KNEC KCSE Past Papers 2017 General Science Paper 2 (237/1)
KCSE Past Papers 2017 General Science Paper 2
Section A: Biology (34 marks)
1. The photographs below show two types of parasites.
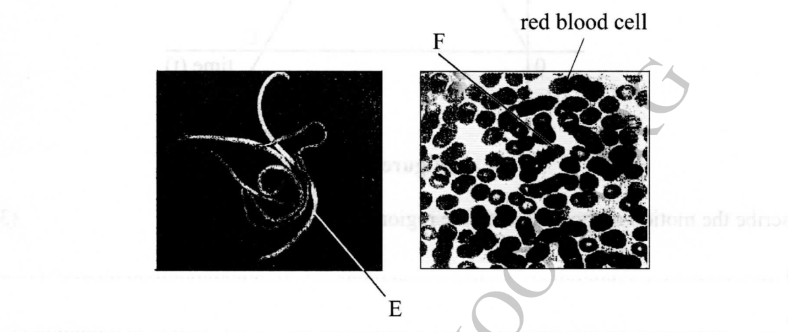
(a) (i) Identify the parasite labelled E and F.
E
F
(ii) Name one living organism which can host the two parasites.
(b) Give three adaptations of the parasite labelled E to its mode of life.
2. Explain how cell biology is an evidence of organic evolution.
3. The diagram below shows a bone found in a mammalian skeleton.

