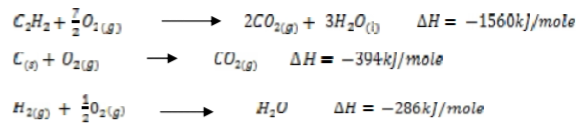KNEC KCSE Chemistry Paper 1 – 2014 Gatundu Mock
Chemistry Paper 1
Describe how you can separate a mixture of solid copper (II) oxide and solid copper (II) nitrate
3 marks
Study the set up below for the electrolysis of copper (II) sulphate solution using copper electrodes.
a. Write ionic equations for the reactions that took place at ;
i. Anode (½ mark)
ii. Cathode (½ mark)
b. State the observation made at each electrode;
i. Anode (½ mark)
ii. Cathode (½ mark)
c. State and explain the observations made on the electrolyte. (1mark)
3 marks
(i) A beekeeper used to apply little sodium hydrogen carbonate to relieve pain when stung by bees. Explain (2marks)
(ii) why would it not be advisable to use sodium hydroxide instead of sodium hydrogen carbonate.
(1mk)
3 marks
Study the diagram below which shows an energy level diagram.
Reaction path
i. Name enthalpy (1½ mark)
ΔH1
ΔH2
ΔH3
ii. Calculate the ΔH1 from the energy level diagram (1½ mark)
3 marks
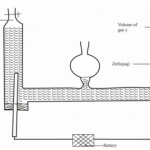
Gas X is highly soluble in water. Gas Y is completely insoluble in water. Describe how you would obtain asample of gas Y from a mixture of gases X,Y and water vapour.
3 marks
Study the standard electrode potentials in the table below and answer the questions that follow. The letters are not the actual symbols of the elements.
(i) Select from the table the strongest reducing agent. Give a reason for your answer. (1mark)
(ii) When Q rod is dipped into a solution of P ions, write the ionic equations of the reaction that occurs.
(1mark)
(iii) Calculate the E value for the above reaction (1mark)
3 marks
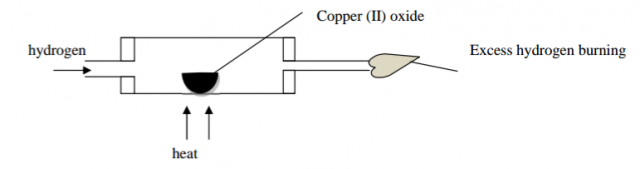
Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow;
(a) State and explain the observation made in the combustion tube. (1mk)
(b) write the equation for the reaction when hydrogen burns in air (1mk)
(c) After the experiment is over, the stream of hydrogen should be continued to be passed over heated oxide of copper until it cools explain. (1mk)
3 marks
Use the thermochemical equations below to answer the questions that follow.
Calculate the enthalpy of formation of ethane.
3 marks
A piece of burning magnesium ribbon was lowered in a gas jar full of chlorine;
(a) State and explain the observation made. (1mk)
(b) Magnesium ribbon is first polished before the reaction starts, give a reason (1mk)
(c) Give a reason why calcium does not readily react with chlorine gas when heated (1mk)
3 marks
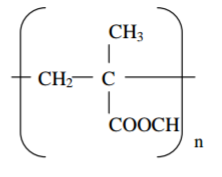
Perspex is a synthetic polymer of formula;
(a) Write the structural formula of the monomer of Perspex. (1 mark)
(b) State the type of polymerization involved in the formation of Perspex. (1 mark)
(c) Give one use of Perspex. (1 mark)
3 marks
Below is a structure of aluminium chloride dimer. Study it and answer the question that follow
Identify bond
X ……………………………………………………………….. (1mk)
Y ……………………………………………………………………… (1mk)
2 marks
The structures below represent two cleaning agents M and P.
Which cleaning agent would be most suitable for use with water containing calcium sulphate? Give a reason.
2 marks
Starting with copper powder describe how copper (II) carbonate can be prepared
3 marks
When potassium nitrate is heated, it produces potassium nitrite and gas C.
(a) Identify gas C. (1 mark)
(b) Name the type of reaction undergone by the potassium nitrate. (1 mark)
2 marks
Draw a well labeled diagram to show a set up that can be used to electroplate a copper ring with a silver coat.
