KNEC KCSE Geography Paper 1 Question Paper / 2015 KCSE Gem Sub-County Joint Evaluation
GEOGRAPHY PAPER 1 QUESTION PAPER
2015 KCSE Gem Sub-County Joint Evaluation
Geography Paper 1
SECTION 1 (25 Marks)
Answer all questions in this ssection
a) Name two isothermal layers of the atmosphere. (2marks)
b) State three ways in which the atmosphere is heated. (3marks)
5 marks
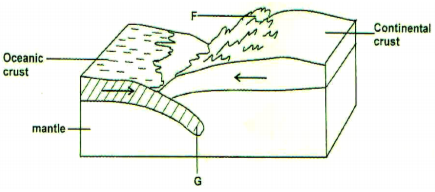
a) The diagram below shows a compressional plate boundary .
Name
i) The feature marked F. (1mk)
ii) The ozone marked G. (1mk)
b) State three effects of plate collision on compressional plate boundaries. (3mks)
5 marks
a) Differentiate between weathering and mass wasting. (2mks)
b) Give three ways in which plants cause weathering in rocks. (3mks)
5 marks
a) Give three conditions necessary for formation of artesian wells. (3mks)
b) State two significance of ground water. (2mks)
5 marks
a) List TWO significance of ground water. (2mks)
b) State three ways in which a gorge is formed. (3mks)
5 marks
SECTION 2 (75 Marks)
Answer question SIX and any other Two question in this section.
Study the map of Migwani (sheet 151/1) provided and answer the following question.
a) i) Convert the scale of the map into statement scale. (2mks)
ii) Identify Two physical features found in Grid Square 1277 to the east the area covered by the map. (2mks)
iii) Which map sheet adjoin Migwani 151/1 to the east? (1mk)
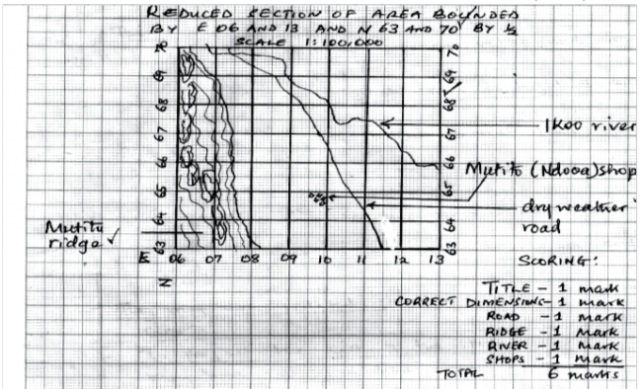
b) i) Reduce the area bounded by Eastings 06 and 13 and Northing 63 and 70 by half. (2mks)
ii) In the reduced area, mark anad name the following features.
-Zombe and Kitui – Yoonge dry –weather road D509.
-Mutito forest ridge.
-Ikoo river
-Mutito (Ndooa) shops. (4mks)
iii) Calculate the new scale of the reduced area. (2mks)
c) Describe the drainage of the area covered by the map. (5mks)
d) Citing evidence from the map, explain TWO conditions that favour cattle rearing in the area covered by the map.
(4mks)
e) Students in your school studied the influence of relief on drainage of the area covered by the map.
i) Formulate a null hypothesis they may have used in their study. (1mk)
ii) State two reasons why they conducted a pre-visit. (2mks)
5 marks
a) i) Differentiate between folding and faulting. (2mks)
ii) List three types of faults. (3mks)
b) State three ways in which faulting can influence drainage system. (3mks)
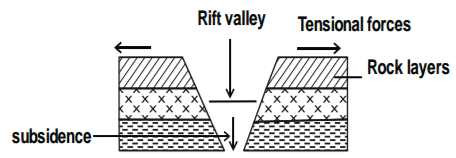
c) Using a well- labeled diagram, describe the formation of rift valley by tensional forces. (7mks)
d) Explain three effects of faulting on human activities. (6mks)
e) Students in your class conducted a field study on a faulted landscape in the Rift Valley of Kenya.
i) State two objectives that would guide their study. (2mks)
ii) State two reasons why you would need a route map. (2mks)
5 marks
a) List two external land forming processes that may lead to the formation of lakes. (2mks)
b) Identify Three sources of water found in a lake. (3mks)
c) Give three ways in which lakes may influence the natural environment in which they are found. (6mks)
d) i) State three characteristics of lakes formed due to faulting. (3mks)
ii)Explain three reasons why some rift valley lakes are drying up. (6mks)
e) You intend to carry out a field study of lake Kanyaboli in Siaya county.