(a) (i) Identify the bone.
(ii) Which bone articulates at point G?
(b) What type of joint is formed at point H?
The figure below shows a tissue from a male human being.
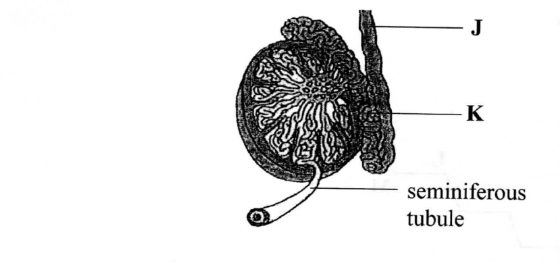
(a) Name the structures labelled J and K.
J
K
(b) Give the functions of structure J and K.
J
K
Give three adaptations of the sperm cell to its function. (3 marks)
In a breeding experiment, plants with red flowers were crossed. The produced plants included 246 red and 82 white flowered plants.
(a) (i) Identify the recessive character. (1 mark)
(ii) Give a reason for your answer in (a) (i) above. (1 mark)
(b) What were the genotypes of the parent plants that gave rise to the plants with red and white flowers? (1 mark)
(c) Determine the genotypes of the plants that were produced from the cross. Show your working. (3 marks)
The graph below illustrates intermittent growth in insects.
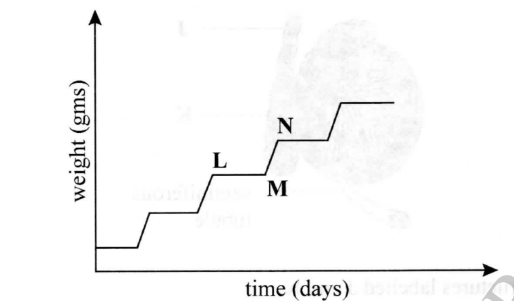
Account for the shape of the graph between
(a) L and M
(b) M and N
The following structure represents a part of the ear responsible for hearing.
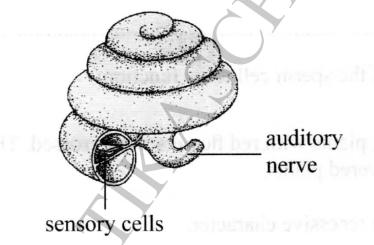
(a) Name the structure
(b) Which structure in the ear detects changes in posture?
(c) Give three causes of deafness in human beings.
SECTION B: CHEMISTRY (33 marks)
9. (a) State Boyle’s Law. (1 mark)
(b) A fixed mass of a gas occupies a volume of 225 cm3 at 330 °C and 740 mmHg.
Calculate the volume the gas will occupy at 13 °C and 780 mmHg. (2 marks)
10. (a) What is meant by a molar solution? (1 mark)
(b) Determine the amount of water that should be added to 15 cm3 of 3M hydrochloric acid to dilute the acid to 1 molar solution. (2 marks)
11. The molecular formula of an organic compound is C5H12.
(a) Draw the structure of the compound. (1 mark)
(b) Name the structure in (a). (1 mark)
12. (a) What is meant by an endothermic reaction? (1 mark)
(b) Hydrogen gas burns in air to form water vapour, releasing 286kj of energy per mole.
Draw an energy level diagram for the reaction. (2 marks)
13. Polymers are large organic molecules formed by combining small molecules.
(a) Name two natural polymers. (1 mark)
(b) State one use of each polymer named in (a) above. (1 mark)
14. Firewood is used as a source of energy. State two disadvantages of this fire]. (2 marks)
15. Calculate the mass of 0.35 moles of calcium hydrogen carbonate. (2 marks)
(Ca=40;H=l.0;C=l2.0;O=16.0)
16. The diagram in Figure 1 shows curves obtained when equal amounts of zinc granules were reacted with different concentrations of hydrochloric acid. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
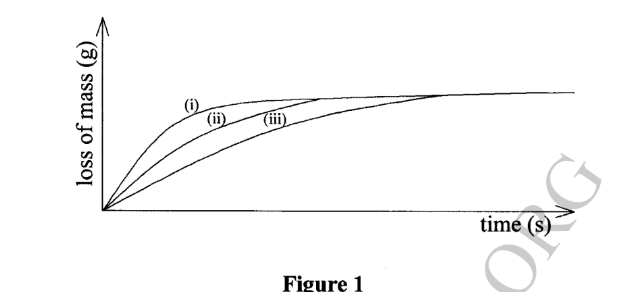
(a) Identify the curve that represents the most concentrated acid. Explain. (2 marks)
(b) State two factors that affect rate of a chemical reaction. (2 marks)
17. Sodium metal is extracted from molten rock salt.
(a) Name the ions present in the molten liquid. (l mark)
(b) Reduction method is not used in the extraction of sodium. Explain. (1 mark)
(c) State two uses of sodium. (1 mark)
18. In the manufacture of sulphuric(VI) acid, sulphur(VI) oxide is absorbed in concentrated sulphuric acid and the product diluted with soft water.
(a) Name the product that is diluted. (1 mark)
(b) Write an equation for the reaction between sulphur(VI) oxide and concentrated sulphuric(Vl) acid. (1 mark)
(c) Concentrated sulphuric(VI) acid was added to a beaker containing sugar crystals.
Explain the observations made. (1 mark)
(a) State the impurities present in the aluminium ore. (1 mark)
(b) Aluminium is preferred to iron in making utensils. Explain. (1 mark)
20. The set-up in Figure 2 was used in the preparation of gas B. Study it and answer the questions
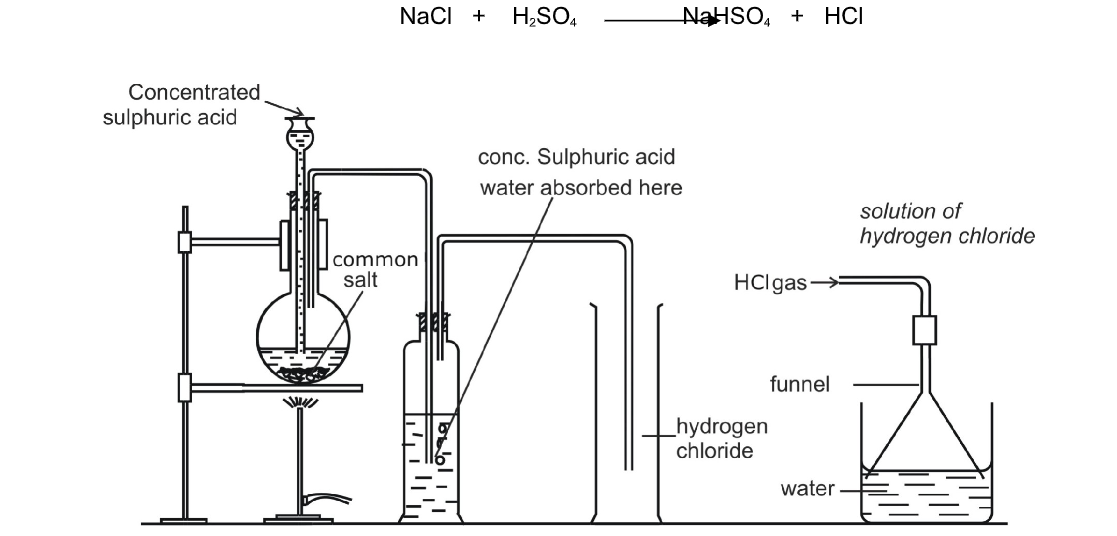
(a) Identify:
(i) Solution A
(ii) Gas B
(b) State the property that enables the gas to be collected as shown.
(c) State two uses of gas B.
SECTION C: PHYSICS (33 marks)
21. Figure 3 shows an opaque object placed between the screen and a point source of light in the form of a small hole in a cardboard placed in front of the source of light.
source of light object screen

