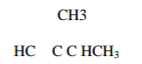KNEC KCSE Chemistry Paper 1 – 2014 Nakuru District Mock
2014 Nakuru District Mock
Chemistry Paper 1
Sodium hydrogen carbonate reacts with water according to the equation below.
NaHCO3 (s) + H20(l) → Na+(aq) + CO32-(aq)(aq) + H3O+(aq)
Identify the base in the reaction and explain your answer.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
2 marks
(a)Explain how you would show that graphite and diamond are both allotropes of carbon.(2marks)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(b) Why is graphite used as a lubricant while diamond is used as an abrasive (2 marks)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
4 marks
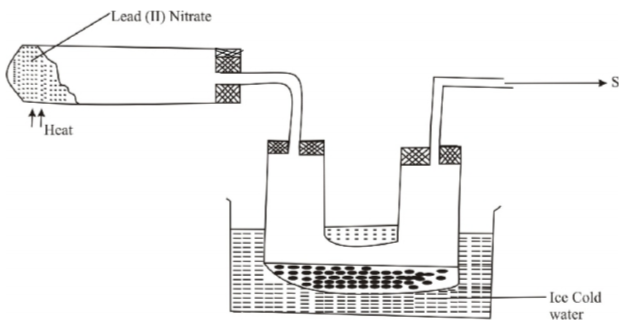
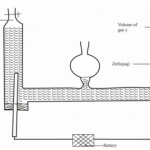
The set up below was used to prepare Nitrogen (IV) Oxide.
(a)(i) Why is nitrogen (IV) oxide collected by this method shown (1 mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(ii)What is the major constituent of the gas escaping at S (1 mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(b) What is observed when burning magnesium is lowered in a gas jar full of nitrogen (IV) oxide
(1 mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
3 marks
soap is added to hard water, lather does not form immediately, but lather eventually
forms on addition of more soap. Explain
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
2 marks
Chlorine gas can be prepared by using the following reagents: Sodium chloride, concentrated
sulphuric (VI) acid and potassium manganate (VII)
(a) What is the role of the following reagents in the reaction?
(i) Concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid (1 mark)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(ii) Potassium manganate (VII) (1 mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(b) Name the bleaching agent formed when chlorine gas is passed through cold and dilute
sodium hydroxide solution? State one other use of the compound named. (2 marks)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
4 marks
Determine the volume of hydrogen gas formed when excess zinc metal is added to 100cm3 of
one molar hydrochloric acid (1 mole of gas occupies 24.0 litres at room temperature and
pressure.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
2 marks
An equilibrium exists between the reaction of chromate ions (CrO42-(aq)) and dichromate ions
(Cr2O72-(aq) as represented by the equation
2CrO42-(aq) + 2 H+(aq) Cr2O72-(aq) + H2O(l)
What would be the effect of adding aqueous sodium hydroxide solution have on the above on
the equilibrium? Explain your answer.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
2 marks
A piece of phosphorus was burnt in excess air. The product obtained was shaken with a
small amount of hot water to make a solution.
(i) Write an equation for the burning of phosphorus in excess air. (1 mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(ii) The solution obtained in (i) above was found to a have a pH of 2.0. Give reasons for this
observation (2 marks)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
3 marks
Copper can be extracted from an ore called Malachite (CuCO3.Cu (OH) 2). Explain how
copper may be extracted from crushed ore.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
2 marks
Give two reasons why helium is used in weather balloons.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
2 marks
(a) Radioactive radon isotope decays as shown below.
Determine the value of m and n (2 marks)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………..
. (b) Give one harmful effect of exposure to radioactive emission (1 mark)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
3 marks
The lattice energy for sodium chloride is +776Kj mol-1 when sodium chloride is attracted to
polar water molecules the energy released is 771 Kj mol-1
(a) Draw an energy cycle diagram to illustrate energy changes when sodium chloride is
dissolved in water.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(b) Use the energy cycle diagram above to calculate the molar enthalpy of solution for sodium
chloride (2 marks)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
4 marks
A student set –up the following apparatus to investigate some properties of the chlorides of
period 3 elements.
(a) State the observation made in set-up 1 and 2 (2 marks)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(b) What name is given to the chemical process taking place in set-up 1? (1 mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
3 marks
Calculate the volume of the gaseous product formed when 75cm3 of oxygen gas was exploded in 75cm3 of carbon(II) oxide gas. All volumes are measured at constant temperatures and pressure.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
2 marks
The table below shows some tests carried out on a sample of water in a school pond and
results obtained recorded.
| Test | observation |
| I Addition of sodium hydroxide solution drop wise until excess |
White precipitate which dissolves in excess |
| II Addition of excess aqueous ammonia | Colourless solution obtained |
| III Addition of dilute hydrochloric acid followed by barium chloride |
White precipitate |
(a) Identify the anion present in the water (1 mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(b)Write the ionic equation for the reaction in test III above (1 mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(c) Write the formula of the complex ion formed in the test (II) above (1 mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
3 marks
Ethanedioic acid (COOH)2 is used instead of methanoic acid (HCOOH) to prepare carbon(II)
oxide and carbon (IV) oxide in the laboratory as it is easily dehydrated by sulphuric (VI) acid
to give equal volumes of the two gases.
