KNEC KCSE Geography Paper 2 Question Paper / 2015 KCSE Kajiado County Joint Examination
2015 KCSE Kajiado County Joint Examination
Geography Paper 2
SECTION A (25 Marks)
Answer ALL the questions in this section
a) Explain three reasons why horticulture farming is more developed in the Netherlands than in Kenya. (3 marks)
b) Give two reasons why the growing of flowers in greenhouses is preferred in Kenya. (2 marks)
5 marks
a) What is ecotourism? (2 marks)
b) State three measures the government of Kenya has taken to attract more tourists. (3 marks)
5 marks
The sketch map below shows the Great Lakes and St Lawrence Seaway. Use it to answer question (a)
a) i) Name the ports marked M and P. (2 marks)
ii) The lake marked N (1 mark)
b) Explain two benefiters of the Great lakes and St. Lawrence Seaway to the economies of USA and Canada. (2 marks)
5 marks
a) State three factors that have led to the growth of Thika as an industrial town. (3 marks)
b) State two problems encountered in New York city (2 marks)
5 marks
a) Apart from floods, give two other environmental hazards. (2 marks)
b) State three measures undertaken in Kenya to control floods. (3 marks)
5 marks
SECTION B (75 Marks)
Answer question 6 and any other two questions from this section
The table below shows the tonnage of trade items in Kenya from various parts of the world in 2005 and 2006. Use it to answer question (a) and (b).
a) i) Which continent had the highest increase in tonnage of trade items in Kenya between 2005 and 2006? (2 marks)
ii) Calculate the percentage increase trade tonnage from Australia and Newzealand between 2005 and 2006. (2 marks)
iii) Draw a divided rectangle 15cm long to represent the tonnage of trade items in Kenya in 2006. (10 marks)
b) i) State two advantages of using divided rectangles to represent geographical data. (2 marks)
ii) tate four reasons why in 2005 and 2006 there were higher tonnage for trade items from Europe compared to that from
Africa continent. (4 marks)
c) State five ways through which the Kenyan government is promoting export trade. (5 marks)
5 marks
a) What is a by-product in mining? (2 marks)
ii) State two methods used in mining diamonds in South Africa. (2 marks)
iii) Name four oil producing countries in the Middle East. (4 marks)
b) Explain four ways in which South Africa has benefited from the mining of gold. (8 marks)
c) i) State three effects of open-cast mining on the environment. (3 marks)
ii) Explain three problems facing the mining industry in Kenya. (6 marks)
25 marks
a) i) Differentiate between renewable and non-renewable sources of energy. (2 marks)
ii) Apart from wind, name three other sources of renewable energy. (3 marks)
iii) State four factors that may lead to energy crisis. (4 marks)
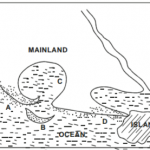
b) The map of African below shows hydroelectric power projects. Use it to answer questions that follow.
i) Name the hydroelectric power projects marked A, B, C and D. (4 marks)
ii) Apart from the presence of a waterfalls. State four factors that influenced the location of Owen Falls power project in
Uganda. (4 marks)
c) i) Explain four ways in which Kenya has benefitted from the development of hydro-electric power schemes.(8 marks)
25 marks
a) i) What is population structure? (2 marks)
ii) Differentiate between population density and population distribution. (2 marks)
iii) State three measures that have been taken by the Kenyan government to reduce infant mortality. (3 marks)
b) Explain how the following influence population growth.
i) Fertility (3 marks)
ii) Migration (3 marks)
iii) Mortality (3 marks)
c) i) State three reasons why .population growth rates have declined in East African. (3 marks)
ii) Explain three problems resulting from decline in population in developed countries such as Sweden. (6 marks)
25 marks
a) State three physical conditions that favour large scale sugarcane farming in Kenya. (3 marks)
b) Describe the commercial cultivation of sugarcane from land preparation to the harvesting stage. (6 marks)
c) Explain five problems facing sugarcane farmers in Kenya. (10 marks)
d) Your class conducted a field study in sugar factory
i) Outline four stages of sugar processing that the class may have observed. (4 marks)
ii) Name two by-products obtained from processing of sugar which class will have identified during the study. (2 marks)
25 marks
GEOGRAPHY PAPER 2 MARKING SCHEME
2015 KCSE Kajiado County Joint Examination
Geography Paper 2
SECTION A (25 Marks)
Answer ALL the questions in this section
a)- There is a high demand for horticulturalcrops in the Netherlands than in Kenya.
