KNEC KCSE Physics Paper 2 Question Paper / 2016 KASSU JET JOINT EXAMINATION
2016 KASSU JET JOINT EXAMINATION
Physics Paper 2
SECTION A: (25 Marks)
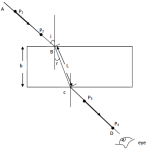
In figure 1 two mirrors M1 and M2 are inclined at right angles to each other.
Trace the reflection of the ray through the two mirrors and find the angle between the
incident ray and reflected ray of mirror M2
2 marks
When rod X was rubbed with material Y it was observed that the material acquired a
negative charge.
a) State the charge on rod X after rubbing (1 mark)
b) Explain how rod X acquired the charge stated in (a) above. (1 mark)
2 marks
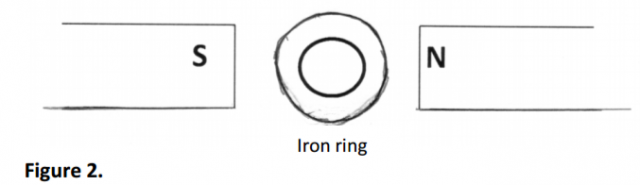
An iron ring is placed between two magnets as shown in figure 2.
(a)Sketch the magnetic field pattern between the poles and mark the neutral point, Xon the
diagram . ( 2 marks)
(b) State one application of the concept tested above. (1mark).
3 marks
A charge of 180 Coulombs flows through a lamp every minute. Calculate the number of
electrons involved. (Take charge of an electron e, =1.6×10-19C).
2 marks
Table 1 shows radiations and their respective frequencies.
| Type of radiation | Yellow light | Gamma rays | Radio waves | Micro waves |
| Frequency (Hz) | 1 x 1015 | 1 x 1022 | 1 x 106 | 1 x 1011 |
Table1
a) Arrange the radiation in order of increasing energy. (1 mark)
b) State the reason why radio waves signals are easier to receive than TV signals in a place
surrounded by hills. (1 mark)
2 marks
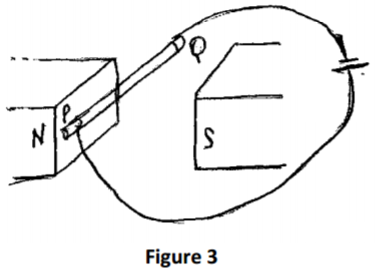
Figure 3shows a metal rod PQ connected to a d.c supply and placed between two magnets.
a) Indicate on the diagram the direction of force on rod PQ and magnetic field pattern
between the two magnetic poles only. (2 marks)
b) State one way in which the direction of force can be made to change. (1mark)
3 marks
An explosion in a quarry takes place at a distance of 70m from an observer. An echo
from a cliff 50m beyond the source of the explosion is heard by the observer 0.5
seconds after he sees the flash from explosion. Calculate the velocity of sound in air.
3 marks
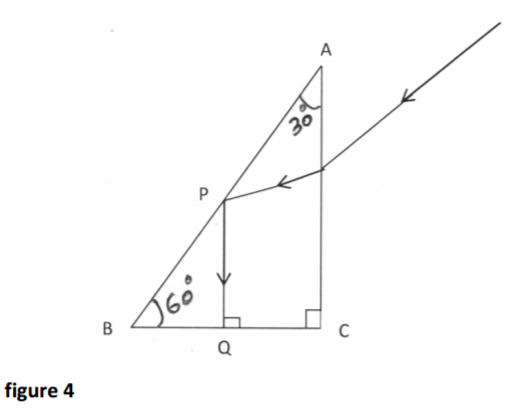
(a) Figure 4below shows the path of a ray of light through a triangular prism ABC of
refractive index 1.50. is parallel to AC.
Determine the angle of incidence on the side AC. ( 3marks)
b) Figure 5 shows the image formed by convex mirror
Sketch rays on the diagram to show the position of object (2 marks)
5 marks
In an experiment to study interference in sound waves two identical loudspeakers are
connected to an audio frequency generator so that they act as coherent sources L1 and L2 as
shown in figure 6.
An observer walking several metres ahead and a long a line to LI L2 identifies pointsAandA1as
the first positions of loud sound on either side after the loud sound at the middle position O
between the two sources. (2 marks)
(a) Explain the meaning of the term coherent source. (1 mark)
(b) Name the type of interference occurring at the points O,A, and A1. (1 mark)
5 marks
Distinguish the n-type and p-type semiconductors.
