KNEC KCSE Biology Paper 1 – 2014 Gatundu Mock
2014 Gatundu Mock
Biology Paper 1
State the functions of the following cell organelles.
(i) Golgi apparatus
(ii) Mitochondria
2 marks
State two ways in which xylem vessels are adapted to their functions.
2 marks
Distinguish between Ecology and Ecosystem.
2 marks
(a) What is Natural selection. (1 mark)
(b) What is meant by the following terms? (4 marks)
(i) Homologous structure
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Example
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(ii) Analogous structure
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Example
5 marks
(a) State two disadvantages of sexual reproduction. (2 marks)
(b) State two adaptations of the human spermatozoa. (2 marks)
4 marks
What adverse effects do skin lightening cosmetics have on the user?
2 marks
Name the structures in liverwarts that produce.
(a) Male gametes
(b) Female gametes
2 marks
State three effects of dumping untreated sewage into a river.
3 marks
State two factors within the seed that cause seed dormancy. (2 marks)
4 marks
Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow.
(a) Name each of the structure labeled P and R. (2 marks)
(b) (i) Name the type of fruit represented above. (1 mark)
(ii) Explain one observable way in which the fruit is adapted to its mode of dispersal. (1
mark)
4 marks
After a person had swum the length of a pool and climbed out of the water their skin temperature is
likely to be very low but their deep body temperature is likely to be normal. Why is the skin surface likely to be cold for sometime after leaving water?
2 marks
State two roles of the secretion of the sebaceous glands.
2 marks
State two adaptations of tracheoles of insects for gaseous exchange.
2 marks
Define the term accommodation of the eye.
1 marks
(a) Identify:
(i) Photochemical pigment for dim light vision. (1 mark)
(ii) Photochemical cell with low visual Acquity. (1 mark)
2 marks
(a) State the functions of each of the following in the mammalian skeleton.
(i) Intervartebral disc (1 mark)
(ii) Vertebraterial canal (1 mark)
(b) State one main structural difference between axis and atlas. (1 mark)
3 marks
(a) Differentiate between continous and discountinous variation. (1 mark)
(b) State one example of numerical chromosomal mutations. (1 mark)
2 marks
The respiratory quotient of an active person is normally in the range of approximately 1.0. If a
person is deprived of food for 24 hours, the RQ drops to 0.75. Explain.
2 marks
Explain what happens to Red blood cells when its placed in hypertonic solution
2 marks
An animal has the following dental formula
I 3 c 1 pm 4 m 2
3 1 4 3
(a) Calculate the number of teeth. (1 mark)
(b) Explain what would result from blockage of bile duct. (2 marks)
3 marks
Explain how the guard cells are adopted to their functions.
2 marks
(a) Give one application of osmosis in humans. (1 mark)
(b)Explain the effect of each of the following on the rate of active transport.
(i) Oxygen concentration (1 mark)
(ii) Glucose concentration (1 mark)
3 marks
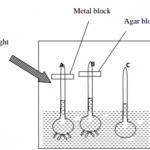
In an experiment, the apparatus shown in the diagram below was left in the light for two days and then leaves 1 and 2 were tested for starch.
(a) What was the aim of the experiment.(1 mark)
(b) Account for the observations made when the leaves 1 and 2 were each tested for
starch. (2 marks)
3 marks
The table below shows an analysis of urine and of blood after filtration in the kidney.
| substance | Percentage of substance in urine | Percentage of substance in blood In urine |
| Glucose Salts Urea water |
0.10 0.30 0.03 90.00 |
0.00 0.60 2.00 97.00 |
(a) Account for the difference in concentration of urea in blood and urine. (2 marks)
(b) Explain why glucose is absent in urine yet present in blood. (1 mark)
3 marks
The graph shows pressure changes in the left atrium and in the left ventricle during the heart beat.
What is the state of the following valves at time x
(i) Semi lunar valve in the aorta (1 mark)
(ii) Bicuspid valve (1 mark)
2 marks
The diagram below shows a section through an eye.
i. Which part helps to focus an image on the retina? (1 mark)
ii. State the functions of each of the parts marked A and B. (2 marks)
3 marks
(a) Name the type of response exhibited by Euglena swimming towards fresh water from saline
water. (1 mark)
(b) State the survival value of this response. (1 mark)
2 marks
(a) State two differences between daughter cells from mitosis and from meiosis. (2 marks)
(b) State one difference between Deoxyribonucleic acid and Ribonucleic acid. (2 marks)
(c)Give one example of numerical chromosomal mutation. (1 mark)
5 marks
The diagram shows the changes that occur to the uterus lining during the menstrual cycle.
i. Name the hormone responsible for;
1. The events that occur in days 4 to 10. (1 mark)
2. Ovulation. (1 mark)
2 marks
The diagram below shows a synovial joint.
(a) Which area contains synovial fluid. (1 mark)
(b) Name the type of synovial joint shown above. (1 mark)
2 marks
Pure breeding pea plants with green pods are crossed with pure breeding pea plants
with yellow pods. All the offspring’s have green pods, plants from these offspring’s
are crossed. What colour are the pods of the next generation?
2 marks