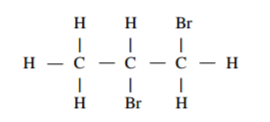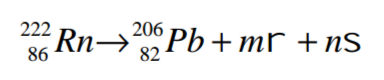KNEC KCSE Chemistry Paper 1 – 2014 KCSE COMA Joint Exam
2014 KCSE COMA Joint Exam
Chemistry Paper 1
Bromine reacted with compound Q to form a compound with structural formula.
(i) Write the structural formula of Q. (1 mark)
(ii) When Q is reacted with concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid compound P is formed which
further reacted with water to form K.
I Identify substance K. (1 mark)
II Write an equation to show how compound K reacts with sodium metal. (1 mark)
3 marks
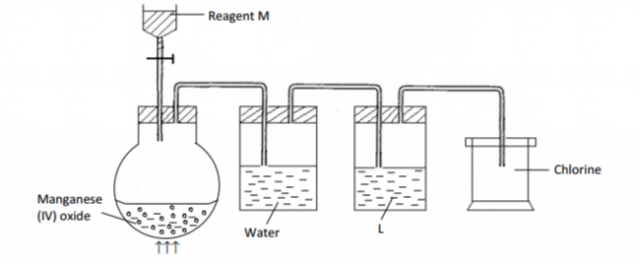
The set-up below was used to prepare dry chlorine gas. Study and answer the questions that follow.
(a) Name reagents M and substance L.
M (½ mark)
L (½ mark)
(b) A warm red phosphorus was lowered into the gas jar of chlorine using a deflagrating spoon:
(i) State any one observation made in this experiment. (½ mark)
(ii) Identify the substance formed in the above reaction. (½ mark)
(c) Both substances in (ii) above undergo hydrolysis when exposed to air. Write an equation to
show how anyone of them undergoes hydrolysis. (1 mark)
3 marks
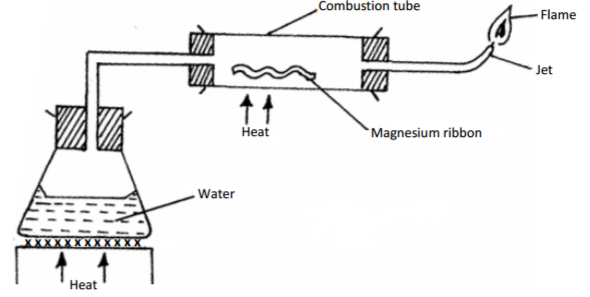
Steam was passed over magnesium ribbon as shown in the diagram below. Study it and answer the
questions that follow.
(a) State one precaution which should be taken before lighting the gas at the jet. (1 mark)
(b) Write a chemical equation for the reaction taking place in the tube.
(i) Combustion tube. (1 mark)
(ii) Jet (burning flame). (1 mark)
3 marks
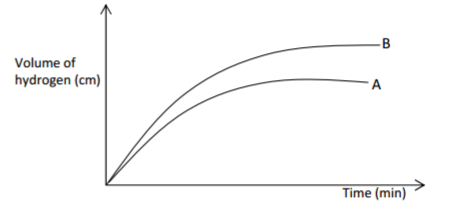
Two experiments were carried out as follows and the volume of hydrogen gas evolved measured at
intervals of 10 seconds for 100 seconds.
(i) 8cm of magnesium ribbon was added to 1M hydrochloric acid.
(ii) 8cm of magnesium ribbon was added to 0.5M hydrochloric acid.
Graphs of volume of hydrogen evolved against time were plotted thus:
(a) Which of the graphs was obtained for reaction (i) Explain? (2 marks)
(b) Explain the general shape of graphs. (1 mark)
3 marks
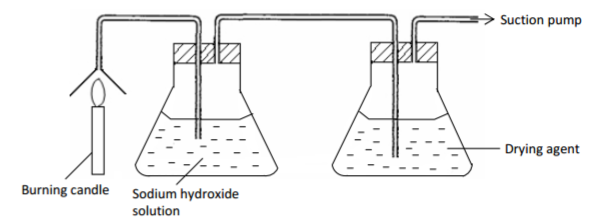
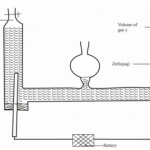
The set up of diagram shown below is used to prepare dry nitrogen gas from air. Study it and
answer the questions that follow.
(a) What is the purpose of using.
