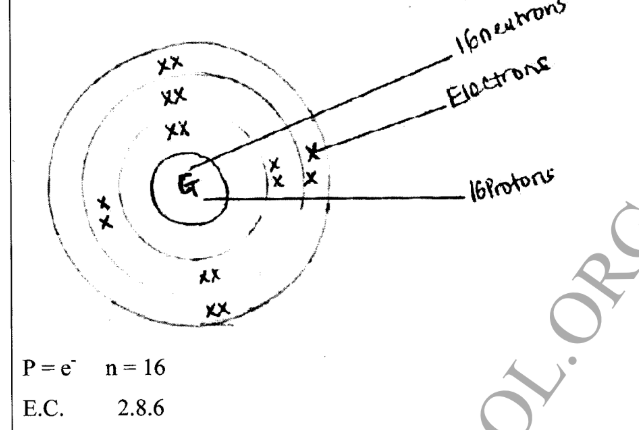
KNEC KCSE Past Papers 2017 General Science Paper 1 (237/1)
Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education
2017 General Science Paper 1
Section A: Biology (34 marks)
1. State the three functions of blood plasma. (3 marks)
2. (a) Name one organism in the Kingdom Monera. (1 mark)
(b) Classify the domestic dog (Canisfamiliaris) into the following taxonomic units:
(i) phylum
(ii) class 3. The diagram below shows a cell organelle found in an animal cell.
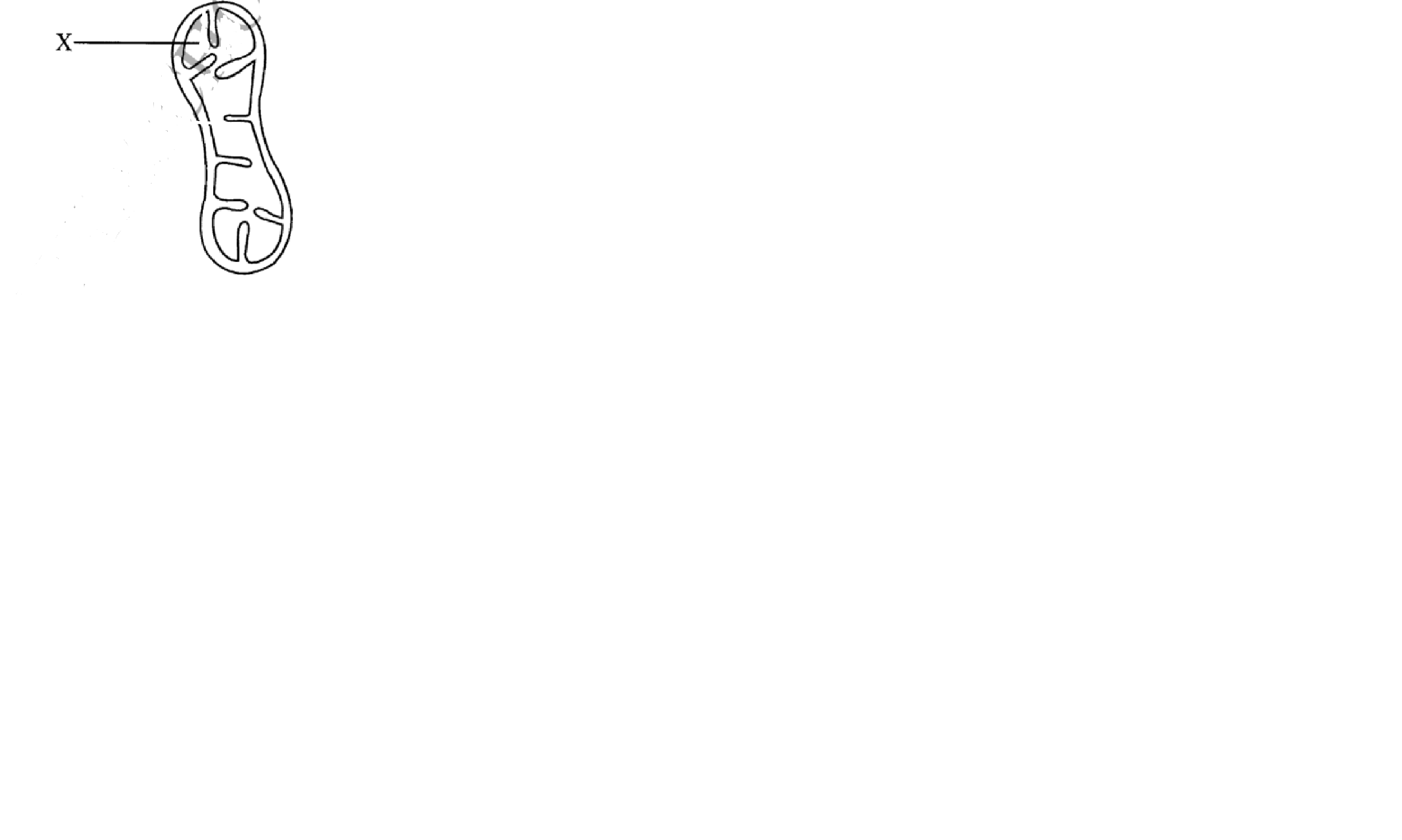
(a) Name the organelle illustrated above
(b) Identify the part labelled X
(c) (i) State the function of the organelle illustrated.
