KNEC KCSE Chemistry Paper 2 – 2014 Nakuru District Mock
2014 Nakuru District Mock
Chemistry Paper 2
The table below shows elements, atomic numbers and their melting points. The letters do not
represent actual symbols of the elements. Study it and answer the questions.
| Elements | Atomic numbers | Melting point |
| J | 11 | 98 oc |
| K | 16 | 115 oc (119 oc) |
| L | 15 | 44 oc |
| M | 14 | 1410 oc |
| N | 12 | 650 oc |
(a) Write the formula of the oxide of M (1 mark)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(b) Choose an element that would give a basic oxide when burned in air. Give a reason. (2 marks)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(c) Element K has two melting points. Explain why? (2 marks)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(d) The melting point of element M is 1410 oc. What is the possible structure of element M. (1 mark)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(e) Compare the reactions of J and water to that of N and water (2 marks)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(f) Choose an element that would form only covalent compounds. Explain (2 marks)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(g) Write an equation for reaction of L and oxygen (1 mark)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
11 marks
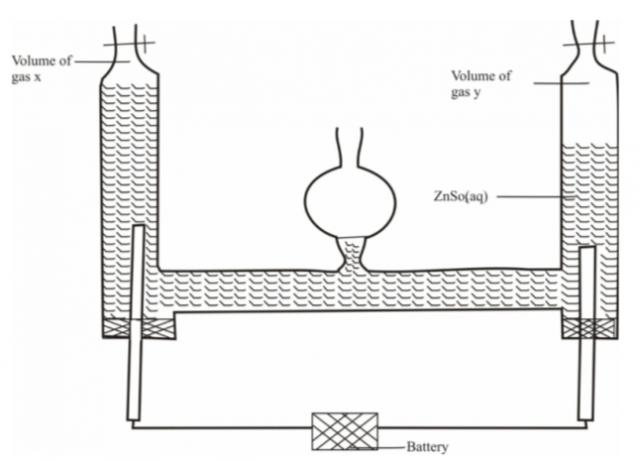
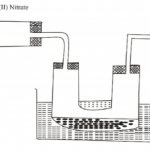
An aqueous solution of zinc sulphate is electrolysed using platinum electrodes as shown below in the
set up.
a)(i) Write down the ionic equation for the reaction taking place at electrode producing gas X (1 mark)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(ii) Identify the gas produced at Y; give a reason …………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………. (2 marks)
(b) 0.22 g of metal g is deposited by electrolysis when a current of 0.06 amperes flows for
99 minutes. (G=184, IF = 96500C)
(i) Find the number of moles of metal deposited (1mark)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(ii) Find the number of moles of electrons passed (3 marks)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(iii) Determine the value of n in the metallic ion Gn+ (2 marks)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
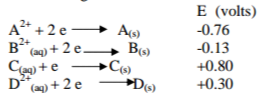
(c) The following are half-cell reactions and their reduction potentials
(i) Write the cell representation for the electrochemical cell that would give the highest E value. (2 marks)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(ii) Give one industrial use of electrolysis (1 mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
12 marks
(a) State Hess’s law (1 mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(b) Using the following thermochemical equations draw an energy cycle diagram.(3 marks)
A. 2C(s) + H2 (g) C2H2(g) ∆H = + 227 Kj/mol
B. C(s) + 02 (g) CO2(g) ∆H = -394 Kj/mol
C H2(g) + ½ O2(g) H20(g) ∆H = -286 Kj/mol
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. …………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(c) Name the heat of change represented by thermochemical equation A (2 marks)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(d) Using thermochemical equations A, B, C. Calculate the molar heat of combustion of ethyne
(3 marks)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(e) Give 3 factors considered for choosing a good fuel (3 marks)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
12 marks
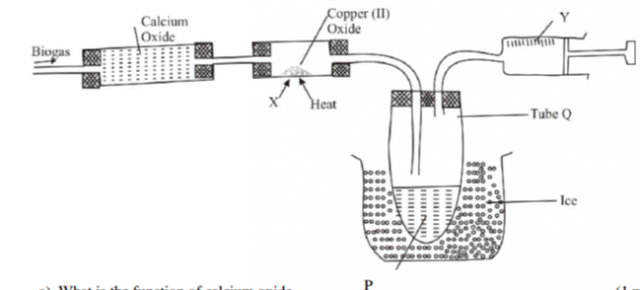
Biogas is made from natural organic waste. A from four student set –up the apparatus below to
investigate the composition of the gas. He passed it over heated copper (II) oxide. After that he
obtained two products. One was cooled in a boiling tube while the other was collected using a
syringe.