(a) Complete the ray diagram to show the shadow formed on the screen. (2 marks)
(b) State what would be the effect on the shadow if the hole is enlarged. (l mark)
22. (a) Draw a simple circuit showing two cells in series with a bulb and a switch. (1 mark)
(b) Indicate on the diagram the direction of current in (a). (l mark)
23. Define the following:
(a) Awave pulse . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
.. (1 mark) (b) Wavelength
24. Explain Why repulsion is the only sure test for the polarity of a magnet. (2 marks)
25. Explain how a glass rod acquires a positive charge when rubbed with silk cloth. (2 marks)
26. Explain how an echo is formed (2 marks)
27. Figure 4 shows the scale of an electrical device used to measure a current.
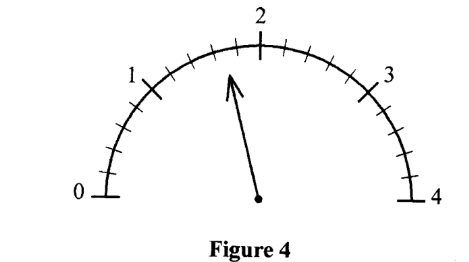
(a) Name the device (l mark)
(b) Record the current shown by the device. (1 mark)
Q 28. Figure 5 shows a pin lying at the bottom ofa beaker full of water and an observer above the E surface of water.
, Draw a ray diagram to show how the observer sees the head of the pin. (3 marks)
F 29. State the energy changes that take place as the electrons travel to the anode for the production l of X-rays in an X-ray tube. (3 marks)
l 30. A house has four 75 W lamps. Determine the cost of using the lamps for 6 hours each day for } 30 days if the cost of electricity is ksh.9.30 per kWh. (3 marks)
I .~ 31. State two properties of an alpha particle. (2 marks)
32. State three advantages of using a Cathode Ray Oscilloscope as a voltmeter instead of a moving coil meter. (3 marks)
33. State how the electrical conductivity of a semiconductor can be increased. (1 mark)
34. State two properties of images fomied by diverging lenses. (2 marks)
35. Name one device that functions by using the heating effect of an electrical current. (1 mark)
KCSE Past Papers 2017 General Science Paper 2
Section A: Biology (34 marks)
1. The photographs below show two types of parasites.

