KNEC KCSE Geography Paper 2 Question Paper / 2015 KCSE Gem Sub-County Joint Evaluation
GEOGRAPHY PAPER 2 QUESTION PAPER
2015 KCSE Gem Sub-County Joint Evaluation
Geography Paper 2
SECTION A (25 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section.
a) Define eco-tourism. (2mks)
b) State three factors which have made Switzerland a major tourist destination. (3mks)
5 marks
a) Name three functional zones of an ideal urban center. (3mks)
b) State two benefits that would arise if more commuters in urban centers in Kenya used public transport. (2mks)
5 marks
a) State three advantages of using containers in the transportation of goods in Kenya. (3mks
b) Give three reasons why there are a few rail links among African countries. (3mks)
6 marks
a) What are tertiary industries ? (2mks)
b) List three reason s why development of the Jua Kali industry is encouraged in Kenya. (3mks)
5 marks
a) State how the following factors have led to the population increase in Kenya.
i) Cultural beliefs (2mks)
ii) Early marriages (2mks)
4 marks
SECTION B (75 Marks)
Answer question 6 and any other two questions from section.
The table below shows the values of Kenya import in million shillings between the years 2005- 2009. Use it to answer the following questions.
Year Crude oil Industrial machinery Pharmaceuticals
2005
2006
2007
2008
2009
91,200
93,700
87,000
120,200
121,900
15,700
17,100
21,200
32,300
37,100
58,300
82,400
72,500
75,600
68,100
a)Calculate :
i) The total value of industrial machinery imported by Kenya from the year 2005-2009. (2mks)
ii)The total value of Kenya’s imports in the year 2008. (2mks)
b)i) Draw a comparative bar graph to show Kenya’s imports between the years 2006 and 2009. Use a vertical scale
of 1cm to represent a value of 10,000 shillings. (9mks)
ii) State two advantages of using a comparative bar graph to represent statistical data. (2mks)
iii) Give two reasons why Kenya imports some of the items it produces. (2mks)
c) i) Outline four reasons why there is little trade between Kenya and other African countries. (4mks)
ii) Explain two steps that can be taken to improve Kenya’s balance of trade. (4mks)
25 marks
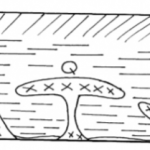
The diagram below shows the cocoa triangle in Ghana. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
a) i) Name the towns marked A, B and C. (3mks)
ii) State four physical factors that favour the growth of cocoa. (4mks)
b) i) Outline the stages involved in the processing of cocoa from harvesting to the time it’s ready for export. (8mks)
ii) State two uses of cocoa. (2mks)
c) i) Name two exotic breeds of cattle reared on commercial ranches in Kenya. (2mks)
ii) Explain three factors that favour the development of beef industry in Argentina. (6mks)
25 marks
a) i) Differentiate between forestry and agro-forestry. (2mks)
ii) Apart from agro-forestry, explain four measures being taken by the government of Kenya to control human
encroachment on forested areas. (8mks)
b) i) Name two exotic species of trees planed in Kenya . (2mks)
ii) Give the difference between softwood in Kenya and Canada under the following sub-headings.
-Harvesting period (2mks)
-Diversity of the softwood trees species. (2mks)
c) i) Name three non- wood products from the natural forest of Kenya. (3mks)
ii) Explain three human problems facing forest in Kenya, apart from human encroachment. (6mks)
25 marks
a) i) Define land reclamation. (2mks)
ii) Give two methods that are used to drain swamps in Kenya. (2mks)
b)Study the map of Mwea Tebere and use to answer the following questions.
i) Name the rivers marked P, V and W. (3mks)
ii)Name the sections marked Q and U. (2mks)
iii) Name the method of irrigation used in Mwea Tebere. (1mk)
c) Explain how the following factors influenced establishment of Mwea Tebere irrigation scheme.
– Topography (2mks)
– Soil (2mks)
– Government policy (2mks)
d)i) State four characteristics of the polders of Netherlands. (4mks)
ii) Describe the processes of land reclamation in Mwea Tebere. (4mks)
25 marks
a) What is drought? (2mks)
b) Explain five negative effects of drought in Kenya. (10mks)
c) You carried out a field study on pollution in Kisumu town.
i) Name f our main types of wastes they came up with after the study. (4mks)
ii) Suggest five ways by which waste within Kisumu Town can be managed. (5mks)
iii) Give four methods that you would use to collect information on pollution. (4mks)
25 marks
GEOGRAPHY PAPER 2 MARKING SCHEME
2015 KCSE Gem Sub-County Joint Evaluation
Geography Paper 2
SECTION A (25 Marks)
Answer all questions in this section.
a) Eco-tourism refers to visiting places of interest for recreational purposes while taking care of animals and plants and their
habitats. (2mks)
b) Three factors which have made Switzerland a major tourist destination.