(i) A burning candle. (½ mark)
(ii) Sodium hydroxide solution. (½ mark)
(b) Name:
(i) One impurity present in nitrogen gas prepared. (½ mark)
(ii) A suitable drying agent used. (½ mark)
(c) Give two uses of nitrogen gas. (1 mark)
3 marks
(i) Using a dot (.) and cross (x) show how NH+4 ion is formed from NH3 molecule and H+ ion.(2 marks)
(ii) State the type of bond that exists between the NH3 and H+
ion. (½ mark)
(iii) Molecular substances have low melting points. Give one reason why they have low melting
points. (½ mark)
3 marks
Study the information in the table below and answer questions that follows:
| Ions | Electron arrangement | Ionic radius |
| Na+ | 2,8 | 0.95 |
| K2+ | 2,8,8 | 0.133 |
| Mg2+ | 2,8 | 0.065 |
Explain why the ionic radius of:
(a) K2+ is greater than that of Na+. (1 mark)
(b) Mg2+ is smaller than that of Na+. (2 marks)
3 marks
(a) Differentiate between exothermic and endothermic reaction. (1 mark)
(b) The table below gives bond energies of some covalent compound.
| Bond | Bond energy KJ mol-1 |
| C – H | 413 |
| O = O | 497 |
| C = O | 804 |
| H – O | 464 |
Calculate the enthalpy change for the combustion of methane in excess oxygen gas.(2 marks)
3 marks
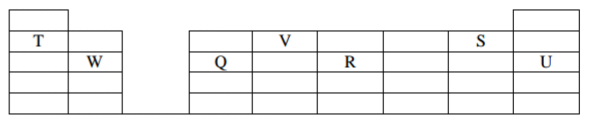
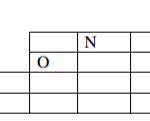
The grid below shows part of the periodic table. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
The letters do not represent the true symbols of the elements.
(a) Which element forms ion with the charge of -3. (½ mark)
(b) What is the nature of oxide formed by Q. (½ mark)
(c) Using crosses (X) and dots (.), show how the ion of S is formed. (1 mark)
2 marks
(a) Define Grahams law of diffusion. (1 mark)
(b) Given that the density of g X is 1.4290 10-3g/cm³ and the density of gas Y is 1.2506
10g/cm³. How many times will gas X diffuse faster than Y? (2 marks)
3 marks
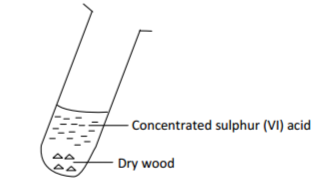
Excess concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid was mixed with pieces of dry wood as shown below.
(a) State the observation made. Explain. (1 mark)
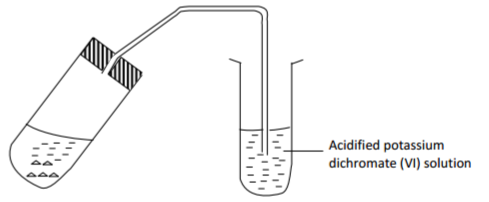
(b) When the reaction was complete, the mixture was heated gently, then strongly and set-up
adjusted as shown below.
Explain the observation made on acidified potassium dichromate (VI) solution. (2 marks)
2 marks
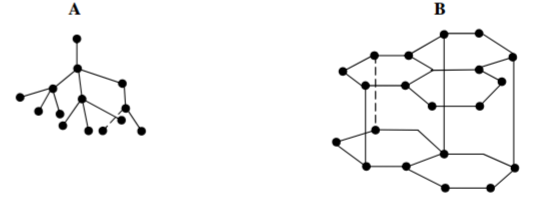
The following diagrams shows the structure of two allotropes of carbon. Study them and answer the
questions that follow.
(a) Name the allotropes. (1 mark)
A
B
(b) Give one use of A. (½ mark)
(c) Which allotrope conducts electricity? Explain. (1½ marks)
3 marks
Write half equations for the electrode reactions when molten sodium chloride is electrolysed using
graphite electrodes.
Anode. (1 mark)
Cathode . (1 mark)
2 marks
Give two reasons why helium is used in weather balloons.
2 marks
80g of a saturated calcium chloride was prepared at 25C. Calculate mass of calcium chloride and
mass of water used to prepare a saturated solution given that the solubility of calcium chloride at
25C is 72g/100g of water.
3 marks
Sulphur (IV) oxide and nitrogen (IV) oxide react as shown in the equation below.