(ii) How is the organelle illustrated above structurally adapted to its function?
4. State three characteristics of respiratory surfaces in animals.
5. State three factors that increase the rate of diffusion.
The diagram below shows a section of the human skin.
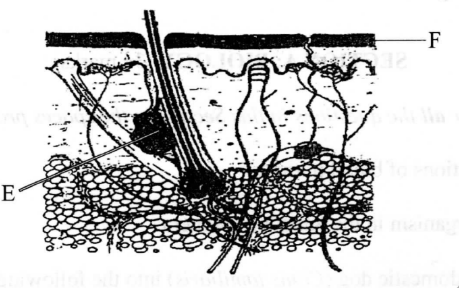
(a) (i) Name the part labelled E
(ii) Give one ftmction of the structure labelled E
(b) How is the part labelled F adapted to its function?
The diagram below represents a section of a human kidney.

(a) (i) Name the structure labelled G.
(ii) Give the function of the structure labelled G.
(b) State two ways of treating kidney failure.
Give three structural factors that increase the rate of transpiration in plants.
State one difference between movement and locomotion.
Below is a word equation of a process in plant nutrition.
Carbon (IV) oxide + water TJ/k L + Oxygen
(a) (i) Name the product labelled L (ii) State the requirements labelled J and K (2 marks)
J ……………………………………
K ………………………………… ..
(b) Explain the importance of the product L. (2 marks)
SECTION B: CHEMISTRY (33 marks)
Answer all the questions in this Section in the spaces provided. Dilute Sulphuric(V1) acid was added to A, which is a compound of magnesium. A reacted with the acid to form a colourless solution B and a colourless gas C which formed a white precipitate with calcium hydroxide solution.
(a) Identify:
(i) Compound A (1 mark)
(ii) Solution B (1/2 mark)
(m) Gas C (1/2 mark) (b) Write an equation for the reaction that took place between compound A and the acid. (1 mark)
(a) Describe how a sample of oil can be extracted from macadamia seeds in a Chemistry laboratory. (2 marks)
(b) Figure 1 shows the steps followed during fractional distillation of liquid air.
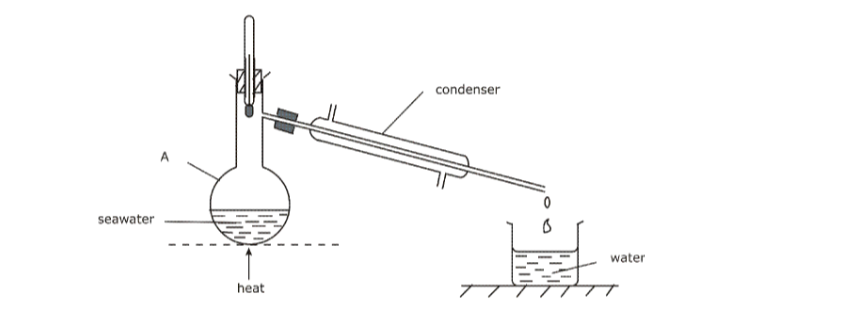
(i) Name the process that takes place at the filter. (1 mark)
(ii) State the role of sodium hydroxide solution in the preparation of liquid air. (1 mark)
(iii) Identify substance D. (2 mark)
(iv) State one use of substance E. (1/2 mark)
(b) Draw and label the structure of G. (2 marks)
Figure 2 is an illustration of one of the methods used to prepare salts

(a) Name solid J. (1 mark)
(b) Name the method of salt preparation demonstrated in Figure 2. (1 mark)
In terms of structure and bonding explain the following statements.
