KNEC KCSE Chemistry Paper 1 Question Paper / 2015 KCSE Kirinyaga West
2015 KCSE Kirinyaga West
Chemistry Paper 1
Study the table below and answer the questions that follow.
Metal Atomic radius (nm)
I 0.133
II 0.090
III 0.157
a) Arrange the metals above in order of reactivity starting with the most reactive. (1mk)
b) Identify the strongest reducing agent of the three. Explain. (2mks)
3 marks
When a few drops of aqueous ammonia were added to copper (II) chloride solution, a pale blue precipitate was formed. On addition of excess aqueous ammonia, a deep blue solution was formed. Identify the substance responsible for the
(a) Pale blue precipitate (1mk)
(b) Deep blue precipitate (1mk)
2 marks
Acompound whose general formula is Z(OH)2 reacts as shown by the equation below.
(a) Name the property exhibited by the compound in the reactions. (1mk)
(b) Name two elements whose hydroxides behave like that of Z. (1mk)
2 marks
A pH of a sample of soil was found to be 5.5. An extension officer advised the farmer to add calcium oxide. State two functions of calcium oxide in the soil.
2 marks
The paper chromatogram below shows the identity of the unknown cations in a mixture R. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
Key
J – Vanadium (V4+)ions
K – Chromium (Cr3+) ions
O – Copper (II) (Cu2+) ions
a) Name the ions present in the mixture of N. (1mk)
b) Mixture M contains all the three ions. On the diagram show the chromatograph of M, (2mks)
3 marks
i) State the role of the following substances during the preparation of nitrogen gas from air.,
I Concentrated sodium hydroxide . (1mk)
II Copper turnings (1mk)
(ii) Nitrogen obtained by air is denser than air obtained from chemicals. Explain. (1mk)
3 marks
(i) State two differences between non-luminous and luminous flames. (2mks)
(ii) Give two reasons why non luminous flame is more preferred for heating that luminous flame. (1mk)
3 marks
The set up below is used to demonstrate the effect of heat on hard water.
(i) Name gas D. (1mk)
(ii) Name the type of hardness present in the hard water. (1mk)
(iii) Write an equation for the reaction that produced gas D. (1mk)
3 marks
The table below shows the test carried out on a sample of water and the results obtained.
Tests Results
1 Addition of sodium hydroxide White precipitate dissolves
2 Addition of ammonia dropwise till in excess White precipitate dissolves
3 Addition of acidified barium nitrate solution White precipitate
a) Write the name of the anion present in water. (1mk)
b) Write an ionic equation for the reaction in test (3) above. (1mk)
c) Write formula of the complex ion formed in test (1) above. (1mk)
3 marks
30cm3 of carbon (II) oxide diffuses in 30 seconds. How long will 60cm3 of nitrogen gas take to diffuse under the same conditions.
( C = 12, O = 16, N = 14)
3 marks
Name the process that takes when
a) Crystals of zinc chloride change into solution when exposed to the air. (1mk)
b) Crystals of magnesium chloride become damp when exposed to the air (1mk)
c) Crystals of sodium carbonate dehydrate. Change to sodium carbonate monohydrate when exposed to the atmosphere. (1mk)
3 marks
i) Complete the table below.
(11/2mk)
ii) The electron configuration of ions x2+ and Y3- are 2, 8 and 2,8,8 respectively.
a) Write the atomic number of elements X and Y. (1 mark)
b) Name the type of bond formed between X and Y. (1/2mk)
3 marks
During an experiment on solubility the information below was obtained.
Use it to answer the questions that follow:-
Temperature of solution = 20oC
Mass of empty dish + watch glass = 50g
Mass of dish + watch glass + saturated solution = 80g
Mass of dish + watch glass + solid salt = 60g
i) Determine the mass of solute and solvent. (1mk)
ii) Determine the mass of solute that dissolves in 100cm3 of water at the temperature. (2mks)
3 marks
Carbon exists in different crystalline forms. Some of these forms are recently discovered in soot and are called fullerenes.
i) Name two other crystalline forms of carbon. (1 Mark)
ii) An organic compound contains by mass 13.5% hydrogen, 21.6% oxygen and the rest carbon.