a) What is the function of calcium oxide (1 mark)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(b) Name products
i) P………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
ii) Y…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. (2marks)
(c) Give the two observations made in tube X (2 marks)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(d) (i) Name the type of reaction taking place in tube X (1 mark)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
ii) Write the equation for the reaction above in (d)(i) (1 mark)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(e) What elements are present in biogas (2 marks)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(f) Explain why one tube in boiling tube Q is longer than the other (2 marks)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
11 marks
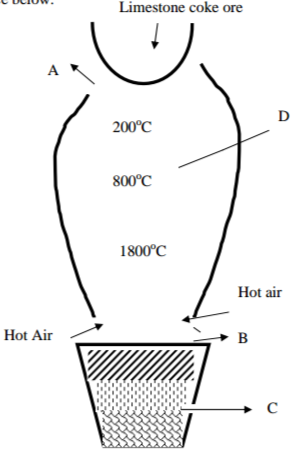
Iron is obtained using the blast furnace below.
(a) Name one ore of iron………………………………………………………. (1 mark)
(b) Name what comes out through points
A……………………………………………………………
B……………………………………………………….
C…………………………………………………………. (3 marks)
(c) Limestone is one of the raw materials in extraction of iron. State its two functions.
(2 marks)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(d) Write an equation for the reaction taking place at point D (1 mark)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(d) Iron reacts with chlorine gas to form iron (III) chloride as shown in the equation.
2Fe(s) + 3Cl2 (g) → 2FeCl3 (s)
Given that total mass of product is 0.5 g. Calculate the volume chlorine gas that reacted with
iron. (Fe = 56, Cl = 35.5, Molar gas volume is 24000 cm3) (3 marks)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(f) Give one industrial use of iron (1 mark)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
9 marks
(a) Production of Nitrogen(II) oxide follows the equation below represented by the equation
N2 (g) + O2 (g)⇌ 2NO(g) ∆H= +180 kJ /mol.
(h) What is meant by the word equilibrium
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(b) With reasons explain what would happen when
(i) Pressure is increased in the system in (a) above (2 marks)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(ii) Temperature is increased (2 marks)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(iii) Nitrogen (II) Oxide is removed (2 marks)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(c) An equilibrium exists between
2NO2 (g) ⇌ N2O4 (g)
On the grid below sketch how the concentration of NO2 varies with the reaction path (3 marks)
9 marks
An organic compound was subjected to combustion. 1.0 g of it formed 1.37 g of carbon (IV) oxide,
1.12 g of water as the only products. (C = 12, H = 1 , 0 = 16)
(a) Calculate the mass of carbon and hydrogen in the compound (3 marks)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(b) What other element must be present ………………………………………………………………………..(1 mark)
(c) Calculate the empirical formula of the compound (2 marks)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(d) What is meant by the term positional isomerism, give an example (2 marks)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(e) Draw the structural formulae of the following
(i) ethanoic acid 1 mark)
(ii) butane (1 mark)
(f) I Ethene can be converted to ethane industrially. Name the reagent and conditions
necessary for this reaction to occur.
(i) Reagent……………………………………………………………………………….. (1mark)
(ii) conditions…………………………………………………………………………. (1 mark)
II What is the importance of the reaction above in I (1 mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. ……
13 marks