(a) Copper is used to make electrical cables. (l mark)
(b) Solid sodium chloride does not conduct heat and electricity. (2 marks)
Use the information in Table 1 to answer the questions that follow.
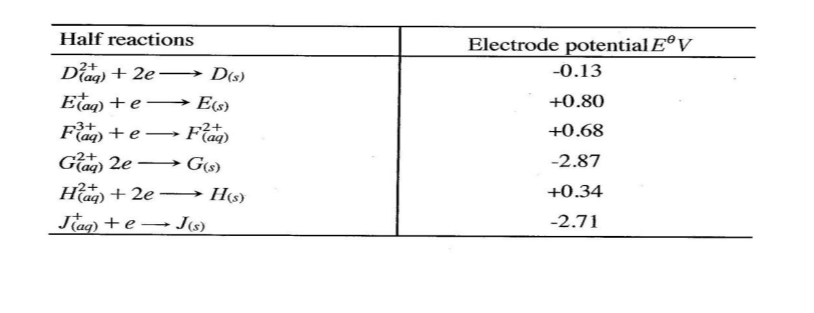
(a) Arrange the elements in order to reactivity starting with the most reactive. (2 marks)
(b) What property of the elements is displayed in Table 1? (1 mark)
17. Explain the following statements:
(a) Group VIII elements are said to be inert. (1 mark)
(b) Magnesium and silicon are solids at room temperature, yet silicon has a higher melting point than magnesium. (3 marks)
18. Figure 3 shows a set up that is used to investigate the effect of an electric current on various substances.
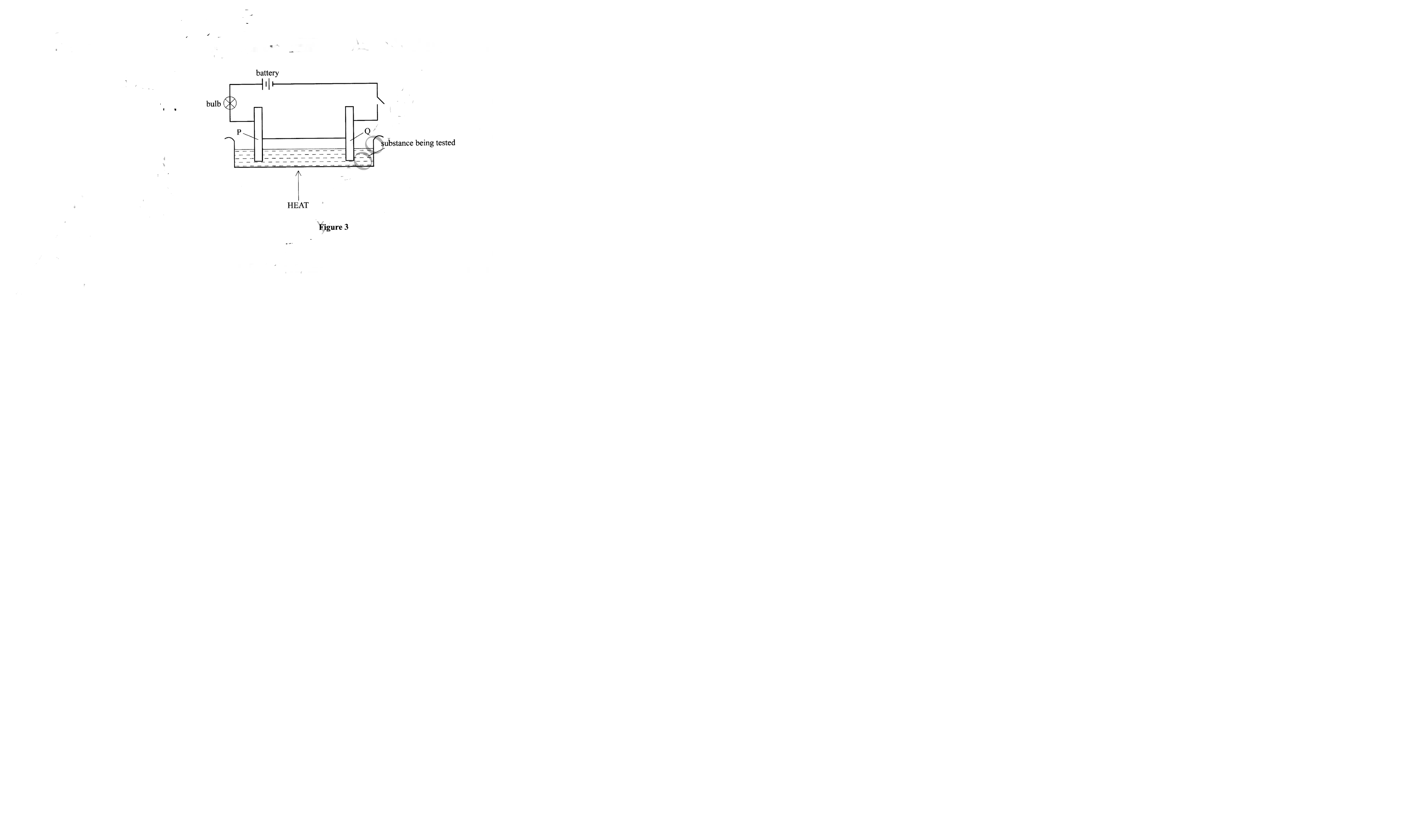
(a) Identify the electrodes labelled
(i) P (1/2 mark)
(ii) Q (1/2 mark)
(b) What observations will be made if lead(II) bromide was the substance under investigation. (1 mark )
19. Explain how water hardness can be removed using the ion-exchange method. (2 marks)
20. The set up in Figure 4 was used to investigate the reaction of calcium with cold water.
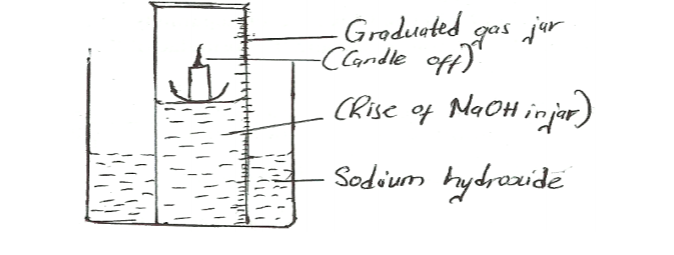
(a) Name gas R. (1/2mark)
(b) Explain the observation that was made when a few drops of phenolphthalein indicator were added to the resulting solution. (1 mark)