1 marks
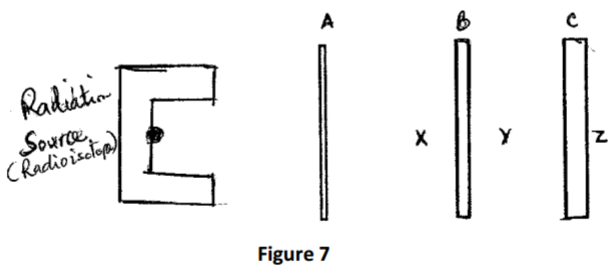
a) Figure 7 shows a source of α,β and r-radiation placed infront of a set of barriers A,B
and C
A is a thick sheet of paper, B is a thin sheet of aluminium foil and C is a thin sheet of
lead. Name the radiation detected in the regions marked X, Y and Z. (3 marks)
X………………………………………………………………
Y………………………………………………………………
Z………………………………………………………………
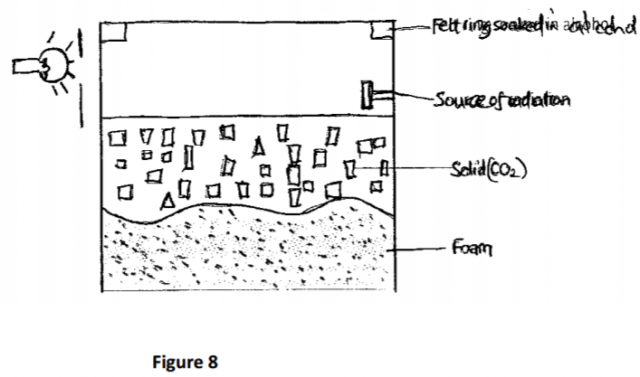
b) The figure 8 below shows the features of a diffusion cloud chamber used for
detecting radiation.
i) Explain how radiation from the source is detected in the chamber. (4marks)
ii) What type of radiation can the device detect? (1mark)
c) The count rate recorded for a certain source is 256 counts per second. What count
rate is recorded 20 days later, if the half-life of the source is 5 days. (2marks)
10 marks
(a) A house has five rooms each with 240V,60W bulbs.If the bulbs are switched on from
7:00pm to 10:30 pm;
(i) Calculate the power consumed in the month of April in Kilowatt-hours.(2marks)
(ii) Find the cost per month for lighting these rooms at Ksh6.70 per unit. (2marks)
(b) A student designed a transformer to provide power to an electric bell marked
24W,6V from a mains supply 240V. He wound coils, 50 turns and N turns on an iron ring
core. When he connected the coil of 50 turns to the bell and N turns coil to the a.c
source, he found out that the transformer was only 80% efficient.Find;
(i) The value of N. (2marks)
(ii) The current in the primary coil. (2marks)
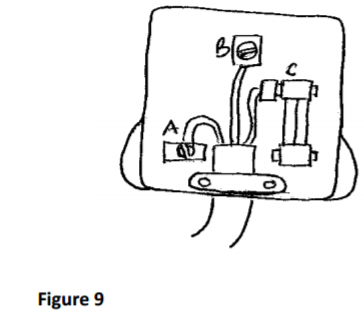
(c) The figure 9. shows a connection to the three- pin plug.
(i) Name the cables A, B and C and state their colours. (3marks)
A………………………………………………………………………………………….
B………………………………………………………………………………………….
C………………………………………………………………………………………….
(ii) Why is the fuse connected to cable C.? (1mark)
(iii) State one reason why in domestic wiring system appliances are connected in
parallel. (1 mark)
13 marks
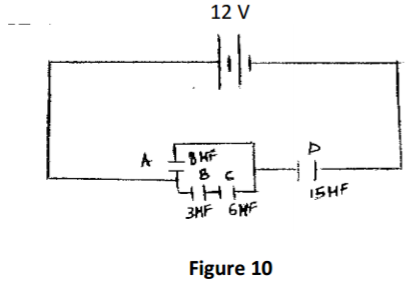
Figure 10 Shows an electric circuit with four capacitors A,B,C and D8 µF ,3µF,6 µF and 15 µF
respectively connected to 12V battery.
(a) Determine ;
(i) the effective capacitance. (3 marks)
(ii) the charge of capacitor D. (2 marks)
(iii) the total energy stored. (2 marks)
(b) Explain one factor that determine the capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor.