− Warm sunny summers allow for swimming and sun-bathing/cold winters encourage winter sports.
− Varied scenery.
− Central position of Switzerland within Europe.
− Political neutrality of Switzerland.
− Diversity of languages spoken in Switzerland.
− Developed transport network to tourist sites.
− Advanced training in the tourist industry/package tours.
− Availability of health resorts/spas.
− Inherent hospitality of the swiss.
− Developed financial institutions for easy transactions.
− Switzerland is the headquarters for some international agencies. (Any 3 x 1 = 3mks)
5 marks
a) 3 functional zones:
− Central business district.
− Residential zone.
− Manufacturing/industrial zone. (3 x 1 = 3marks)
b) Two benefits for commuter using public transport.
− It would help save fuel/petrol.
− It would help to ease traffic congestion.
− Create more room for parking.
− Government would save foreign exchange on fuel. (Any 2 x 1 = 2mks)
5 marks
a) State three advantages of using containers in the transportation of goods in Kenya.
− Containers guard against theft of goods since they are sealed.
− They are even in shape hence occupy less space.
− They guard against destruction of goods.
− Saves time when loading and offloading since containers have a large capacity.
− Make loading and offloading easy since they are fitted with hooks/rings for handling (Any 3 x 1 = 3mks)
b) Give three reasons why there are few rail links among African countries.
− Steep terrain/thick forests make it expensive to construct lines.
− Competition from other means of transport leads to neglect of railway transport.
− The rail lines are of different gauges making it difficult for the countries to link them.
− Inadequate capital limits to construction of new lines/maintenance of railways.
− Limited trade links due to the production of similar commodities make it unjustifiable to construct railway lines.
− Political difference/instability discourages attempts to link the line.
− Large areas of the continents are economically unproductive thus it would be uneconomical to link railways.
(3 x 1 = 3mks)
6 marks
a) What are tertiary Industries (2mks)
− These are industries that provide services.
b)
− Some of Kenya’s Juakali industrial goods are exported thus earning foreign exchange.
− It has created more employment opportunities hence raising the standard of living.
− It has led to increased rural development reducing rural-urban migration.
− Requires low capital investment therefore most Kenyans can afford to establish the industries.
− Uses locally available raw materials hence saves foreign exchange.
− It has led to the reduction of importation of some industrial goods thus saving foreign exchange (3 x 1 = 3mks)
5 marks
State how the following factors have led to the population increase in Kenya.
i) Some cultures encourage large families; in almost all culture, there is a tendency of preferring male children. This may lead to those who are not getting male children to have a large family as they hope to get boys/males.
ii) Early marriages
i) People who marry early are likely to get more children because they have a long period during which they can get children.
4 marks
SECTION B (75 Marks)
Answer question 6 and any other two questions from section.
a) Calculate;
i) The total value of industrial machinery imported by Kenya from the year 2005 up to 2009.
123,400,000,000/ 123, 400 million (2mks)
ii) The total value of Kenya’s imports in the year 2008.
228,100,000,000/228,100 million.(2mks)
b (i) Draw a comparative bar graph to show Kenya’s imports between the years 2006 and 2009. Use a vertical scale of 1cm to
represent a value of 10,000 shillings. (9mks)
ii) State two advantages of using a comparative bar graph to represent statistical data.
i) Gives a clear visual impression.
ii) Easy to draw/construct.
iii) Easy to compare the components.
iv) Easy to read/interpret. (2 x 1 = 2mks)
iii) Give two reasons why Kenya imports some of the items it produces.
− To carter for inadequate supply of similar item.
− For its citizens to have a variety of the same items.
− To maintain bilateral relationship with other countries.
− Some of the items it produces are expensive to produce. (2 x 1 = 2mks)
c (i) Outline four reasons why there is little trade between Kenya and other countries in Africa.
− Production of similar goods among the African countries.
− There is poor transport and communication links for efficient transactions.
− They are limited/diversified products among African countries.
− There is inadequate capital for some traders which makes them unable to expand their trading activities.
− Insecurity in some countries discourages the traders due to huge loses.
− Complication in clearance of goods at border points or ports delays delivery of some goods and increase the cost of goods.
− Unexpected trade restrictions are sometimes imposed on Kenya’s exports hence lower reproduction of such commodities.
− Some goods are inferior. (4 x 1 = 4marks)
A COMPARATIVE BAR GRAPH SHOWING THE VALUE OF KENYA’S IMPORTS IN MILLION SHILLINGS
BETWEEN THE YEAR 2006 AND 2009
c (ii) Explain two steps that can be taken to improve Kenya’s balance of trade.
− Encouraging the development of Jua kali industries which do not require importation of heavy/expensive machinery so that
Kenya can export the Jua kali product.