(c) If magnesium ribbon was used in place of calcium, explain why it was necessary to clean the magnesium with steel wool before its reaction with Water. (1/2 mark)
21. Study Figure 5 and answer the questions that follow.
a brown gas + oxygen Figure 5 (a) Name solid T. (1 mark)
(b) Identify the brown gas. (1 mark)
SECTION C: PHYSICS (33 marks)
22. State one reason why students should not carry or eat food in the laboratory. (l mark)
23. Figure 6 shows a metre rule being used to measure the length of a block of wood.
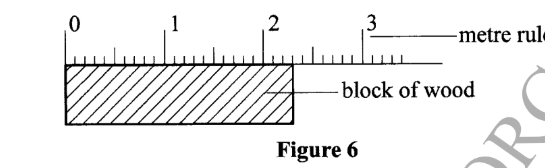
Record the length of the block of wood. (1 mark)
24. Complete the Table 2 below. (2 marks)
Table 2 Physical Quantity I SI Unit | Symbol of Unit Mass 1 I l | Newton i 25. Define the term Power. (l mark)
26. Two students A and B are taking milk using a straw. A is standing on top of a high mountain while B stands at the foot of the mountain. State with a reason which student takes the milk more easily.(2 marks)
27. Explain why a gas occupies the whole space of the container in which it is placed. (2 marks)
28. (a) A student observed that gaps between rails along a railway line were larger in the moming than in the afiernoon. Explain the observation. (2 marks)
(b) State the purpose of the consnietion in a clinical thermometer (1 mark)
29. Figure 7 shows an immersion heater being used to heat water in a jug and a thermometer placed in the water with its bulb below the heating coil.