i) Design a working schedule you will use for your study. (3mks)
ii) Why would it be important to hold group discussion during breaks in the process of data collection. (2mks)
5 marks
a) i) Define the term karst scenery. (2mks)
ii) Outline three conditions necessary for the formation of karst scenery. (6mks)
b) Using a well- labeled diagram, describe how the following features of limestone areas are formed.
i) Stalactite (5mks)
ii) Dolines (5mks)
c) Explain three ways in which limestone landscape influence human activities. (3mks)
d) Form four students of your school undertook a field study on a karst landscape.
i) State two objectives of their study. (2mks)
ii) Give two reasons why they concluded that some areas of karst landscape were unsuitable for settlement. (2mks)
5 marks
a) Name two earthquake zones of the world. (2mks)
b) Apart from vulcanicity, give three causes of earthquakes. (3mks)
c) Using a well labeled diagram, describe how a composite cone is formed. (7mks)
d) Explain four negative effects of vulcanicity on the physical and human environment. (8mks)
e) You intend to carry out a field study on resultant of vulcanicity in the Rift Valley.
i) List three features you would study. (3mks)
ii) Give two methods you would use to record your data. (2mks)
5 marks
GEOGRAPHY PAPER 1 MARKING SCHEME
2015 KCSE Gem Sub-County Joint Evaluation
Geography Paper 1
SECTION 1 (25 Marks)
Answer all questions in this ssection
a) Isothermal layer
− Tropopause
− Stratopause
− Mesopause (2 x 1 = 2mks)
b) State 3 ways in which the atmosphere is heated.
− Sun’s heat in transmitted outwards equally in all directions in waves through radiation.
− Heat is transferred through matter without moving the matter through conduction.
− Heat is transferred by movement of fluids e.g air or water through convection. (3 x 1 = 3mks)
5 marks
a) i) F – fold mountain
ii) Subduction zone
b) Effects of plates collision on compression boundaries.
− Leads to volcanicity/islands
− Causes Earthquakes.
− Development of trenches.
− Formation of coastal fold mountains.
5 marks
a) Weathering is the mechanical breakdown or chemical decay of rocks in situ as a result of their exposure on the earth surface while mass wasting is the down slope movement of material under the influence of gravity.
b) Ways in which plants cause weathering in rocks.
− Plant roots grow in cracks and joints in rocks enlarging them.
− Plant decay to release organic acid that accelerate the rate of weathering.
− Plants like algae and lichens cover the rock surface keeping them moist thereby encouraging chemical weathering.
− Plant roots break rock as trees fall during strong winds. 3 marks
5 marks
a) Conditions for formation of Artesian wells.
− Aquifer must be sand witched between impermeable rocks so that it can retain water
− Aquifer must outcrop in a region which is a source of water. This could be a rainy area or beneath a lake.
− Aquifer must dip from a region of water intake and the rock layers must form a broad syncline or basin.
− The mouth of the well must be lower then the intake area. This allows the water to be forced to the surface by pressure without need of pumping it.
b) Significance of ground water.
− Some ground water form sources of some rivers.
− Ground water can be used for irrigation purposes.
− Source of domestic fresh water.
− Hotsprings have been tapped and pumped into cold houses in cold seasons e.g Iceland.
− Source of minerals.
− Tourist attractions e.g. springs, artesian wells.
5 marks
a) Processes of river erosion
i) Corrosion
ii) Hydraulic action
iii) Solution
iv) Altrition
b) Ways in which a gorge is formed.
− Gorge formed where a river maintains its course across land which is being uplifted/Antecedent gorges.
− Gorge formed where there is an abrupt fall in the base level causing river to renew its erosive activity.
− Gorge formed due to river rejuvenation.
− Gorge formed where the river flows along a line of weakness /cracks
− Gorge formed where a waterfall retreats upstream
− Gorge formed where a river flows across a plateau.
5 marks
SECTION 2 (75 Marks)
Answer question SIX and any other Two question in this section.
50000 = 50000 x 1÷100000 = 0.5km
ii)
i) Gentle plain
ii) River/stream
iii)
iii) i) Nguni 137/4
ii) Nuu 151/2
iii) Mwitika 151/ (1mk)
b) i) Refer to graph paper attached
ii)
1/5000 x 1/2 = 1:10000 = 1/100000
(2mks)
c)
− There are many rivers e.g R. Munyuni.
− Most rivers are permanent e.g R. Ikoo.