(a) (i) Identify the parasite labelled E and F.
E– Roundworms/Ascaris
F– Plasmodium ovale/Plasmodium vivax
(ii) Name one living organism which can host the two parasites.
– Human beings
(b) Give three adaptations of the parasite labelled E to its mode of life.
— Thick and hard protective covering/pellicle to resist digestion by enzymes;
— Covered by mucus to resist digestion by the host enzymes;
— Can respire anaerobically to survive in the oxygen-deficient intestines;
— Eggs are enclosed/covered by hard shells to resist digestion in the intestines and harsh external environment;
— Has two hosts to increase servival chances
2. Explain how cell biology is an evidence of organic evolution.
– Similar cell organelles/and (some) biological molecules; are found in the cells of almost all living organisms; suggesting that the organisms had a common ancestiy/phylogenically related
3. The diagram below shows a bone found in a mammalian skeleton.

(a) (i) Identify the bone.
– Fermur
(ii) Which bone articulates at point G?- Tibia
(b) What type of joint is formed at point H?– Hinge joint
The figure below shows a tissue from a male human being.

(a) Name the structures labelled J and K.
J – Vas deferens/sperm duct
K– Epididymis
(b) Give the functions of structure J and K.
J – Conveys sperms from the epididymis to the urethra during ejaculation
K – Storage of mature sperms
Give three adaptations of the sperm cell to its function. (3 marks)
– Head has acrosome which produces hydrolytic enzyme that digests the vitelline wall of the ovum during fertilization;
– Head has a nucleus which contains genetic materials that determine the characteristics/traits of the offspring.
– Middle part has numerous mitochondria to provide sufficient energy required for swimming; towards the ovum;
– Has a long tail for propulsion/swimming towards the ovum
In a breeding experiment, plants with red flowers were crossed. The produced plants included 246 red and 82 white flowered plants.
(a) (i) Identify the recessive character. (1 mark)– White flower gene
(ii) Give a reason for your answer in (a) (i) above. (1 mark)-Red and white flowered plants are produced in the ratio of 3: l
(b) What were the genotypes of the parent plants that gave rise to the plants with red and white flowers? (1 mark)– Red — Rr, Rr
(c) Determine the genotypes of the plants that were produced from the cross. Show your working. (3 marks)

The graph below illustrates intermittent growth in insects.

Account for the shape of the graph between
(a) L and M
– Slow growth rate; because the exoskeleton has hardened and is limiting growth
(b) M and N
– Rapid growth occurs after moulting; before the exoskeleton hardens
The following structure represents a part of the ear responsible for hearing.