(i) Using oxidation number of either sulphur or nitrogen show that this is a redox reaction.(2 marks)
(ii) Identify the reducing agent. (1 mark)
3 marks
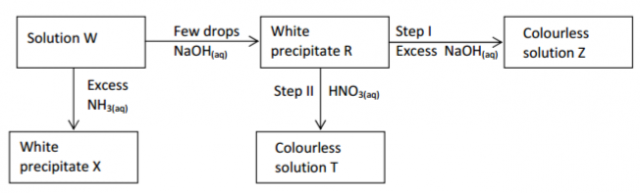
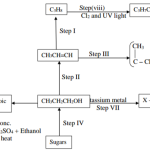
Study the reaction scheme below and answer the questions that follow.
(a) What property of the white precipitate R is demonstrated by steps I and II. (1 mark)
(b) If the metal ion in solution W is divalent suggest its identity. (1 mark)
(c) Write an ionic equation for the reaction taking place in step I. (1 mark)
3 marks
The PH – values of various solutions are given in the table below. Study it and answer the equations
that follow.
| Solution | PH – value |
| W | 14.0 |
| X | 6.0 |
| Y | 7.0 |
| Z | 2.0 |
(a) Select a pair of solutions that if reacted would have the highest heat change of the reaction
(DHR). Give a reason for your answer. (2 marks)
(b) Select the solutions in which a sample of aluminium oxide is likely to dissolve. (1 mark)
3 marks
Describe how a sample of lead (II) chloride can be prepared using the following reagents:
– Dilute nitric acid.
– Dilute hydrochloric acid and lead (II) carbonate.
3 marks
(a) Radioactive isotope decays as shown below.
Determine the values of m and n. (2 marks)
(b) Give one harmful effect of exposure to radioactive emission. (1 mark)
3 marks
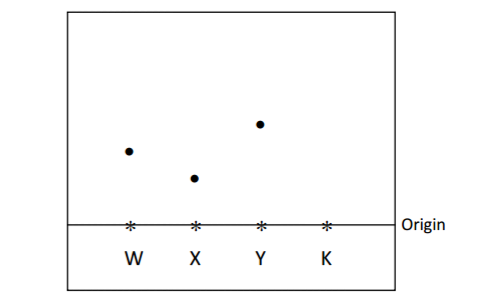
The diagram below represents a paper chromatogram of pure W, X and Y. A mixture K contains
W and Y only.
(i)Indicate on the diagram the chromatogram of K. (2 marks)
(ii) Show the solvent front. (1 mark)
3 marks
A compound has an empirical formula C3H6O and relative formula mass of 116.
(a) Determine its molecular formula. (H = 1, C = 12, O = 16). (2 marks)
(b) Calculate the percentage composition of carbon by mass in the compound. (1 mark)
3 marks
In the laboratory hydrogen sulphide gas is prepared by the action of dilute hydrochloric acid on
metal sylphides.
(a) Name the metal sulphide that can be used in preparing the gas. (1 mark)
(b) Write down the equation for the reaction in (a) above. (1 mark)
(c) Give one chemical test for hydrogen sulphide gas. (1 mark)
3 marks
The table below gives atomic numbers of elements represented by the letters A, B, C and D.
Use the information to answer the questions that follow.
| Elements | A | B | C | D |
| Atomic numbers | 15 | 16 | 17 | 20 |
(a) Name the type of bonding that exists in the compound formed when A and D react. (1 mark)
(b) Select the letters which represents the best oxidizing agent. Give a reason for your answer.
(2 marks)
3 marks
Element T is in period 2 of the periodic table and forms a stable ion, T2+.
(a) State the atomic number of element Q which is directly below T in the periodic table. (1 mark)
(b) Compare the reactivity of T and Q with chlorine. (2 marks)
3 marks
20.0cm³ of a solution containing 4.5gdmˉ³ of sodium hydroxide reacted exactly with 24.0cm³ of
dilute sulphuric acid solution, using methyl orange as indicator. Calculate the molarity of the
sulphuric acid.
3 marks
Ammonia is produced in large scale by Haber process.
(i) Write an equation for the formation of ammonia gas. (1 mark)
(ii) State two optimum condition for obtaining a high yield of ammonia in the process. (2 marks)
3 marks
The table below gives elements represented by letters which are not the actual symbols.
| Element | U | V | W | X | Y | Z |
| Atomic No. | 8 | 12 | 13 | 15 | 17 | 20 |
(i) Select an element that can form divalent anion. (1 mark)
(ii) What is the structure of the oxide of W? (1 mark)
(iii) Compare the atomic radius of W and X. (1 mark)
3 marks