KNEC KCSE Geography Paper 1 Question Paper / 2014 Kakamega County Mock
2014 Kakamega County Mock
Geography Paper 1
(a) What is an isobar? (1 mark)
(b) (i) Name one method used for measuring cloud cover. (1 mark)
(ii) State two characteristics of cumulonimbus clouds. (2 marks)
4 marks
(a) State the period within which each of the following planets complete a revolution around the sun.
(i) Mercury. (1 mark)
(ii) Earth. (1 mark)
(b) Give two reasons why the earth is flattened at the poles and bulged at the equator. (2 marks)
4 marks
(a) State three causes of earthquakes. (3 marks)
(b) Name two major earthquake zones of the world. (2 marks)
5 marks
The tables below represent temperature and rainfall for two stations X and Y. Study them and answer
the questions that follow.
(a) (i) Calculate the annual range of temperature for the stations X and Y. (2 marks)
(ii) Calculate the annual rainfall for station Y. (1 mark)
(b) Describe the characteristics of rainfall for station X. (3 marks)
6 marks
(a) Name two types of boundaries associated with plate tectonics theory. (2 marks)
(b) State four evidences that support the continental drift theory. (4 marks)
6 marks
SECTION B (75 Marks)
Answer question 6 and any other two questions from this section.
Study the map of KITALE (Sheet 75/3, Scale 1:50 000) provided and answer the questions that follow
(a) (i) Give the six figure grid reference for the Air Photo Principle point marked 95 found in the
north – western part of the area covered by the map. (2 marks)
(ii) Name two human made features found at grid square 4514. (2 marks)
(b) (i) Name two other districts covered by the map apart from Trans Nzoia District. (2 marks)
(ii) What was the magnetic declination at the time when the map was drawn? (2 marks)
(c) (i) Calculate the area covered by Kapolet Forest reserve. Give your answer in square
kilometres. (2 marks)
(ii) Measure the distance of the all-weather road loose surface C 641 from the junction at grid
square 2413 up to the junction at grid square 3121. Give your answer in kilometres. (2 marks)
(iii) Calculate the gradient of the same road in (c) (ii) above (2 marks)
(d) (i) Using a vertical scale of 1cm to represent 50 metres, draw a cross-section from grid reference
290140 to 355180. (4 marks)
(ii) On the cross-section, mark and name: Dry Weather Road C 637 (1 mark) Wattle Plantation (1 mark) River Koitobos (1 mark)
(e) Describe the drainage of the area covered by the map. (4 marks)
25 marks
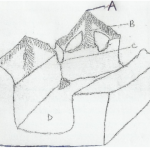
(a) The diagram below shows a glaciated upland area. Study it and answer the questions.
(i) Name the features marked R, S and T (3 marks)
(ii) Describe two distinctive characteristics of a fiord. (2 marks)
(b) With the aid of a well labeled diagram, describe how the following features are formed
(i) Cirque (6 marks)
(ii) Hanging Valley (4 marks)
(c) Explain two factors that may influence glacial erosion in uplands. (4 marks)
(d) Your class intends to carry out a field study on glaciated lowland. (i) Name one type of moraine you are likely to identify during the study. (1 mark)
(ii) Give two reasons why you would need the map of the area. (2 marks)
(iii) State three importance of glacial features you are likely to identify. (3 marks)
25 marks
The figure below shows the distribution of hot deserts in the world. Use it to answer question (a) (i).
(a) (i) Identify the hot deserts marked A, B and D. (3 marks)
(ii) Explain two reasons why most hot deserts are found on the western margins of continents. (4 marks)
(b) With the aid of well labeled diagram; explain how the following features are formed.
(i) Deflation hollows. (4 marks)
(ii) Barchans. (6 marks)
(c) State four ways in which arid regions can be used to benefit human. (4 marks)
(d) You are required to carry out a field study on water erosional features in arid areas.
(i) State three items you may be required to carry for the field study. (3 marks)
(ii) Why would a working schedule be important in the field study? (2 marks)
25 marks
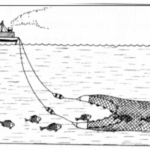
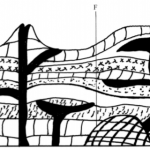
The diagram below shows features resulting from underground water. Use it to answer the (a).
(a) (i) Name the features labeled P, Q and R. (3 marks)
(ii) State three ideal conditions for the formation of the feature labeled Q (3 marks)
(b) Explain three factors that influence the existence of underground water. (6 marks)
(c) (i) What is “karst landscape?” (1 mark)
(ii) Describe three characteristics of karst landscape. (3 marks)
(d) Explain two ways in which a spring may be formed. (4 marks)
(e) (i) Name three surface features found in limestone areas. (3 marks)
(ii) State two problems that are likely to be experienced by the people living in areas with karst
landscapes. (2marks)
25 marks
(a) (i) Differentiate between volcanicity and vulcanicity. (2 marks)
(ii) Name two types of volcanic eruptions. (2 marks)
(b) The diagram below represents features of vulcanicity. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
(i) Name the features labeled K, L and M. (3 marks)
(ii) Give two examples of the feature labeled N in East Africa (2 marks)
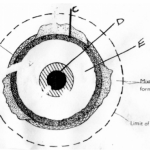
(c) The diagrams below shows formation of a caldera through volcanic explosion. Study it and answer
the questions that follow.
Describe the processes shown by the diagrams E, F and G (6 marks)
(d) Explain two ways in which the geysers and hot springs at Ol Karia are of significance to the
economy of Kenya. (4 marks)
(e) Students from Maranda School intend to conduct a field study on volcanic features in the Rift
Valley of Kenya.
(i) Other than Ol Karia, name two other places they are likely to visit for the study. (2 marks)
(ii) State two methods of data recording they are likely to use during the study. (2 marks)
(iii) What problems are they likely to encounter during the study? (2 marks)
25 marks