(a) Write an equation for the dehydration of ethenedioic acid. (1 mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(b) Explain how dry carbon(II) oxide can be gotten from the mixture of the two gases.(2 marks)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
3 marks
Below is a list of potential differences obtained when metals R, S, T, U and V are used
in the following electrochemical cell.
Metal(s) /metal ions(aq)// Zn2+(aq) /Zn(s)
| Metal | E(volts) |
| R | -1.10 |
| S | -0.46 |
| T | 0.00 |
| U | +0.45 |
| V | +1.16 |
(i) Identify the role of metal T. Explain (1 mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(ii) Which two of the above metals in the electrochemical cell would produce the largest
potential difference ( 1mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(iii) Which one of the metal above cannot be displaced by any of the other metals in the list?
Explain. (1 mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
3 marks
(a) Write a chemical equation to show what happens when excess carbon (IV) oxide gas is
bubbled through lime water. (1 mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(b) State two properties that makes carbon(IV) oxide gas suitable for use in a fire extinguisher.
(2 marks)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
3 marks
Give the IUPAC name of the following organic compounds.
i.
ii.
2 marks
Explain in terms of structure and bonding why silicon (IV) oxide exists as a solid of high
melting point while sulphur(IV) oxide exist as a gas.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………
2 marks
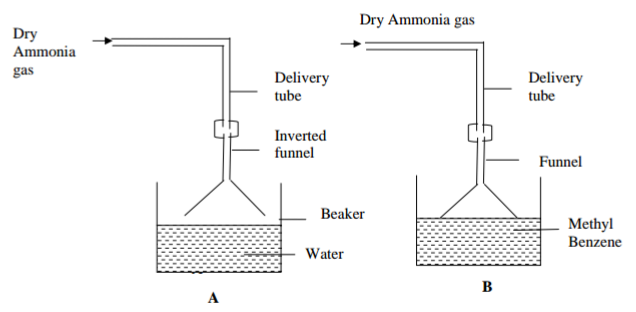
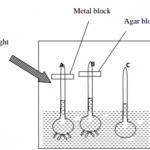
A form (IV) student set up the apparatus below in an experiment and recorded the observations
(i) State the observation made when both blue and red litmus papers were dipped in the resulting
solution of experiment A and B. ( 1 mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(ii) Explain your observations in (i) above (2 marks)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
3 marks
(a) State two uses of solubility curves. (1 mark)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(b) The solubility of salt A at different temperatures is as shown below.
| Temperature (oc) | 60 | 100 |
| Solubility g/100g of water | 40 | 48 |
(i) What mass of salt would saturate 150 g of water at 60oC (1 mark)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(ii) Calculate the mass of salt A that crystallizes out when 150 g of water is saturated with salt A
and cooled from 100oc to 60oc (2 marks)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
3 marks
Five solutions A, B, C and D were tested to find their pH values. The results obtained were
recorded as below.
| Solution | pH value |
| A | 10 |
| B | 1 |
| C | 14 |
| D | 5 |
(a) Name the reagent used to measure the pH and describe how it is carried out (2 marks)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(b) Identify the solution which when warmed with ammonium chloride produces ammonia gas.
( ½ mark)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
2.5 marks
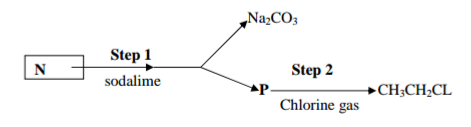
Study the reaction scheme below and answer the questions that follow.
(a) Name substance N and P
N………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… P………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. (1 mark)
(b) Give the reaction conditions in step I and II (2 marks)
I………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
II ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(c) Write an equation for the reaction that took place in step I (1 mark)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
4 marks
An element Q has the electronic arrangement 2.8.6 and a mass number of 32.
(i) How many protons does element Q have (½ mark)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(ii) What is the number of neutrons in the nucleus of Q? (½ mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(iii) What type of bond would be formed between Q and oxygen (½ mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
1 marks
The table below gives three experiments on the reactions of excess sulphuric (VI) acid and
0.5 g of zinc done under different conditions. In each case the volume of gas was recorded
at different time intervals
| Experiment | Form of Zinc | Sulphuric (VI) acid solution |
| I | Powder | 0.8 |
| Ii | Powder | 1.0 |
| Ii | Granules | 0.8 |
On the same axis below sketch and label the three curves (I, II, III) that could be obtained
from each results.
3 marks
The standard reduction potential of two half-cells are
Cu2+(aq) + 2e– Cu(s) E = + 0.34 V
2H20(l) + 2e– H2(g) + 2OH– (aq) E = – 0.83 V
Draw a labelled diagram of an electrochemical cell that can be constructed using the two half –cells.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
3 marks
When pure water is heated at 1 atmospheric pressure at sea level, the temperature of the water
does not rise beyond 100oC even with continued heating. Explain this observation.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
2 marks
What is the name given to each of the following?
(a) Ability of aluminium metal to be drawn into a sheet
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………( 1 mark)
(b) Minimum energy required for a reaction to start
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… (1 mark)
2 marks