(a) Name the structure
– Cochlea
(b) Which structure in the ear detects changes in posture?
– Vestibular apparatus>
(c) Give three causes of deafness in human beings.
– Hereditary abnormalities in the ear;
– Injury to the brain/auditory nerve/cochlea
– Damage (mechanical/physical) of the eardrum
– Ear infections;
SECTION B: CHEMISTRY (33 marks)
9. (a) State Boyle’s Law. (1 mark)
– A volume of a fixed mass of a gas is inversely proportional to its pressure provided the temperature remains constant
(b) A fixed mass of a gas occupies a volume of 225 cm3 at 330 °C and 740 mmHg. Calculate the volume the gas will occupy at 13 °C and 780 mmHg. (2 marks)
p1v1/T1 = p2v2/T2
vv2=740x225x286/603×780 =101.24cm3
10. (a) What is meant by a molar solution? (1 mark)
– A solution that contains one mole of a substance in ldm3/ 1000 cm3of solution.
(b) Determine the amount of water that should be added to 15 cm3 of 3M hydrochloric acid to dilute the acid to 1 molar solution. (2 marks)
– ilution formular C1V1 = C2V2 V2= C1V1/C2
15×2/1 =45
45-15=30cm3
11. The molecular formula of an organic compound is C5H12.
(a) Draw the structure of the compound. (1 mark)
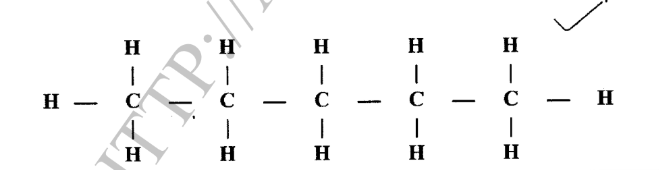
(b) Name the structure in (a). (1 mark)– Pentane
12. (a) What is meant by an endothermic reaction? (1 mark)
– A reaction where heat is absorbed from the surrounding
(b) Hydrogen gas burns in air to form water vapour, releasing 286kj of energy per mole.
Draw an energy level diagram for the reaction. (2 marks)
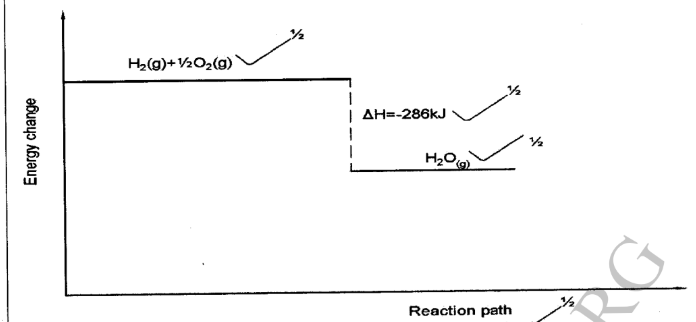
13. Polymers are large organic molecules formed by combining small molecules.
(a) Name two natural polymers. (1 mark)
Cellulose, rubber, cotton, carbohydrate, protein, silk
(b) State one use of each polymer named in (a) above. (1 mark)
– Manufacture of clothing/fibres Manufacture of tyres
14. Firewood is used as a source of energy. State two disadvantages of this fire. (2 marks)
– Deforestation cutting down trees.
– Produces Carbon(IV) oxide which causes global
15. Calculate the mass of 0.35 moles of calcium hydrogen carbonate.C=40;H=l.0;C=l2.0;O=16.0) (2 marks)
R.Formula(Ca(HCo3)2
R.F.M= 40+2+24+96)=162 =
Mass of Ca(HCo3)2=0.03×162
62.7g
16. The diagram in Figure 1 shows curves obtained when equal amounts of zinc granules were reacted with different concentrations of hydrochloric acid. Study it and answer the questions that follow.

(a) Identify the curve that represents the most concentrated acid. Explain. (2 marks)
– Curve i
– The gradient for curve (i) is steeper hence the reaction is faster implying the concentration is higher
(b) State two factors that affect rate of a chemical reaction. (2 marks)
– Temperature;
– Surface area of solid reactants;
– Catalyst
– Concentration
17. Sodium metal is extracted from molten rock salt.
(a) Name the ions present in the molten liquid. (l mark)
Na+ , C1-
(b) Reduction method is not used in the extraction of sodium. Explain. (1 mark)
– Sodium is more reactive than carbon and the ore is not an oxide
(c) State two uses of sodium. (1 mark)
– Coolant in nuclear reactions;
– Sodium lamp;
– Extraction of gold.
– Extraction of titanium
18. In the manufacture of sulphuric(VI) acid, sulphur(VI) oxide is absorbed in concentrated sulphuric acid and the product diluted with soft water.
(a) Name the product that is diluted. (1 mark)
– Oleum
(b) Write an equation for the reaction between sulphur(VI) oxide and concentrated sulphuric(Vl) acid. (1 mark)
– SO2(g) +H2SO4(l) —> H2S2O7(l)
(c) Concentrated sulphuric(VI) acid was added to a beaker containing sugar crystals.
Explain the observations made. (1 mark)
The sugar turned brown then a black mass is formed because conc. H2SO4 dehydrates /removes the elements of Water from sugar
(a) State the impurities present in the aluminium ore. (1 mark)
– Silica;
– iron(II) oxide.
(b) Aluminium is preferred to iron in making utensils. Explain. (1 mark)
– Aluminium is a better conductor of heat.
– Aluminium does not corrode easily because it forms a layer of insoluble oxide.
20. The set-up in Figure 2 was used in the preparation of gas B. Study it and answer the questions