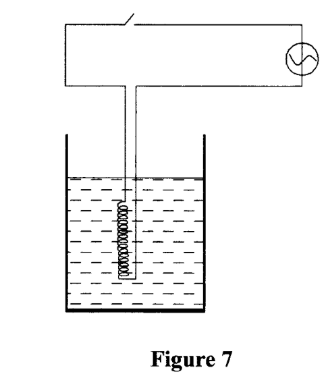
It was observed that when the water started to boil the thermometer reading was lower than the boiling point of water. Explain this observation (2 marks)
30. A uniform plank of wood of length 5 m is pivoted at its centre. A girl of mass 32 kg sits at one end of the plank. Determine how far from the pivot a boy of mass 40 kg should sit in order to balance the plank. (3 marks)
31. (a) A ball rests on a level floor. Name its state of equilibrium. (1 mark)
(b) State how the area of the supporting base affects the stability of the object. (l mark)
32. (a) Define “elastic limit” (l mark)
(b) A spring supporting a weight of 30N extends by 1.5 cm. Determine the spring constant. (3 marks)
33. Figure 8 shows the velocity time graph for a vehicle. velocity (V)
Describe the motion of the vehicle in the regions.
AB ………………………………………
………………………………. ..
CD ……………………………….
34.(a). Define inertia.
(b).Explain how striking a matchstick on a matchbox causes fire. 35.(a). State the law of flotation.
(b).Explain why an object Weighs more in air than when fully immersed in water. (3 marks)
KCSE Past Papers 2017 General Science Paper 2
General Science Paper 1
Section A: Biology (34 marks)
1. State the three functions of blood plasma. (3 marks)
– Acts as a transport medium for food substances/waste products (from tissues to excretory organs)
– Transport of hormones (to target organs);
– Transfer of heat within the body; – Provides medium in which (soluble) substances, ions are transported
2. (a) Name one organism in the Kingdom Monera. (1 mark)
-Bacterium;
-Blue algae
(b) Classify the domestic dog (Canisfamiliaris) into the following taxonomic units:
(i) phylum
Chordata
(ii) class
Mammalia
3. The diagram below shows a cell organelle found in an animal cell.
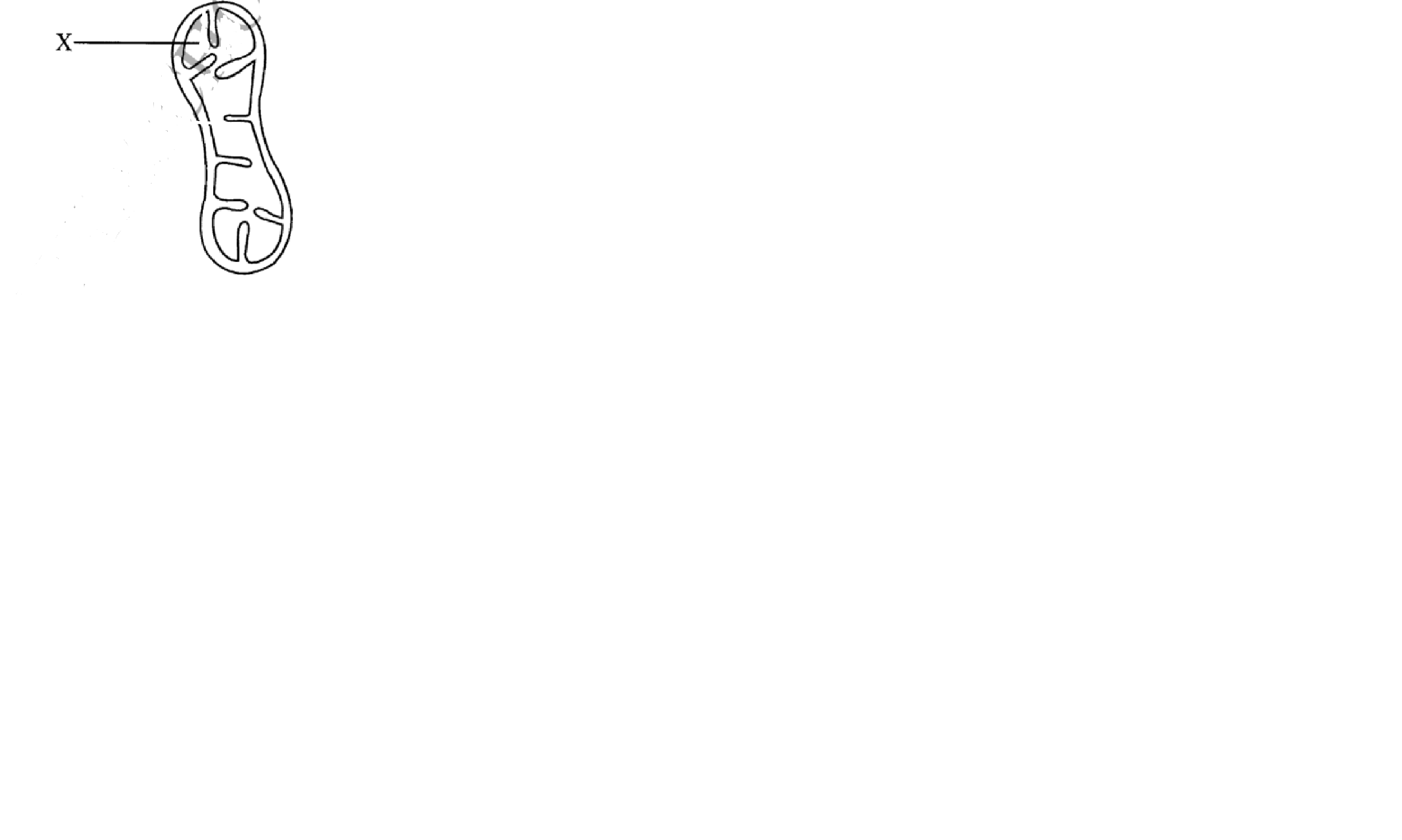
(a) Name the organelle illustrated above
Mitochondrion
(b) Identify the part labelled X
Matrix
(c) (i) State the function of the organelle illustrated.
(ii) How is the organelle illustrated above structurally adapted to its function?
(i) Acts as a site for energy synthesis/respiration;
(ii) Inner membrane is folded (into infoldings/cristae); to increase surface area for attachment of respiratory enzymes (increasing surface area for respiration)