− Most rivers have their sources in the Kitui hills.
− Most rivers flow towards the South East from NE – SE.
− Main river is river Ikoo.
− Most rivers have a dendritic pattern e.g Ikoo
− Some rivers have their sources at springs e.g rivers flowing from Mutito forest.
− Rivers draining from Mutito forest have parallel pattern.
− R. Ikoo has trellised drainage pattern at GR 0272.
d)
− The sparse population evidenced by the dispersed settlement in the N.East of provider wide tracts of land for cattle rearing.
− The presence of scrub vegetation and scattered trees in Usiani provides plentiful pasture for cattle.
− The relatively high altitude of 1200 – 1500m at Kamutotya GR 9374/Mutito forest provide cool conditions suitable for cattle growing.
− The dense settlement at Mutitu(Ndooa) in the S.E provides market for cattle/cattle products.
− The availability of good transport network e.g Thitani Thokoa all weather road (bound surface) eases transport of cattle/cattle
products to the market.
− There are numerous permanent rivers providing plenty of water to the cattle.
e)
− There is no relationship between relief and drainage of Migwani.
− Most rivers do not originate from the highland west of area covered.
− Most rivers in Kitui hills do not have dendrific pattern.
II)
− Identify suitable points from which data could be collected.
− They may have isolated possible problems they may likely face.
− To project the cost of the study.
− May have identified the availability of data they would require.
− Confirm the suitability of their equipment for the environment in which they studied.
5 marks
a) Folding is the bending of crustal rocks due to crustal distortion while faulting is the cracking of crustal rocks due to tensional or compression forces. (2mks)
ii) Types of faults
− Normal faults
− Reverse faults
− Anticline faults
− Tear/shear faults (3 x 1 = 3mks)
b) Ways in which faulting influence drainage systems.
− Vertical faulting across rivers cause waterfalls.
− Rift faulting results in the formation of lakes/basin drainage / centripetal drainage patterns.
− Some rivers flow along fault lines, forming fault-guided drainage pattern.
− Land uplift may cause reversal in direction of rivers
− Rivers may disappear into faults.
− Fault scarps expose impermeable rock layers to the surface resulting in formation of springs.
c) Formation of a rift valley by Tensional forces
− Rock layers are subjected to tensional forces
− Parallel normal faults or lines of weakness develop.
− The middle block gradually sinks/subsides.
− The sunken middle block form along trough – like feature with steep parallel sides known as a Rift valley.
d) Effects of faulting on human activities
− Features of faulting result in unique sceneries which attract tourists hence earns forex.
− Faulting causes displacement of rocks, exposing minerals thus making mining easy.
− Faulting lead to formation of block mountains which attract relief rainfall on the windward side thus give rise to rivers which
are harvested for HEP production or domestic use/industrial use.
− Deep faults allows underground steam jets to escape, which are then harvested for geothermal power production.
− Rivers flowing over fault scarps form waterfalls used for generation of HEP. (3 x 2 = 6mks)
e (i) Objectives
i) To find out features resulting from faulting
ii) To establish or investigate how faulting has influenced settlement and human activities in the area.
ii) Importance of route map
i) For direction to area of field study.
ii) Ensure little time used in transport to the area of study.
5 marks
a) External land forming processes leading to the formation of lakes.
− Glaciation
− Erosion by wind
− Down warping
− River and wave deposition. (2 x 1 = 2mks)
b) Sources of lake water.
− Rivers
− Rainfall
− Underground water
− Melt water
− Magmatic water (3 x 1 = 3mks)
c) Influence of Lakes on Environment.
− Land/breezes may lead to formation of convectional rainfall.
− Lakes harbour microbes which are habitats for disease causing microbes like mosquitoes and snails
− Lakes may lost dangerous animals that cause destruction to men and property.
− Breezes may strengthen direct or reverse the prevailing winds.
− Evaporation of lake H2O increases the relative humidity over the surrounding areas by supplying extra moisture.
− Winds from the lake to the land lower the temperature of the surrounding area during the hot periods.
3 × 2 = 6 marks
d) Characteristics of lakes formed due to faulting.
− Most are narrow.
− Most are steep sided.
− Most are salty.
− most of them are long 3 × 1 = 3 marks
e) Working schedule for the field study.
8.00am – Collect and assemble equipment/tools
9.00am – Departure
10.00am – Report to authorities
10.15am – Collect data
11.00am – Break/Discussion/collate
2.00am – Report back to authorities.
3.00am – Departure 3 marsk
(ii) Importance of group discussions.