(a) Identify:
(i) Solution A– dilute hydrochloric acid
(ii) Gas B– sulphur(lV) oxide
(b) State the property that enables the gas to be collected as shown.- – denser/ heavier than air
(c) State two uses of gas B.
– Manufacture of sulphuric(VI) acid;
– Bleaching agent;
– Fumigating houses;
– Preservative SECTION C: PHYSICS (33 marks)
21. Figure 3 shows an opaque object placed between the screen and a point source of light in the form of a small hole in a cardboard placed in front of the source of light.
source of light object screen

(a) Complete the ray diagram to show the shadow formed on the screen. (2 marks)
(b) State what would be the effect on the shadow if the hole is enlarged. (l mark)
– The shadow formed would have two regions.
22. (a) Draw a simple circuit showing two cells in series with a bulb and a switch. (1 mark)
(b) Indicate on the diagram the direction of current in (a). (l mark)
23. Define the following:
(a) A wave pulse – A pulse is a single disturbance that moves through a medium from one point to another
(b) Wavelength – The distance between two successive crests (or troughs) Or The distance between two successive points in a wave that are in phase.
24. Explain Why repulsion is the only sure test for the polarity of a magnet. (2 marks)
– Repulsion takes place only between like poles of a magnet while attraction can occur between unlike poles of magnets or between a magnet and any magnetic material.
25. Explain how a glass rod acquires a positive charge when rubbed with silk cloth. (2 marks)
– On rubbing the glass loses some electrons to the cloth, it therefore gets a net positive (2 mark) charge.
26. Explain how an echo is formed (2 marks)
– When sound from a source is reflected by a barrier and reverses direction. (2 mark) Reflected sound (echo) is received by observer.
27. Figure 4 shows the scale of an electrical device used to measure a current.

(a) Name the device (l mark)
– Ammeter/millimeter/micro ammeter
(b) Record the current shown by the device. (1 mark)
– Current= 1.7 A
Q 28. Figure 5 shows a pin lying at the bottom ofa beaker full of water and an observer above the E surface of water.

Draw a ray diagram to show how the observer sees the head of the pin. (3 marks)
29. State the energy changes that take place as the electrons travel to the anode for the production of X-rays in an X-ray tube. (3 marks)
– Electrical energy(electric field) —> Kinetic energy (of electrons) —> heat and X-rays
30. A house has four 75 W lamps. Determine the cost of using the lamps for 6 hours each day for 30 days if the cost of electricity is ksh.9.30 per kWh. (3 marks)
Energy consumed = 4x75x6x30/1000
= 54 kW
Cost = 54×9.3
=Ksh. 502.20
31. State two properties of an alpha particle. (2 marks)
– Carries a positive charge.
– Can ionize gas/air strongly
– It is equivalent to helium ion
– Can be stopped by a thick sheet of paper
– Is deflected by both electric and magnetic fields
32. State three advantages of using a Cathode Ray Oscilloscope as a voltmeter instead of a moving coil meter. (3 marks)
– Can measure both alternating and direct voltages
– Responds instantaneously unlike ordinary meter
– Does not affect the circuit due to its high resistance
– Can measure large voltages without getting damaged.
33. State how the electrical conductivity of a semiconductor can be increased. (1 mark)
– Raise temperature/by doping
34. State two properties of images formed by diverging lenses. (2 marks)
– Virtual
– Diminished
35. Name one device that functions by using the heating effect of an electrical current. (1 mark)
– Electrical kettle/electric iron/filament lamps/soldering gun/electric heater




I like your website