(i) Acts as a site for energy synthesis/respiration;
(ii) Inner membrane is folded (into infoldings/cristae); to increase surface area for attachment of respiratory enzymes (increasing surface area for respiration)
4. State three characteristics of respiratory surfaces in animals.
– Moist; to dissolve respiratory gases for faster gaseous exchange;
– Highly vascularized/supplied with dense network of blood capillaries for efficient transportation of respiratory gases;
– Lined with one-cell-thick/ thin epithelia to reduce the diffusion distance
5. State three factors that increase the rate of diffusion.
– Increased/high temperature (to a given optimum);
– Increasing surface area to volume ratio;
– Increasing concentration gradient;
– Reducing the sizes of diffusing particles/using smaller diffusing
6.The diagram below shows a section of the human skin.

(a) (i) Name the part labelled E
– Sebaceous gland
(ii) Give one function of the structure labelled E
– Produces sebum which is antiseptic and prevents cracking/drying of the skin/keeps it moist/supple
(b) How is the part labelled F adapted to its function?
– ls made up of dead cells to protect inner (delicate) parts from mechanical damage, microbial attacks, desiccation, etc;
– Is perforated to allow for elimination of (nitrogenous) wastes;
– Lined with hair for insulation/thermoregulation
The diagram below represents a section of a human kidney.

7.(a) (i) Name the structure labelled G.
– Ureter
(ii) Give the function of the structure labelled G.
– Drains urine into the urinary bladder;
(b)
(b) State two ways of treating kidney failure.
8. Give three structural factors that increase the rate of transpiration in plants.
– Broad leaf surface;
– Thin cuticle;
– Lack of absence of epidermal hair;
– Increased number/numerous stomata on the upper leaf surface;
9. State one difference between movement and locomotion.
Locomotion involves the displacement/movement of the entire body (of organism) from one place/point to another while movement may only be limited to (some) parts of an organism (for instance, roots/shoot) or the entire organism
Below is a word equation of a process in plant nutrition.
