks
a) Describe secondary growth in flowering plants. (14 marks)
b) Describe one method that can be used to measure the average growth rate of a single leaf. (6 marks)
20 marks
a) what is organic evolution? (2 marks)
b) Distinguish between homologous and analogous structure. (4 marks)
c) How does natural selection bring about adaptations of species to its environment. (14 marks)
20 marks
BIOLOGY PAPER 2 MARKING SCHEME
2015 KCSE Tharaka South Joint Examination
Biology Paper 2
SECTION A : (40 Marks)
a). Pedigree
b). Grand mothers; and by mututation
c). i) Grand parents XHY, XHXh
ii). The two couples Xh
Yh
; Xh
Y;Xh
Y, Xh
XH
iii). Xh
Y/Xh
Xh
/Xh
Y
iv). Bleed profusely for long period even from the slightest cut, inject with vitamin K to cause blood clotting which
seals up the would
v). Inject with vitamin K to cause v=blood clotting which seals up the would
8 marks
a). X – anther / male part
Y – style / pistil / female part
b). Epigyneous / superior flower / ovary above the other floral parts
c). i). Wind pollinated flower
ii). Anther located above the stigma
rej. Brightly coloured petals / scented nectarines
d). X /W
e). 30 chromosomes
f). Anthers located below the stigma self sterility / incompatibity Protandry / male parts (stamen) maturing earlier than the
female parts (pistill) Protagyny / female parts (pistil) maturing earlier that the male parts stamens any one stated correctly
1 mk
8 marks
a). Hawk and water snail 2mk
b). decrease in phytoplankton 1mk
increase in population of small fish
c). Hawk, top predator, amount of energy decrease in successive trophic levels / energy is lost through respiration
Undigested / uncovered food (mark any reason 1 x 1 = 1mk )
d). i) Cause decomposition / recycling of nutrients 1mk
ii). Root nodules have bacterial / rhizobium sp to convert free nitrogen into nitrates in the soil 1mk
e). Capture – recapture or capture release recapture 1mk
8 marks
a). Ball and socket joint 1mk
b). Z – femur
U – articular cartilage 2 mks
c). Shoulder / pectoral girdle, hip/pelvic
girdle
rej – (pector / pelvic alone)
d). – Reduction of friction / lubrication
Absorption of shock / distribution of pressure 2mks
e). Smooth muscles 1mk
8 marks
a) A – Afferent arteriole
N – Proximal convoluted tubule 2 mks
b). Bowman’s capsule, proximnal convoluted tubule, distal convoluted tubule 1mk
all named or none
c). Loop of Henle
d). Antidiuretic hormone / vasopresin
e) i). Cell lining tubule have numerous mitochondria which provide energy for reabsorption
iii). Tubule long / highly coiled to increase surface area
iv). Coiling of tubule reduce speed of flow of filtrate to allow more time for efficient reabsorption
v). Tubule is well supplied with blood capillaries for efficient transport / reabsorption any correct first two
8 marks
SECTION B : (40 Marks)
Answer question6 (compulsory) in the spaces provided and either question 7 or 8 in the spaces provided after question 8
a) Title 1mk
Labelled axes 1mk
Correctly used scale 2mk
Plotting of points (Any 3 corredtly plotted points in each case 1mk each 1 x 2 = 2mk)
Labeling of curves 1mk each 2mk
b). Carbohydrates formed during photosynthesis
0+0+5+30+60+30+5+0+0= 130mg ½ mk
Carbohydrates used during respiration
10+10+10+10+10+10+10+10+10+10= 90mg ½ mk
c). 6:36a.m + 10 minutes 1mk
5:24p.m + 10 minutes 1mk
d). i) No carbohydrates 1mk
ii). Gradual increase in carbohydrates 1mk
fromed due to increasing light internsity 1mk
e). Reduced light available, hence carbohydrates formed becomes low 1mk
f). Carbon (IV) oxide 1mk
moisture / water 1mk
g). Starch ½ mk
Glycogen ½ mk
20 marks
a). Secondary thickening id facilated by meristamatic cells known as cambium which are located between phloem and xylem in
vascular budles of plants the cambium divides radically to form a rine (cylinder) of cambium rissue with the xylem inside the
ring and the phloem outside the ring, cells of the cambium ring divide to four secondary phloem outside intervascular
cambium (between vascular bundles) divide to form secondary phloem outside. Intervascular cambium (between vascular
bumdles) divided to form secondary parenchyma, thereby increasing the growth of meducary easy much more xylem is
formed than phyloem thus pushing phlem and cambium outwards the rate of secondary growth is dependant on the season /
rainy resulting in annualar rings,. Cork. Camvium / phellogen divides to form new cork / bark rissue to accommodate
increased growth on outside and secondary cortex on the inside. 14mks
b). Choose / identify a yound leaf which is folded, use the same leaf throughout measure the total length of the whole leaf (acc.
Measure of any part of the leaf / record / length) repeat the procedure at regular interval, until no change occurs in length /
until it gets constant length the average rate of growth is equal to toatal increase in length divided by the period taken to
achieve final length
20 marks
a). Organic evolution is a gradual change of living organism from simple life forms to more complex forms, over a long period of time
b). Homologous structures are structures of the same embroyonic origin that become modified in the course of evalution to perform different ecological niches Analogous structures are structures of different embryonic origin that become modified in the course of evolution to perform similar functions in the same ecological niches. 2 mks
c). How natural selection brings about adaoptation id the species ro its environment
− organisims in the same environment are always competing for resources such as food mates, shelter etc as well as enduring the harshness of the environment.
− This phenomenon is described as a struggle for existence
− those organisms that best adapted to survive to productive maturity and give tise tooffrsprings of the next generation.
− the less well adapted die yound, hence survival of the fittest
− if the favourable charaxteristics possessed by the ‘fittest’ organisms are genetic they are passed onto the offspring
− this leads to a natural occurrence of variation onto the offsprings
− this leads to a natural occurrence of various without a species
− if these variations are genetic change in the characteristics of the species making it better adapted to its environment
− accumulation of small variations over a long period of time lead to the emergence of new dorms of life i.e ne species
− if suited and well adpted to the new environment these new forms reproduce successfully and pass on their characteristics
− if not suited these new forms are eliminated by nature leaving mutant forms which are better adapted to the environment
− through this process nature selects those oragnisns with better adaptations while ensuring the elimination of those not able to adapt to the changing environment.
− thus the changing eniviroment (nature) forces and organism (a species ) to adapt or otherwise be eliminated
Total 18
Max 16
20 marks