– Netherlands uses advanced technology than Kenya.
– Netherlands has well developed and efficient transport network
– Netherlands has highly skilled labour for production and handling of horticultural products .
– Advanced research takes place in Netherlands while in Kenya is less advanced.
– Netherlands is centrally located in Europe which gives it an advantage of the European market.(Any 3×1)
b) – The plants free from the effects of excessive rainfall, haustenes and strongwinds.
– The spread of pests and diseases is easily controlled.
– Amount of moisture required by flowers is easily controlled
– To maintain uniform and constant climatic conditions.
– It is easy to control weeds. (Any 2×1).
5 marks
a) Ecotourism is an environmentally friendly tourism whereby a tourist enjoys watching what
nature has provided while at the same time protecting nat2 × 1
b) -Improving roads and feeder roads to the attraction sites.
-Building of more hotels to increase accommodation capacity.
-Promoting traditional culture
-Providing package tours.
-Advertising tourist attraction abroad.
-Improving links (air links) to facilitate direct movement of tourists to Kenya.(Any 3×1)
5 marks
a) (i) M – Duluth 1 mark
P – Buffalo 1 mark
(ii) Lake marked N-L.Huron 1 mk
b) – Has provided cheap means of transport for exports and imports.
– The dams along the route provide H.E.P for both domestic and industrial use.
– Has led to the growth of ports and towers along the route.
– The seaway is a tourist attraction which generates income.
– The seaway has created employmentopportunities in the transport industry thus raising the living standards of the area people.
– The lakes and dams are sources of water for both domestic and industrial use.
– The Governments earn revenue from toll charges levied on ships that use the route. Any 2×1)
5 marks
a) Factors that have led to growth of Thika town.
– it is surrounded by agriculturally productive district such as Kiambu, Maragua, Muranga etc which provide raw materials for industries.
– Access to abundant water supply from Rivers Chania and Thika used in the industries and for domestic use.
– Good road and railway lines which have made it easy to receive raw materials and transport industrial products to the markets.
– The High production of Thika has provided ready market for industrial products.
– Many investors have preferred to establish industries in Thika which is near Nairobi due to congestion in Nairobi.
– There is expansive flat land for setting up industries and for expanding the etc(Any 3×1)
b) Problems facing New York city.
– Traffic congestion
– Terrorism
– Increase pollution
– Increase crime due to unemployment 2 × 1 = 2 marks
5 marks
a) Environmental hazards
– Lightning
– Draught
– Pests and diseases
– Earth quakes
– Fires
– Windstorms
– Pollution
– Volcanic eruptions etc 2 × 1
b) Measures to control flood in Kenya.
– Construction of diversion channels / canals.
– Construction of artificial leeves.
– Construction of dams along the river channels. (Any 3×1)
5 marks
SECTION B (75 Marks)
Answer question 6 and any other two questions from this section
a) i) Which continent had the highest increase in tonnage of trade items in Kenya between 2005 and 2006.
Europe (2×1=2mks
ii) Calculate the percentage increase of the number of trade tonnage from Australia and New Zealand between 2005
and2006.
2005 =19,000
2006 =24,000 =5,000×100
Difference 5,000 19,000
=26.32%
or 26.3% or 26% or 26 6
/19 (2mks)
iii) Draw a divided rectangle 15cm long to represent the tonnage of trade items in Kenya in 2006.