3 marks
30cm3 of Hydrogen gas diffuse through a porous plug in 120 seconds. How long will 150 cm3 of hydrocarbon gas of molecular mass 72 take to diffuse through the same plug under same conditions? (H = 1, C = 12).
2 marks
(i) Define solubility. (1 mark)
(ii) Salt X has a solubility of 30g / 100g of water. 60g of salt X is stirred in 65g of a solution which contains 10g of salt, determine the amount of the salt that remained undissolved. (2marks)
3 marks
A compound X is made of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen whose percentage composition by mass are 62.1%, 10.3% and the rest oxygen respectively.
The relative molecular mass of X is 58 (H = 1, O = 16, C = 12) Determine the molecular formula of the compound.
3 marks
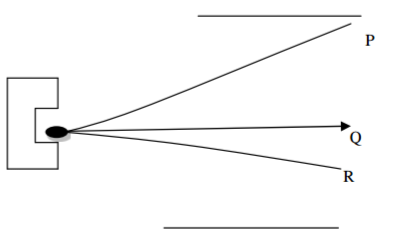
The diagram below shows three radiations from an element x subjected through an electric field
(a) Identify the radiations P, Q and R. (1½ marks)
ii. Why is Q not deflected along the electric field? (1mark)
(b) Give one use of Q (½ mark)
2 marks
Study and complete the table below;
| Alloy | Composition | Properties | Uses |
| Brass | ……………… Zinc |
harder than pure metal golden in colour |
………………. |
| Bronze | ………………..
Tin |
Harder than pure metal | …………………. |
| Stainless steel |
Iron
……………….. |
Tough, does not corrode | ………………… |
3 marks
Aqueous hydrogen chloride reacts with potassium manganate (VII) to produce chlorine gas, while a solution of hydrogen chloride in acetone (C3H6O) has no effect on potassium manganate (VII) solution. Explain this observation.
2 marks
The graph below is a plot of concentration against time for a given reaction.
(a) What is represented by curve A? Explain. (1mk)
(b) Explain why curve B drops fast initially. (1mk)
(c) What does point X represent on the graph? (1mk)
3 marks
The diagram below represents a cross section of concentric pipes used in the Frasch process to extract sulphur.
State what passes through pipes;
3 marks
(a) Define allotropy. (1mk)
(b) Explain why graphite conducts electricity while diamond does not. (2mks)
3 marks
A farmer has three plots each measuring 0.25 acre . He applied nitrogenous fertilizers as follows
- Plot A 250 kg of ammonium phosphate
- Plot B 250 kg of urea CO(NH2)2
- Plot C 250 kg of ammonium nitrate
Which plot received the highest nitrogen content? H=1, N= 14, O= 16, P= 31, C=12,
3 marks
(a) Draw the following organic compounds; (2mks)
(i) 2,2,3-trimethylpentane
(ii)2,3-dimethylbut-2-ene
(b) Draw and name the chain isomer of the compound in a)( ii) above. (1mk)
3 marks
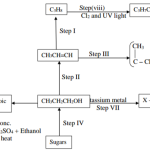
Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow
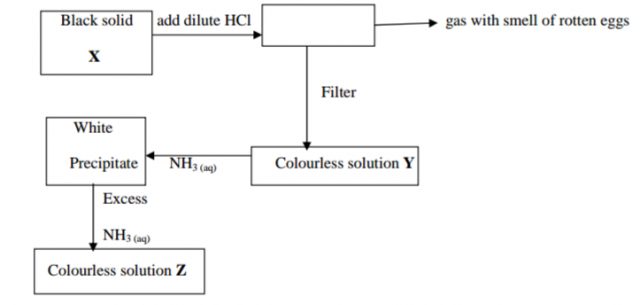
(i) Solid X (1mk)
(ii) The white precipitate (1mk)
(b) Write the formula for the complex ion in solution Z. (1mk)
3 marks
A burning wooden splint and a burning magnesium ribbon were lowered in gas jars full of carbon (IV) oxide separately as shown below;
State and explain the observations made in
(a) Set up (I)(1½mks)
(b) Set up (II) (1½mks)
3 marks