(1 mark)
8 marks
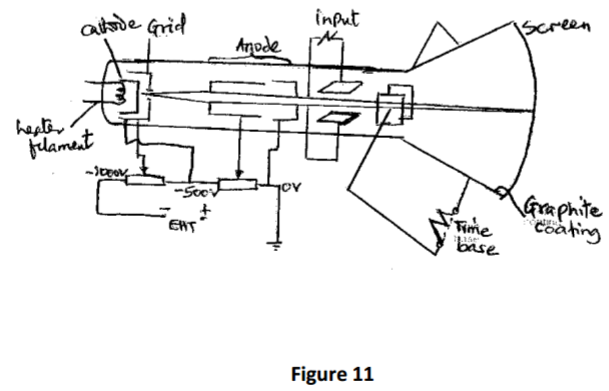
(a)Figure 11shows the features of a cathode ray tube.
(i) Explain how the electrons are produced in the tube. (1 mark)
(ii) What is the purpose of the anodes? (2 marks)
(iii) Why is the tube evacuated? (1 mark )
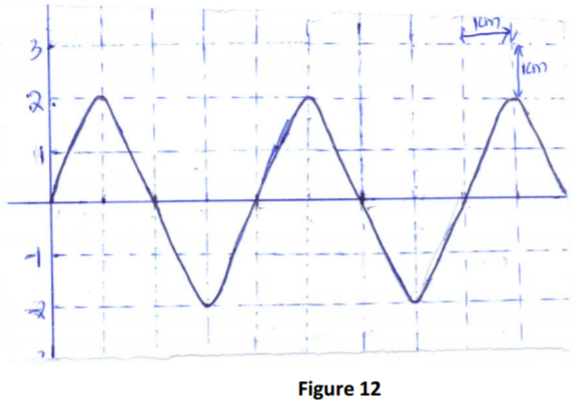
(b) Figure 12shows the voltage of an a.c. generator on the screen of a C.R.O.
If the time base calibration is 20 milliseconds/cm and the y- gain is 5V/cm ,
calculate;
(i) the frequency of the generator. (2 marks )
(ii) the peak voltage of the generator. (2 marks )
(c) A potential difference of 40kV is applied across an x-ray tube. Given that the
charge of an electron is 1.6 × 10-19𝐶𝐶 and the mass of an electron is 9.1 × 10-31𝑘𝑘𝑘𝑘 and Planck’s constant = 6.63 × 10-34Js;
(i) What is the effect of increasing the potential difference across the x-ray
tube? (1 mark)
(ii) Calculate the velocity with which the electrons strike the target.
(3 marks)
12 marks
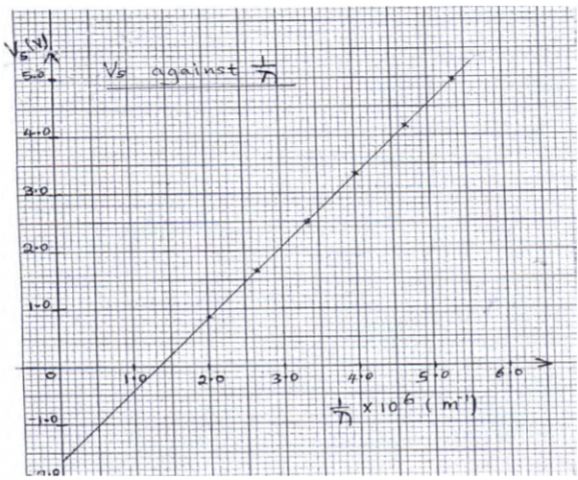
A Form 4 student carried out on experiment to investigate photoelectric effect. From
the results a graph of stopping potential Vs (y-axis) against the inverse of the wavelength
1/λ was plotted and was as shown below.
The equation of the graph is 𝑉
Where: c = 3.0 × 108𝑚ms-1 ,speed of light in air
e= 1.6 × 10-19𝐶C𝐶, charge of an electron
h = is the Planck’s constant.
(a) From the graph, determine;
(i) The slope s of the graph. (2 marks)
(ii) The Planck’s constant h. (2 marks)
(iii) The threshold wavelength λ𝑜𝑜 (2 marks)
(iv) The threshold frequency 𝑓𝑓𝑜𝑜 (2 marks)
(v) The work function 𝑊𝑊𝑜𝑜 in electron volts (e.v) (2 marks)
(b) On the same graph, sketch a graph which would be obtained if the student used
a metal with greater threshold frequency, explain your answer. (2 marks)
12 marks