Europe – 985,000 X 15 =10.29cm/10.3cm
1435,000
Africa – 154,000 x 15 =1.60cm/1.6cm
1435,000
Asia – 128 x 15 =1.33/1.3cm
1435,000
North America – 103,000 x 15 =1.076/1.1cm
1435,000
Australia and New Zealand
24,000 x15 ==0.25/0.3cm
1435,000
All other countries – 41,000 x15=0.42/0.4cm
1435,000
b) (i) State two advantages of using divided rectangles to represent geographical data.
– They give clear visual impression
– They allow comparison
– They can be used to represent a wide rage of data
– Easy to draw
– Easy to interpret (Any 2×1= 2mks)
ii) State four reasons why in 2005 and 2006 there was higher tonnage for trade items form Europe compared to that from Africa
continent.
– Inefficient transport facilities between Kenya and other different railway gauges etc.
– Ignorance of what is produced in member countries in Africa.
– low level of technology in Africa limits production of processed goods.
– Different political ideologies among member counties in Africa restrict trade.
– Political problems such as civil wars in some African trade limit trade.
– Trade in Kenya still follow colonial pattern ie Kenya was colonized by Britain (Europe) hence established trade/political pattern. 4×1=4mks)
c) State five measures through which the Kenyan Government is promoting export trade.
– Signing international trade agreements with other countries e.g COMESA, GTT etc.
– Establishing the export processing zone (EPZ) to produce more goods for export.
– Reduce import duty on raw materials.
– Introduced export compensation scheme locally.
– Encouraging foreign investors to establish industries to increase export goods.
– Licensing export to those willing to engage in export trade.
– Participating in trade fairs and international exhibitions to display export items.
– Encouraging industries and farmers to produce quality goods for export market.
– -Improved transport and communication for easy flow of commodities. (Any 5×1=5mks)
5 marks
(a) (i) Is an incidental secondary product obtained during the processing of some minerals. (2×1=2mks)
(ii) Deep – shaft mining
Open – cast mining
Alluvial/placer mining 2 × 1=2mks)
(iii) Iran
Saudi Arabia
United Arab Emirates
Bahrain
Iraq
Kuwait
Qatar (1×4=4mks)
b) – Gold earns the country foreign exchange through export to other countries.
– Gold has been used as a unit exchange for paying international debts.
– Gold mining in South Africa is a major source of employment.
– Gold mining regions has triggered the development of towns.
Gold based revenue has led to development of other sectors such as infrastructure , residential and
entertainments. 4 × 2 = 8 marks
c) i)- It destroys the natural vegetation which is cleared before mining.
– Water collects in hollows caused by the mining creating disease vectors habitats.
– It causes displacement of population and also hinders settlements.
– Heaping of mining rocks and open quarries leads to dereliction.
– Clearing of the land before mining encourages soil erosion. 3 × 1 = 3 marks
ii)- Insufficient capital for exploitation of minerals leading to expensive foreign loans borrowing.
Inadequate skilled labour personnel .
Dereliction of the land making the land ugly and dangerous for ruse by man and animals.
Pollution of the air by dust and smoke from blasting and quarrying. 3 × 2 = 6 marks
25 marks
(a)
(i) Renewable sources of energy are those sources that can be regenerated and be used for a long time which non-renewable sources of energy are those that once used become exhausted. × 1=2mks)
ii) – Sun
-Water
-Wood
-Biomass
-Geothermal steam
-Drought animals 3 × 1 = 3 marks
iii) Withholding oil by the oil-producing countries.
– Increase in the price of oil triggered by a sharp rise in demand.
– Rapid depletion of oil reserves.
Political disagreements
– Unequal distribution of petroleum products to countries by oil producingcountries. 4 × 1 = 4 marks
b) i) A -Aswan high dam1 mark
B -Kainj 1 mark
C -Inga 1 mark
H -Cabora Bassa 1 mark
ii) – Constant volume of water throughout the year from lake Victoria which is a natural reservoir.
– Hard basement rock firm for the reservoir.
– Availability of space to a reservoir to form.
– Large local market as well as foreign market in Kenya.4×1(4mks)
c) – Provision of electricity for domestic and industrial use.
– Reservoirs are also used as fishing grounds.