− To minimise on time lost.
− To asses on data collection course.
− To remain on course.
(iii) Reasons why Rift valley lakes are almost at the verge of extinction.
− Some loose water through underground seepage/through faults at the bed.
− Some loose water through high evaporation because of Lakes location in ASALS.
− Reduced rainfall in their catchment areas due to forest destruction thus little volume of rivers flowing into them/dried rivers.
− Increased siltation due to deforestation and improper agricultural practices in the surrounding areas hence reduced depth.
− Increased demand for water from the feeding rivers for domestic/agricultural/industrial use reduce volume of rivers flowing into lakes. 3 × 2 = 6 marks
5 marks
a) Karst scenery is any rugged landscape whose surface rocks are limestone or dolomite and which has been acted on by
carbonation and solution by rain and river water to produce features typical of limestone surfaces.
ii) Conditions necessary for karst scenery formation.
− Surface rock and rock beneath should be thick limestone dolomite or chalk to allow seepage of acid rain.
− Rock should be hard and well jointed to enhance chemical process by solution process.
− Climate should be warm or hot.
− Rainfall should be moderate to high to enhance solution and carbonation process.
− Water table in the rocks should be deep below the surface. (3 x 2 = 6mks)
Formation of:
b) Stalactiles
− Carbon IV Oxide of the atmosphere combines with rain water to form weak carbonic acid rain water.
− The acidic rain falls on the surface of the land and reacts with some rocks e.g limestone dissolving the soluble CaCO3 into CaHCO3 solution.
− The solution of CaHCO3 seeps through the joints into the cave.
− The temperatures in the cave is hot or higher
− Evaporation of water occurs in the cave leading to formation of precipitate of CaCO3 deposit from the top of the roof of the
cave.
− Continuous deposition of CaCO3 downwards leads to formation of a fingure like projection from the roof hanging downwards This is called stalactite. 5 marks
Doline
− Atmospheric CO2 mixes with rain war to form weak carbonic acid rain.
− Acid rain falls on limestone rocks on the surface dissolving it by solution and carbonation process.
− Acid rain widens the joints forming swallow holes.
− iv) Continuous subsidence of swallow holes enlarges the sinkholes forming a large hollow called dolines 5 marks
c) Ways in which limestone landscape influence human activities. (3mks)
− Features formed in limestone areas e.g dolines, uvulas, form unique attractions site to tourists earning forex.
− Limestone rock provide raw materials used in the manufacture of cement used in building and construction.
− Ruggedness of limestone area discourage settlements, agriculture and infrastructure development. (3mks)
d (i) Objectives of studying a karsts landscape.
− To find out features formed in limestone areas.
− To establish effect of limestone landscape on human activities. (2 x 1 = 2mks)
ii) Reasons why karst landscape is unsuitable for settlement:
− The area is rocky.
− Area has thin soils.
− Area has poor vegetation.
− Area has inadequate surface H2O supply.
− Area has rugged landscape
5 marks
a) Earthquake zones of the world (2mks)
− Circum pacific belt.
− Great Rift valley belt.
− Mid- Atlantic Ocean.
− The Tethyan – Mediterranean belt.
b) Causes of Earthquakes
− Underground nuclear tests trigger vibrations.
− Movement of trains generate vibrations.
− Use of explosives during mining, quarrying trigger vibrations.
− Construction of large reservoirs activate or inactivate faults triggering off tremors.
− Isostatic adjustment.
− Plate tectonic movements.
− Tectonic forces.
c) Describe formation of composite volcano.
− Volcanic eruption eject solid materials (pyroclasts) onto the surface.
− Eruption of intermediate lava follows which covers the solid materials ejected.
− Subsequent eruptions joins alternating layers of ash and lava.
− The main vent may block forcing eruptions through other points of weakness on the sides of the cone leading to formation of parasitic cones. The feature formed is called composite cone.
Composite cone.
Text – 5 marks
Diagram – 2 marks
d) Negative effects of volcanicity on human and physical environment.
− Cause great loss of life and damage of property.
− Steep volcanic slopes discourages settlements.
− Steep volcanic slopes are barriers to construction of transport and communication lines.
− Volcanic ashes and granites lead to poorly drained soils discouraging agriculture.
− Volcanic mountains create rain shadow effect on the leeward side.
e) i) Hot-springs
− Geysers
− Caldera
− Craters
ii) Methods used to record data.
− Photographing
− Note taking
− Sketching diagrams/maps
5 marks




Thanks for the paper