Calculate the empirical formula of the organic compound. (2mks)
(H = 1, C = 12, O = 16)
3 marks
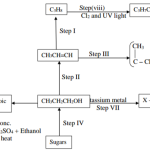
The flow chart below shows a series of reactions starting with propan-1-ol.
Study it and answer the questions that follows.
i) Give the names of substances labelled F, G and H. (3 Marks)
ii) Name the process labelled L. (1/2mk)
iv) Name one reagent required for process to take place. (1mk)
1.5 marks
During the preparation of oxygen, hydrogen peroxide was decomposed in the presence of Manganese (IV) oxide as shown below.
2H2O2(aq) 2H2O(l) + O2(g)
i) State the role played by Manganese (IV) oxide in the reaction. (1mk)
ii) Calculate the volume of oxygen gas produced at r.t.p if 25cm3 of 2M solution of hydrogen peroxide was used.
(Molar gas volume = 24dm3). (2mks)
3 marks
Dry ammonia gas was passed over hot zinc oxide as shown in the diagram below
a) Identify gas N.
b) State observation made in the combustion tube.
c) Name the reagents required to produce ammonia gas. (1mk)
3 marks
State and explain the observation that would be made when hydrogen chloride as is bubbled through a solution of silver nitrate solutions.
3 marks
200cm3 of 1M sulphuric acid was electrolysed using the set up represented by the diagram below.
i) Name the gas labelled Q and P. (1 Mark)
ii) Explain the difference in brightness if 200cm3 of 1M ethanoic acid was used instead of sulphuric (IV) acid.(2mks)
3 marks
Dry carbon (II) oxide gas react with heated copper (II) oxide as shown in the equation below.
CuO(s) + CO(g)
a) (i) Name the process undergone by Carbon (II) oxide. (1mk)
(ii) Give a reason for your answer a(i) above. (1mk)
b) Name another gas that can be used to perform the same function as carbon (II) oxide gas in the above reaction.
(1mk)
3 marks
During the extraction of aluminium from its ore, the ore is first purified to obtain molten aluminium
oxide (Alumina). The flow chart below shows the stages in the extraction of alumium form aluminium
oxide.
a) Name
i) Chief ore of aluminum (1mk)
ii) Process D1 and Reagent E1 (1mk)
iii) Give two reasons why aluminium is used extensively in making of overhead electrical cables. (1mk)
3 marks
The rate of decay for radioactive element X is as shown in the table below.
Number of days Mass
0 768
1080 96
a) Calculate the half life of element X. (2mks)
b) Give one industrial use of radioactivity. (1mk)
3 marks
A current of 2.0A was passed through dilute sodium chloride for 30 minutes. Calculate the volume of oxygen gas produced at anode during electrolysis.
(1 mole of gas occupies 24 litres, 1F = 96500 C)
Cu(s) + CO2(g)
3 marks
A certain mass of a metal was reacted with excess dilute sulphuric (VI) acid at 250
C. The volume of hydrogen gas
released was measured after every 20 minutesseconds.The results were presented asshown in the graph below.
30
25
20
15
10
5
0 20 40 60 80 100 120
Time (s)
a) Name one piece of apparatus that may be used to measure the volume of hydrogen gas released. (1mk)
b) i) On the same diagram sketch the curve that would be obtained if the experiment wasrepeated at 400
C. (1mk)
ii) Explain the shape of your curve in (b) (i) above. (1mk)
3 marks
An equilibrium exists between reactants and products as shown in the equation below.
State and explain the observation made if a few drops of conc. Sulphuric (VI) acid is added to the mixture.
3 marks
When hydrogen sulphide gas is passed through a solution of iron (III) chloride, the colour changes from brown to green and a yellow precipitate is formed. Explain these observations.
3 marks
2.12g of sodium carbonate were dissolved in 100cm3 of water. Calculate the molar concentration of carbonate ions in the solution. (Na = 23, C = 12, O = 16)
3 marks
i) Group 8 elements are called. (1mk)
ii) State one use of group 8 elements. (1mk)
2 marks