– Local climate is modified by large reservoirs.
– Control of floods down stream.
– Foreign exchange is saved that would have been used to import power.
– It has triggered infrastructural development. 4×2 (8mks) must explain
25 marks
(A).
i) Population structure is the composition of population in terms of age and sex at a particular time.2×1 (2mks)
ii) Population distribution is the way people are spread out on land and population density is the number of people per unit area
of land.2×1(2mks)
iii) – Encouraging parents to give their children balanced diet.
– Expanding family planning methods/programmes to cover more people.
– Improved research methods on infant related diseases to curb them.
– Modernisation of medical facilities so as to improve immunization of children.
– Education the masses on child care for healthy children. 3×1=3mks)
b. – High fertility rate leads to high population growth rate while lower fertility leads to low population growth rate. High fertility rates may result from low level of education traditional attachments and poor methods of family planning. 3 × 1
– When people migrate from a country to a foreign country the population declines and the population of the recipient countries increases. 3×1 (3mks)
– High death rate has a negative effect on population growth as it reduces the number of people.
A low death rate would affect the population growth positively in that the number of people increases as the birth rate is higher than death rate.3×1 (3mks)
c ) i) Natural calamites e.g. floods, droughts, civil wars.
– embracing family planning 3 × 1
ii) – Inadequate manpower which makes labour expensive.
– High old age population dependency ratio.
– Underutilization of soil amenities such as schools, hospitals.
– Rural depopulation due to increased urbanization.must explain – 3×2 = 6mks)
25 marks
a) State three physical conditions for largescale sugarcane.
– Warm temperatures through out the year/temperature of 210
C to 270 C through out the year.
High rainfall (1250mm-2000mm) whichis well distributed through out the year.
– Dry and sunny period before and during harvesting.
– Deep, clay or black cotton soil.
– Flat/gently sloping land for ease in mechanization.
– Attitude between sea level and 1600mm (3×1=3mks)
b) Describe the cultivation of commercial sugarcane from land preparation to the harvesting stage.
– First, and is cleared.
– The land is then ploughed several times using tractors.
– Furrows are made/internal between 1.25 & 1.8m.
– Cuttings obtained from old sugar can/setts
– The sugar cane cuttings (called setts) are dipped in insecticides before planting.
– The setts are buried or planted in the furrows.
– Fertilizer is applied in the field severally.
– Weeding is done severally sometimes sprayed with herbicides.
– Can mature at about 18 months.
– The cane may be burnt before harvesting.
– Harvesting is done manually using pangas and the cane is filed in heaps for transportation.(6×1=6mks)
c) Explain five problems facing sugar cane farming in Kenya.
– Frequent fire outbreak-burning of caves by arsonists cause great losses to the farmers due to the destruction of cane.
– Flooding of the local market with cheap imported sugar reducer the market for the locally produced.
– High cost of farm inputs such as fertilizers, leaver farmers with less profits.
– Poor management of sugar cane factories which threatens some firms with closure due to inadequate funds e.g Ramisi
– Pest and diseases e.g Raton stunting, wilt and stalk borer reduce the quality and quantity of sugar cane.
– Delayed payments to farmers lowers their morale hence lowering their production.
Adverse weather especially drought make it difficult for cane to mature.
– Poor infrastructure reduce the rate at which sugar cane is delivered to the factories from farms.
– Low prices of sugar cane discourage farmers who then direct their efforts elsewhere.
– Delays in harvesting of sugar can reduces the quality and tonnage, thus causing a lot of wastage of cane and less earnings for
farmers.(5×2=10mks)
d) Stages of sugar processing.
– Weighing of cane
– Washing of cane
– Cutting of cane into pieces
– Crushing cane pieces between rollers
– Boiling of juice with lime.
– Crystallization of massecuite (mollases and sucrose mixture).
– Growing of sugar crystals in tanes
– Separation of sugar crystals from molasses.
– Refining of sugar. 4 × 1 = 4 marks
ii) Sugar by-products
– Bagasse
– Molasses 2 × 1 = 2 marks
25 marks