Carbon (IV) oxide + water TJ/k L + Oxygen
(a) (i) Name the product labelled L
– Glucose
(ii) State the requirements labelled J and K (2 marks)
J – Light energy;
K – Chlorophyll
(b) Explain the importance of the product L. (2 marks)
-It is oxidized/broken down; to release energy during respiration
SECTION B: CHEMISTRY (33 marks)
Dilute Sulphuric(V1) acid was added to A, which is a compound of magnesium. A reacted with the acid to form a colourless solution B and a colourless gas C which formed a white precipitate with calcium hydroxide solution.
(a) Identify:
(i) Compound A– Magnesium carbonate (MgCO3) (1 mark)
(ii) Solution B – Magnesium sulphate solution (MgSO4(aq) (1/2 mark)
(iii) Gas C – Carbon(IV) oxide / Carbon(V) oxide (CO2)(1/2 mark)
(b) Write an equation for the reaction that took place between compound A and the acid. (1 mark)
MgC03)(s) + H2SO4(aq) —> MgSO4(aq) + CO2) + H2O(l)
(a) Describe how a sample of oil can be extracted from macadamia seeds in a Chemistry laboratory. (2 marks)
- Crush the seeds in a mortar using a pestle;
- Continue crushing the seeds while adding acetone / propanone a little at a time;
- Q Decant the resulting solution into an evaporating dish/basin;
- Leave the solution in the sun for some time. Propanone evaporates because of its low boiling point. The residue liquid is the oil.(b) Figure 1 shows the steps followed during fractional distillation of liquid air.
(i) Name the process that takes place at the filter. (1 mark)– Electrostatic precipitation
(ii) State the role of sodium hydroxide solution in the preparation of liquid air. (1 mark)
– NaOH (aq) is an alkali hence it absorbs Carbon(IV) oxide from the air.
(iii) Identify substance D. (2 mark)
– Nitrogen.
(iv) State one use of substance E. (1/2 mark)– used in filling electric light bulbs; -used as an insulator during welding of metals
13. Draw and label the structure of G.Mass number of G 32 and Atomic number of G is 6 (2 marks)
Figure 2 is an illustration of one of the methods used to prepare salt
(a) Name solid J. (1 mark)– Lead(II) iodide
(b) Name the method of salt preparation demonstrated in Figure 2. (1 mark)
– Precipitation / double decomposition
In terms of structure and bonding explain the following statements.
(a) Copper is used to make electrical cables. (l mark)
– Copper is used in electrical appliances due to its good electrical conductivity because of presence of delocalized electrons
(b) Solid sodium chloride does not conduct heat and electricity. (2 marks)
– Sodium chloride is an ionic compound in which the ions are immobile when in the solid state hence it does not conduct heat and electricity.
Use the information in Table 1 to answer the questions that follow.
(a) Arrange the elements in order to reactivity starting with the most reactive. (2 marks)– K, M, L, N —>Decreasing reactivity
(b) What property of the elements is displayed in Table 1? (1 mark)
– Competition for combined oxygen / reduction
17. Explain the following statements:
(a) Group VIII elements are said to be inert. (1 mark)
– Group VIII elements are inert since the highest occupied energy level is completely filled with electrons thus electronically stable.
(b) Magnesium and silicon are solids at room temperature, yet silicon has a higher melting point than magnesium. (3 marks)
– Magnesium has a giant metallic structure in which the positive nucleus are immersed in a sea / cloud of electrons While silicon has a giant atomic stmcture in which the atoms are joined by strong covalent bonds hence silicon is harder than Magnesium metal hence the high melting point.
18. Figure 3 shows a set up that is used to investigate the effect of an electric current on various substances.
(a) Identify the electrodes labelled(i) P (1/2 mark)
– Anode
(ii) Q (1/2 mark)
– Cathode
(b) What observations will be made if lead(II) bromide was the substance under investigation. (1 mark )
– Brown fumes at the electrode P / anode; -grey pellets at electrode Q / cathode
19. Explain how water hardness can be removed using the ion-exchange method. (2 marks)
Ion-exchange process:
– Hard water is passed through a column filled with a complex sodium compound (sodium permuttit) / ion exchanger;
– The Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions in the hard water are precipitated and remains in the column while the sodium ions from the column comes out with the water hence becoming soft.