− Restricting the import of luxury items through taxation.
− Establishing/protecting import substitution industries to cut down on importation of some commodities.
− Developing alternative sources of energy in order to reduce importation of fuel/petroleum.
− Diversifying the agricultural export base to enable the country to have variety of exports.
− Opening new markets to avoid dependency on trading partners. (2 x 2 = 4mks)
25 marks
a) i)Name the towns marked A, B, and C
A – Takoradi
B – Kumasi
C – Aera 3 × 1 = 3 marks
ii) State four physical factors that favour the growth of cocoa.
− High rainfall/heavy rainfall/1270mm – 1500mm
− Well distributed rainfall throughout the year.
− High temperatures throughout the year/ 24o
c – 30o c.
− High relative humidity throughout the year/80% – 90%.
− Deep soil.
− Well drained soils.
− Loamy soils/light soils/volcanic soils.
− Shade from strong sun rays for the seedlings.
− Sunshine for ripening of pods. (4 x 1 = 4mks)
b i) Outline the stages involved in the processing of cocoa from harvesting to the time it’s ready for export.
− The ripe pods are removed from the trunk and branches using a long sharp knife.
− The pods are collected and piled at a central place.
− The pods then split open with a sharp knife and beans scooped out by hand.
− The beans are put in heaps or mats and covered with banana leaves. They are allowed to ferment for 5 – 6 days during which
the juicy pulp drains away.
− Fermented beans are washed and cleaned. Beans are spread on tables covered with mats to dry in the hot sun.
− The beans are turned frequently and as they dry and slowly they turn brown.
− Dry beans are put in sacks and sent to the harvest buying centre.
− At the centre the dry beans are weighed and graded ready for export.
− From the harvest buying centre, the dry beans are transported by rail to the ports or Accra, Takoradi and Tema from where
they are shipped to many countries of Africa and Europe. 8 marks
ii) State two uses of cocoa.
− Cosmetics
− Drugs
− Confectioneries
− Beverages. (Any 2 x 1 = 2mks)
c)
− Aberdeen Angus
− Hereford
− Charolais
− Red Angus
− Short horn Galloway
− Santa Gertrudis. 2 × 1 = 2 marks
ii) Explain three factors that favour the development of beef industry in Argentina.
− Replacement of coarse grass with alfalfa/corn has improved the quality of pastures/feeds for the beef cattle.
− Cross breeding of the traditional cattle with higher quality breeds/Hereford/Aberdeen Angus/short Horn has improved the
quality of the yields.
− The maritime/warm and wet climate of the area makes cattle grazing possible throughout the year.
− Availability of water supplied using wind pumps ensures constant supply of water for cattle.
− Availability of vast lands/pampas/extensive grasslands suitable for cattle grazing encourages beef cattle ranching.
− There is a well developed railway network for taking beef to factories.
− Availability of market both local and external encourages the farmers to expand the beef industry/sustains the industry.
− Availability of refrigeration facilities enable beef to reach far off markets. 6 marks
25 marks
a) i) Forestry is the science of planting, caring and using trees/forest and their associated resources, while agro forestry is the
deliberate growing of trees and crops/keeping of livestock on a piece of land.
ii) Gazzetment of forested areas to delimit the areas and reduce encroachment by the public.
− Evicting people who have encroached forested areas in order to rehabilitate the forests.
− Educating the public/creating awareness on the importance of conserving forests to gain their support on conservation.
− Enacting/enforcing laws to prohibit cutting of trees within the gazetted areas.
− Employing forest guards to patrol forest reserves to ensure that illegal activities are reported.
− Encouraging people to use other sources of energy in order to reduce the demand for wood fuel.
− Fencing off forested areas/maintaining of buffer zones to keep away any intrudes into the forest.
b) (i) Pine
Cypress
Blue gum/eucalyptus
Wattle
Kei – apple
Jacaranda
Bombay
Granville
Cedar
Casuarinas
Silky oat
ii) Tree harvesting
− In Kenya harvesting of trees is done throughout the year while in Canada harvesting is done in winter and early spring.
− In Kenya harvesting is done selectively in most cases while in Canada indiscriminate cutting of trees is done.2 marks
Transportation of the logs.
− In Kenya, logs are transported by road/trucks while in Canada transport is mainly by water/rivers.
− In Kenya, transportation is expensive while in Canada it is cheap. 2 marks
Diversity of the softwood tree species.
i) The various types of softwood tree species in Kenya are low while in Canada, a wide variety of such trees prevail.
c (i) Resins
Gums
Tannin
Mushroom
Tubers
Nuts
Fibres
Silk
Vegetables
Fruits
Medicinal herbs
Honey. 3 marks
c (ii) Explain three human problems facing forests in Kenya.
− The degazettement of state forests which reduces the total acreage under forests in the country.