20. The set up in Figure 4 was used to investigate the reaction of calcium with cold water.
(a) Name gas R. (1/2mark)– Hydrogen
(b) Explain the observation that was made when a few drops of phenolphthalein indicator were added to the resulting solution. (1 mark)
– When a few drops of Phenolphthalein indicator are added to the resulting solution, the solution changed/turned pink. This is because Calcium reacted with water to form Calcium hydroxide which is alkaline hence the pink colour
(c) If magnesium ribbon was used in place of calcium, explain why it was necessary to clean the magnesium with steel wool before its reaction with Water. (1/2 mark)
– Magnesium reacts with air to form a layer of Magnesium oxide which has to be removed before it can react with water.
21. Study Figure 5 and answer the questions that follow.
(a) Name solid T. (1 mark)Copper(II) nitrate / Cu(NO3)2(b) Identify the brown gas. (1 mark)– Nitrogen(IV) oxide /NO
SECTION C: PHYSICS (33 marks)
22. State one reason why students should not carry or eat food in the laboratory. (l mark)
– o avoid eating contaminated food.
23. Figure 6 shows a metre rule being used to measure the length of a block of wood.
Record the length of the block of wood. (1 mark)– 2.3 cm24. Complete the Table 2 below. (2 marks)
Table 2 Physical Quantity I SI Unit | Symbol of Unit Mass 1 I l | Newton i 25. Define the term Power. (l mark)
– The rate of doing work.
26. Two students A and B are taking milk using a straw. A is standing on top of a high mountain while B stands at the foot of the mountain. State with a reason which student takes the milk more easily.(2 marks)
– B Atmospheric pressure is higher at the foot of the mountain hence the milk gets into the straw much more easily
27. Explain why a gas occupies the whole space of the container in which it is placed. (2 marks)
– The intermolecular forces very weak. \/ (1) hence molecules move randomly in all directions.
28. (a) A student observed that gaps between rails along a railway line were larger in the morning than in the afternoon. Explain the observation. (2 marks)
– In the afternoon it is hotter than in the morning. / (1) hence rails expand more reducing the gaps.
(b) State the purpose of the consnietion in a clinical thermometer (1 mark)
– To prevent the liquid from flowing back to the bulb
29. Figure 7 shows an immersion heater being used to heat water in a jug and a thermometer placed in the water with its bulb below the heating coil.
It was observed that when the water started to boil the thermometer reading was lower than the boiling point of water. Explain this observation (2 marks)– Water above the coil was heated by convection currents;
while below the coil water is heated by conduction but water is a poor conductor of heat.
30. A uniform plank of wood of length 5 m is pivoted at its centre. A girl of mass 32 kg sits at one end of the plank. Determine how far from the pivot a boy of mass 40 kg should sit in order to balance the plank. (3 marks)
– Sum of clockwise moments = sum of anticlockwise moments.
40x = 32x 2.5
x=32 x 2.5/40 = 2.0m
31. (a) A ball rests on a level floor. Name its state of equilibrium. (1 mark)
– Neutral
(b) State how the area of the supporting base affects the stability of the object. (l mark)
– The wider the supporting base the more stable the object is
32. (a) Define “elastic limit” (l mark)
– Force beyond which the extension is not proportional to the applied force..
(b) A spring supporting a weight of 30N extends by 1.5 cm. Determine the spring constant. (3 marks)
f=ke
1.5=30
k=20Ncm-1 or 200Nm-1
33. Figure 8 shows the velocity time graph for a vehicle. velocity (V)
Describe the motion of the vehicle in the regions.AB vehicle moves with uniform velocity.
BC vehicle decelerates uniformly until it comes to rest
CD vehicle moves in the opposite direction with increasing velocity.
34.(a). Define inertia.
– Resistance to change the state of motion of a body.
(b).Explain how striking a matchstick on a matchbox causes fire.
– By striking there is friction between the matchstick and the matchbox (1) friction causes/generates heat
35.(a). State the law of flotation.
– A floating body displaces its own weight of the fluid in which it floats
(b).Explain why an object Weighs more in air than when fully immersed in water. (3 marks)
– When in air the upward force (upthrust) is negligible / (l) when in water the object experiences an upthrust (1) hence when in water the net downward force is less than when (l) in air (when only the weight acts on the body)