− The outbreak of forest fires by hunters and honey harvesters which destroys the forests.
− Over-exploitation to meet the high demand for forest products particularly timber which reduces the area under forest cover
greatly.
− High population growth which leads to encroachment of forests for purpose of farming and settlement causing cutting down
of forests.
− Illegal logging which destroys large forest lands.
− Corruption by forest officers which results into massive cutting down of trees hence reducing the area under forest cover.
− Remoteness/inaccessibility of forest areas which hampers regular forest patrols for security purposes.
25 marks
a) Define land reclamation
i) Is a process of converting less productive land to a state for agricultural or settlement purposes.
ii) Name methods that are used to drain swamps in Kenya.
− Constructing drainage pipes.
− Digging open ditches/canals.
− Pumping out the water
b (i) Name the rivers marked P, V and W
P – Thiba
V – Tebere
W- Nyamindi 3 marks
ii) Name the sections marked Q and U
Q – Mwea
U – Tebere 2 marks
iii) Name the method of irrigation used in Mwea Tebere.
i) Canal irrigation 1 mark
c) Explain how the following factors influenced establishment of Mwea Tebere irrigation scheme.
i) Topography
− The gently sloping land makes it possible for water to flow by gravity out of the irrigated field.
− The gently sloping land allows for mechanization which allows large areas to be put under cultivation. 2 marks
ii) Soils
i) Presence of black cotton soil which is suitable for cultivation of rice retains water for a long time. 2 marks
iii) Government policy
− i) There was need to keep political detainees busy. This made the colonial government to set up the scheme where
there was large detention camp. 2 marks
ii) State four characteristics of the polders of the Netherlands
− The soils are highly desalinized.
− They are protected by dykes against gales/sea encroachments.
− They are surrounded by Ring Canals to facilitate drainage.
− They are divided into specific land use activities.
− The land is intensively utilised.
− Horticulture is the predominant agricultural activity.
− They are large in acreage/area/size.
− They are relatively flat.
− They are largely flat.
− They are largely below the sea level. 4 marks
d) Describe the process of reclamation of Mwea Tebere irrigation scheme.
− The vast land of 14721 acres is divided into plots of 1Ha.
− Each plot is surrounded by ridges of earth to hold water.
− A main canal is constructed to direct water from the Rivers Thiba/Nyamidi.
− From the main canal, smaller canals are dug to access the plots/farms.
− Water flows into the main canal then to the smaller canals/plots of land by gravity.
− The plots of land get flooded in readiness for paddy rice cultivation.
− Fertilizers application takes place to upscale soil drainage and fertility. 5 marks
25 marks
a) What is drought?
− Drought is the drops of precipitation significantly below normal levels. (1 x 2 = 2mks)
b) Explain five negative effects of drought.
− Reduced agricultural production due to low precipitation/soil erosion leading to a weak economy/loss food supply/causes
famine.
− The displacement of people who will be a burden to maintain in the new areas of settlement.
− The loss of species/biodiversity which will limit scientific research.
− The migration of wild animals which will mark the collapse of the tourist industry.
− Increased health and hygienic risks which cause death/poor health due to inhalation of dusty air particles.
− Increased conflicts by communities over resources such as water, fertile land resulting into death.
− Increased poverty which will lead to low standard of living of the people.
− The collapse of forest related industries due to the loss of trees.
− Reduced fisheries which will lead to low fish harvests. (Any 5 x 2 = 10mks)
i) Name four main types of waste they came up with after the field study.
− Electronic waste/E – waste.
− Household waste.
− Industrial waste.
− Biomedical/clinical waste.
− Commercial/Business waste.
− Agricultural waste.
− Construction/Demolition waste.
− Sewage/sludge. (Any 4 x 1 = 4mks)
ii) Suggest three ways by which wastes within Kisumu can be managed.
− By recycling waste so as to produce useful products to the people.
− By encouraging non-governmental organizations to play a key rule in waste collection and transformation into useful products.
− By awareness creation on the significance of sound waste management practices by urban populace.
− By penalizing severely those companies/
− individuals/firms which flout waste management legislation.
− By reducing the use of products which once quickly disposed off raise the scale of waste accumulation in the town.
− By raising certain products which lessen the chances of heightening the scale of waste spread in the town.
− By asking local companies/firms/county government to thoroughly treat waste prior to disposing it off to the local surroundings.
− By placing many wastes collection bins to reduce the haphazard manner of disposal which makes the town to be insight.
− To discourage the use of plastic bags which are non-biodegradable and thus a serious pollutant of the land.
(Any 5 x 1 = 5mks)
(iii)
− Observation.
− Collecting samples.
− Taking photographs/video taping.
− Administration of questionnaire.
− Interviewing.
− Content analysis. (Any 4 x 1 = 4mks)
25 marks